One of the most popular and controversial articles on my Asian-Nation.org site is the one on Interracial Dating and Marriage. This is a topic that has provoked much discussion and debate among Asian Americans through the years and continues to do so today. Within the larger range of opinions on interracial dating and marriage, many Asian Americans and non-Asians alike consider dating and marrying someone outside of your racial/ethnic group as a natural progression of Asian Americans becoming more integrated into the mainstream, while others see it as renouncing one’s Asian identity.
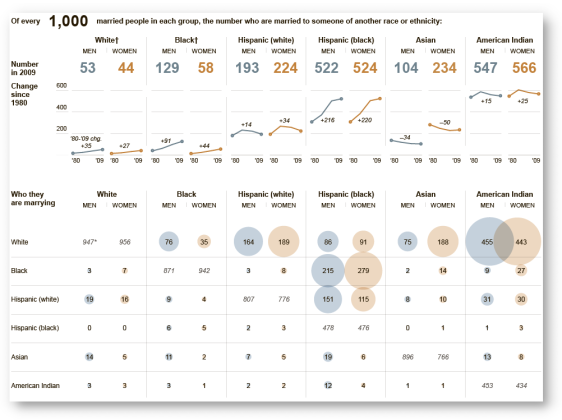
As the saying goes, you are entitled to your opinion, but not your facts. In that context, as a sociologist, I try to make an empirically-sound and objective contribution to this debate by presenting updated data and statistics from the 2010 U.S. Census American Community Survey (ACS) on the racial/ethnic marriage patterns of Asian Americans for both men and women and the six largest Asian ethnic groups. The full tables are presented in my Interracial Dating and Marriage page, but below is a summary of recent trends and changes from 2006, the last time I updated these statistics:

- Consistently, rates of marriages involving Asian Americans and Whites have declined. Specifically, among those marriages in which both spouses are U.S.-raised (either born in the U.S. or immigrated before age 13, and thereby socialized within the U.S. racial/ethnic landscape), for five of the six Asian American ethnic groups, the rates of having a White spouse for both men and women declined from 2006 to 2010. Among men/husbands, the largest decline involved Asian Indians and Koreans. For women/wives, the largest decline was for Filipinos and Koreans.
- The only exceptions to this trend of declining rates of White-Asian marriages were for Asian Indian women/wives (whose rate slightly increased from 2006 to 2010) and for both Vietnamese men/husbands and women/wives. For Vietnamese men, their rates of having a White wife increased from 15.0% to 21.9% while for Vietnamese women, their rate for having a White husband jumped from 28.3% to 41.3%.
- Strangely, the population sizes for U.S.-raised married Vietnamese American men and women declined from 2006 to 2010. For example, in 2006, there were about 40,500 and 45,200 U.S.-raised Vietnamese men and women respectively who were married. In 2010, those numbers declined to 26,795 and 34,998. Some possible explanations are that many who were married in 2006 got divorced, U.S.-raised Vietnamese men and women are delaying getting married, and/or many U.S.-raised Vietnamese have changed their ethnic identity to some other ethnic group, such as Chinese or Hmong.
- In contrast to the declining rates of Asian-White marriages, the rates for Pan-Asian/Other Asian marriages have increased notably from 2006 to 2010 (having a spouse of a different Asian ethnicity). This increase was almost universal across all the six ethnic groups and for both genders (the only exception was for Filipino women). Among U.S.-raised men/husbands, Vietnamese Americans experienced the biggest increases in having a pan-Asian spouse — from 5.8% in 2006 to 13.7% in 2010 for men and from 7.8% to 12.2% for women/wives.
This article originally published at Asian-Nation.org and is copyrighted © 2013