Course Guide for
SEXUALITY AND SOCIETY
(last updated 01/2012)
Developed by Amanda M. Jungels
Georgia State University
Integrating/Interrogating Biological and Social Views of Sexuality
Challenging Evolutionary Perspectives on Sex/Sexuality
Social Construction of (Biological) Sex
- The Question of Caster Semenya’s Sex
- “Creating” Normative Genitals
- Conflating Gender, Sex, and Sexual Orientation
Social Construction: Changing Views on Sexuality
- Buy Virginity for Just $14.99
- Marketing the Tampon: “Will I Still Be A Virgin?”
- Changing Biology: Age at First Menstruation
- Masturbation and “Social Hygiene” in 1922
Sexuality and Social Categories
Social Construction of Gender
- Teens and Transgendered Women: Threats to Society
- On the J. Crew Pink Toenails “Controversy”
- Semenya’s Makeover: Gender as Performance
- “Some Men Just Need to Be Slapped”: Policing Masculinity
- A Beauty Regime for the “New Man”
- Karate Studio Ad: Gender Policing and Unofficial Marketing Materials
- One Family’s Experience with “Curing” Gender Non-Conformity
Transgender/Third Gender/Gender Queer
- On Being Gender Queer
- A Third Gender in Oaxaca, Mexico
- Argentinian Bank Depicts Transgendered Positively
Social Construction of Sexual Orientation
- How Useful is the Concept of Sexual Orientation?
- Are We Born Gay? And If We Were, How Would We Know?
- What Seems “Gay”?
- Was Franklin D. Roosevelt Gay?
- What Does a “Prehomosexual” Look Like?
- Homosexuality and Our Collective Consciousness
- Destabilizing Heteronormativity
- Normalizing Lesbian Couples
- Gay Couple in Budweiser’s “Coming Home” Ad?
- Survey Finds Different Levels of Acceptance for “Gays” Versus “Homosexuals”
- “Homosexual” vs. “Gay”: Discourse in the Culture Wars
- Public Opinion on the Cause of Homosexuality
Learning about Sex/Sex Education
Sex Education
- How Government Policies Impact Sex Education and Reproduction
- Sources of Sex Education Information for Teens
- Teens as Objects of Control
- British TV Commercial Promotes Abortion Services
- Anti-Teen Pregnancy PSA
- Teen Motherhood Sucks…Unless You’re Bristol Palin
Abstinence vs. Comprehensive Sex Ed
- Boys Receive Less Sexuality Education Than Girls
- Explaining Variation in Teen Pregnancy Rates by State: Race and Sex Education
- Consequences of U.S. and Dutch Approaches to Teen Sex
- Sexing Up Abstinence
- Abstinence Billboards
Sexual Practices
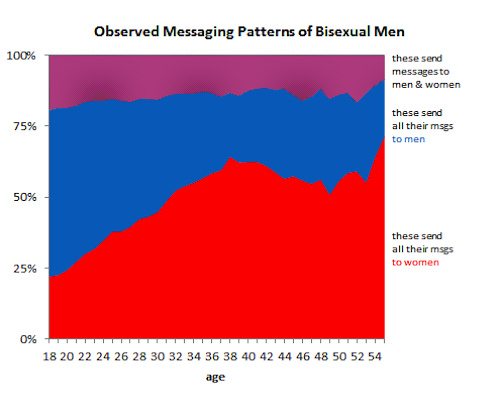
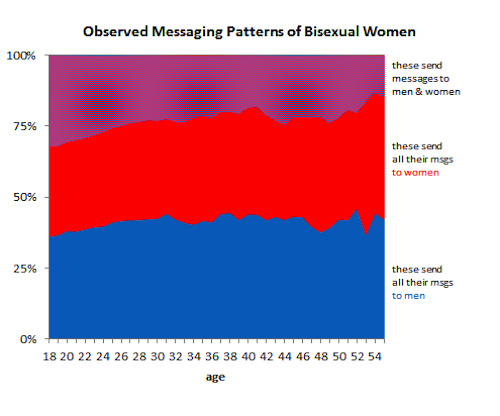
- Sexual Orientation and Sexual Behavior: OkCupid Data
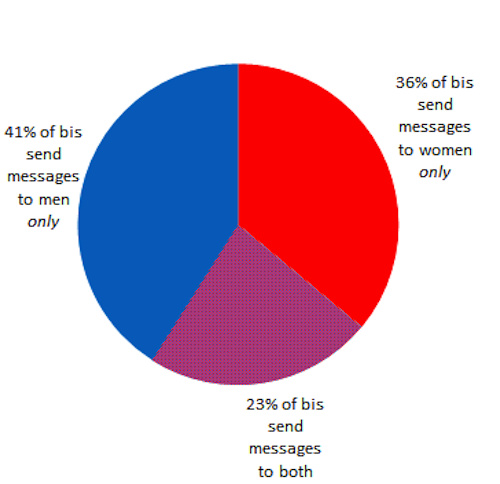
- Bisexuality and Dating on OkCupid
- Promise and Perils of Hook-Up “Culture”
- MTV on Hook-Up Culture
The Sexual Body
The Female Body
- Orgasmic Birth and the Myth of the Vaginal Orgasm
- How Vulvas Vary
- Gender Differences in Body Regimens
Menstruation
- Weird Tampon Ad from Australia
- Kotex Sells Tampons by Making Fun of Selling Tampons
- Re-Framing Menstruation
- Race, Gender and Aggression in Ads for Menstrual Pains Meds
Presenting the Female Body as Unclean: Removing Body Hair
- Summer’s Eve’s “Hail to the V” Campaign
- Shave or Men Will Never Find It
- Mow the Lawn
- Civilize Your Bush
- Encouraging Hair Removal for Children?
- The Miss of Sisyphus
- PETA Attacks Pubic Hair
- Advertising Against Bush
- Anxiety about “Objectionable Hair” = Money in Someone’s Pocket
- Nair Hair Removal Products for Teens
Presenting the Female Body as Unclean: Douching
Bodily Modification and Female Genital Cutting
- Spanish Ads Compare Women with Genital Cutting to Fuck Toys
- Female Circumcision Endorsed in a Vintage Playgirl
- When Vaginoplasty Meets Contemporary Television
- Pelvic Fitness Spa: More Things for Women to Worry About (NSFW)
- Vajazzling Revealed
Social Construction of the Male Body/Male Sexuality
- Social Construction of Sperm
- Medicalization of Impotence
- Conflating College Achievement with Sexual Prowess
- A Historical Look at the Popularity of Male Circumcision
- Fetishizing Black Men
Presenting the Penis as a Dangerous Weapon
- Safer Sex PSAs Conflate the Penis with a Firearm (NSFW)
- Safer Sex PSAs
- Presenting the Penis as a Dangerous Weapon (NSFW)
Representing Sex
Sexualization of Children’s Products
- Sexualized vs. Sexual: The Case of Thylane Blondeau
- Dora the Explorer’s Makeover
- Strawberry Shortcake: Extreme Makeover Edition
- Sexy Toy Makeovers: Lisa Frank, Trollz and Cabbage Patch Kids
- More Sexy Toy Makeovers: My Little Pony, Rainbow Brite and Candy Land
Sex in the Media
Ejaculation and Phallic Imagery
- Ejaculation Imagery
- Sexual Overtones in Cologne Ad
- Ejaculation Imagery in a Dutch Creamer Ad
- Phallic Imagery in a Skyy Vodka Ad
- Pornification of Advertising
Sex and Violence
- Violence Against Women on Prime-Time Up Since 2004
- Re-thinking the Famous Dolce and Gabbana Gang Rape Ad
- More Sexualized Violence in Fashion (NSFW)
- Calvin Klein Ad Implies Sexual Violence
- Even More Violence in Fashion Images
Objectification
- Objectification of Women: Everybody Wins!
- Gender, Sexualization and Rolling Stone
- Sexualized Images of Female Dominance
Infantilization of Women
Forced/Coerced Sex
Sexual Script
Rape Culture
- Making Light of Rape in the Purdue University Newspaper
- Yale Frat Pledges Chant “No Means Yes, Yes Means Anal”
- Do Full-Body Scans or Pat Downs = Sexual Groping?
- Ad Aimed at Discouraging Teen Drinking Threatens Prison Rape, Homosexuality
Use of Alcohol as a Tool for Coercive Sex
- Alcohol as a Tool in the Dating Game
- Booze=Sex
- Beer, Sex, and “The Hunt”
- Drunk Women are Easy Targets
Sexual Assault Prevention Campaigns
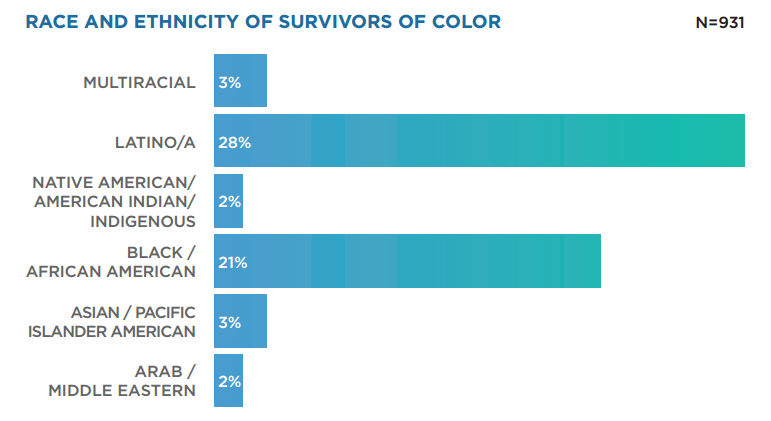
- Framing Recovery from Child Sexual Abuse (Trigger Warning)
- Resistance, Language and the Toronto Slutwalk
Commercial Sex
Pornography
- Online Porn Subscription in Liberal vs. Conservative States
- Finally an Ad that Acknowledges What High-Speed Internet is For
- Are Kids Watching Internet Porn?
- Mainstreaming of Pornography
- Gail Dines on Pornography
- Cindy Gallop on How Porn is Shaping Our Sex Lives
Contemporary Views on Prostitution
- Sex Work in Las Vegas
- Humanizing Sex Workers?
- Facebook, Technology and Prostitution
- Disparate Trends in Permissiveness: Homosexuality and Prostitution
- What Does the Sex Industry Look Like?
- Disparate Trends in Permissiveness: Homosexuality and Prostitution
Historical Perspectives on Prostitution
- 1890s Guide to New York City Brothels
- Personifying Danger: Women as Vectors of STIs
- The Virgin-Whore Binary in WWII VD Propaganda
- STI Transmission: Wives, Whores and the Invisible Man
- Loose Women and the War Effort
Sex Trafficking
- Misleading Measurement of Anti-Trafficking Enforcement
- Thinking Critically about Sex Trafficking
- Disney Still Makes Light of Sex Slavery
Other Forms of Sex Work
Social Control of Sex Work
- Halloween Hall of Shame: Fat Lap Dancer Costume
- Sex Work, Disrespect and Women’s Empowerment
- How Can You Tell If You’re a Prostitute?
- Questioning the Benefits of “Rescue” from Prostitution
- Posters Opposed to the Criminalization of Prostitution
Reproduction/Abortion
Reproduction
- To Whom Do Children “Just Happen”?
- Protecting Boys with Condoms for Kids
- Pre-Conception Care: Good for Babies, Bad for Women?
- The Pill and the Invention of the Monthly Cycle
- Visualizing the Fetus
- Thomas Beatie, the Pregnant Man, in the Public Sphere
- Threat of (Brown) Women’s Fertility
Abortion
- Why are Insured Women Paying for Abortions?
- Mis-Illustrating Abortion
- Framing the Abortion Debate
- Racializing the Abortion Debate
- Racialized Abortion Campaigns and Rethinking Choice
- More on the Racialization of the Abortion Debate
- Trends in the Rate of Abortion: New Data Shows a Plateau
- Measuring Abortion Beliefs
- Public Opinion on Abortions in Select Countries
- Public Opinion on Abortion by Party and Gender
- Abortion Laws Around the World
- Reproductive Politics, Race and Obama
Sterilization
- No Family for You: Examples of State Disruption
- Coercive Sterilization? Think of the Children!
- Breaking Down the Force/Choice Binary in the Sterilization of Women of Color
Contemporary GLBT Issues
Gay Rights Movement
- Images from the Early Gay Rights Movement
- Historic Photos of the Stonewall Riot and Its Aftermath
- Police Raids and the Stonewall Riots
- Increasing Cultural Acceptance of Gay and Lesbian Rights
- Should We Vote on People’s Rights?
- Opinions of Gay Rights Issues by State
- Attitudes Toward Gays and Lesbians
GLBT Parenting
Same-Sex Marriage
- Anti-Gay Marriage Ads
- Global Recognition of Same-Sex Marriages
- The Tipping Point for Support of Same Sex Marriage?
- Acceleration for Support of Same-Sex Marriage
- Who is Driving Increasing Acceptance of Gays and Lesbians?
- Turbo Tax Wants to Know if You are Gay Married
- Support for Same-Sex Marriage by Age and State
- On Gay Marriage and the Contact Hypothesis
- Gay Marriage and the Social Construction of Social “Problems”
- Views about Same Sex Marriage by Generation
- Rhetorical Strategy in the Gay Marriage Debate
GLBT-Related Legislation