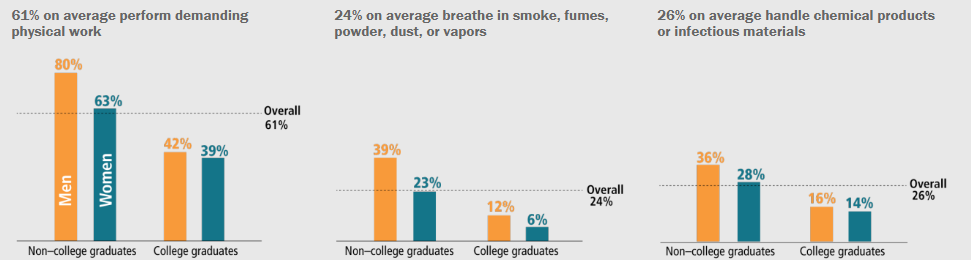In recent weeks, we’ve seen multiple examples of women on the political right straddling two kinds of womanhood: the girlboss and the tradwife. The visibility of these women exposes a hidden link between conservative womanhood and girlboss feminism that deserves our attention.
Katie Britt broadcast her response to the State of the Union from her kitchen. Michelle Morrow, the conservative activist from North Carolina who has just been elected state Superintendent of Education in North Carolina, burnishes her credentials as a wife and mother above all else.
They aren’t the first to do this; #tradlife has been trending since at least 2019. Tradwife influencers perform a version of femininity that leans on a strong husband providing financial support so they can devote themselves to caring for children and the home. There is almost always an apron, a kitchen, and a perfectly coiffed, carefully made-up woman in a serene environment cooking from scratch recipes — a vibe that belies the real chaos of having young humans to care for in a home.
We might assume that tradwives hearken back to an earlier “backward” mode of femininity and marriage. But this way of being in the world is unmistakably modern because it involves “choice” and entrepreneurship. It is not enough for a tradwife to simply focus on her husband and kids, she must be entrepreneurial about it. She must blog about it, vlog about it, become an influencer. This is where the “girlboss” mentality comes in.
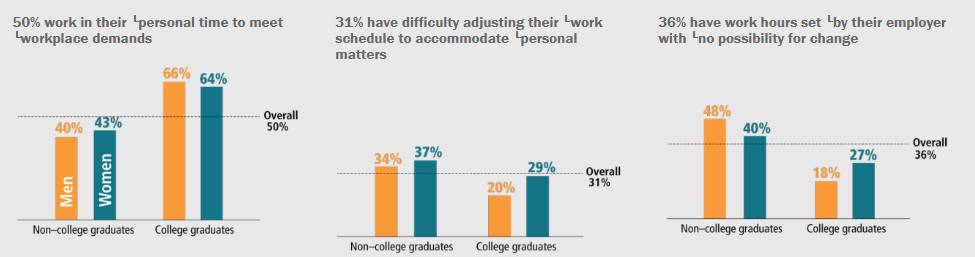
Sheryl Sandberg’s 2013 book Lean In told women that if they would just ask for what they wanted in the workplace, like the men, they too would advance. But women continue to face barriers in corporate America and marginalization in labor markets. Despite this girlboss feminism has been incorporated into our culture across the political spectrum. US women widely believe structural problems are with women ourselves. With individual effort, good planning, the right domestic help, and a little luck and chutzpah, we can overcome societal inequalities. We rely on a myth of mutuality that belies the true gender division of labor in American families.
It turned out lean-in feminism was both colorblind and a sham. And the #tradwives know it – there are even Black tradwife influencers. They say proudly: we have decided it’s way too exhausting to run the family and corporate America at the same time. So we will focus on our family and “opt out” of the vulnerability and constant stress of the labor market, which values our labor less. And in doing so, we take a stand with men and shore up the dying ideology of the father as breadwinner. We choose this, and you too can see just how great this choice is on our successful TikTok channels.
As we discuss in depth in our new book, The Gender Order of Neoliberalism, U.S. has long drawn soft power from the idea that its women are “empowered.” Not “backward,” like those oppressed women in the Middle East or India or Africa, who are poor and come from patriarchal cultures. Our women, we like to tell the world, make choices of their own, work outside the home in high-powered jobs, fly planes, and even save women in other parts of the world.

But focusing on the individual choices of women who must “do it all” was not always what “women’s empowerment” meant. We show in our book that women involved in transnational feminist organizing in the 1950s and 60s lobbied for reproductive justice, fair pay for fair work, universal childcare, universal healthcare, and fair trade between countries. Those visions of empowerment have all but disappeared from our collective political imaginations. What would a joyful life look like if there were community kitchen tables, childcare collectives, and widely available healthcare? Where are the inviting visuals for that kind of empowerment?
Our impoverished feminist imagination leaves us straddling the skinny divide between tradwives and girlbosses and reinforcing the notion that women should continue to be America’s social safety net.
Smitha Radhakrishnan is Marion Butler McLean Professor in the History of Ideas and Professor of Sociology at Wellesley College. She is author of Making Women Pay: Microfinance in Urban India.
Cinzia D. Solari is Associate Professor of Sociology at University of Massachusetts Boston. She is author of On the Shoulders of Grandmothers: Gender, Migration, and Post-Soviet Nation-Building.