Originally posted at Montclair SocioBlog.
Is Donald Trump undermining the legitimacy of the office of the presidency? He has been at it a while. His “birther” campaign – begun in 2008 and still alive – was aimed specifically at the legitimacy of the Obama presidency. Most recently, he has been questioning the legitimacy of the upcoming presidential election and by implications all presidential elections.
If he is successful, if the US will soon face a crisis of legitimacy, that’s a serious problem. Legitimacy requires the consent of the governed. We agree that the government has the right to levy taxes, punish criminals, enforce contracts, regulate all sorts of activities… The list is potentially endless.
Legitimacy is to the government what authority is to the police officer – the agreement of those being policed that the officer has the right to enforce the law. So when the cop says, “Move to the other side of the street,” we move. Without that agreement, without the authority of the badge, the cop has only the power of the gun. Similarly, a government that does not have legitimacy must rule by sheer power. Such governments, even if they are democratically elected, use the power of the state to lock up their political opponents, to harass or imprison journalists, and generally to ensure the compliance.
Trump is obviously not alone in his views about legitimacy. When I see the posters and websites claiming that Obama is a “tyrant” – one who rules by power rather than by legitimate authority; when I see the Trump supporters chanting “Lock Her Up,” I wonder whether it’s all just good political fun and hyperbole or whether the legitimacy of the US government is really at risk.
This morning, I saw this headline at the Washington Post:
Scary. But the content of the story tells a story that is completely the opposite. The first sentence of the story quotes the Post’s own editorial, which says that Trump, with his claims of rigged elections, “poses an unprecedented threat to the peaceful transition of power.” The second sentence evaluates this threat.
Trump’s October antics may be unprecedented, but his wild allegations about the integrity of the elections might not be having much effect on voter attitudes.
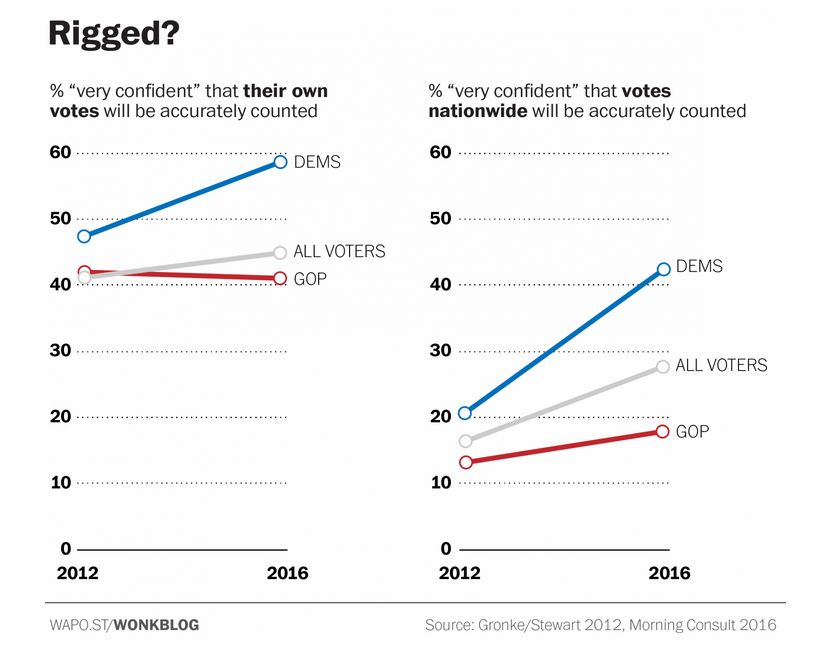
Here’s the key evidence. Surveys of voters in 2012 and 2016 show no increase in fears of a rigged election. In fact, on the whole people in 2016 were more confident that their vote would be fairly counted.
The graph on the left shows that even among Republicans, the percent who were “very confident” that their vote would be counted was about the same in 2016 as in 2012. (Technically, one point lower, a difference well within the margin of error.)
However, two findings from the research suggest a qualification to the idea that legitimacy has not been threatened. First, only 45% of the voters are “very confident” that their votes will be counted. That’s less than half. The Post does not say what percent were “somewhat confident” (or whatever the other choices were), and surely these would have pushed the confident tally well above 50%.
Second, fears about rigged elections conform to the “elsewhere effect” – the perception that things may be OK where I am, but in the nation at large, things are bad and getting worse. Perceptions of Congressional representatives, race relations, and marriage follow this pattern (see this post). The graph on the left shows that 45% were very confident that their own vote would be counted. In the graph on the right, only 28% were very confident that votes nationwide would get a similarly fair treatment.
These numbers do not seem like a strong vote of confidence (or a strong confidence in voting). Perhaps the best we can say is that if there is any change in the last four years, it is in the direction of legitimacy.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.