Within the last decade, the grain quinoa has emerged as an alleged “super food” in western dietary practices. Health food stores and upscale grocery chains have aisles dedicated to varieties of quinoa, packaged under many different brand labels, touting it to be a nutritional goldmine. A simple Google search of the word returns pages of results with buzzwords like “healthiest,” “organic,” and “wholesome.” Vegan and health-enthusiast subcultures swear by this expensive food product, and the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) even declared the year 2013 International Year of the Quinoa, owing to the grain’s popularity.
The journey of the grain — as it makes it to the gourmet kitchen at upscale restaurants in countries like the United States — however, is often overlooked in mainstream discourse. It often begins in the Yellow Andes region of Bolivia, where the farmers that grow this crop have depended on it as almost a sole nutritional source for decades, if not centuries. The boom in western markets, with exceedingly high demands for this crop has caused it to transition from a traditional food crop to a major cash crop.
While critical global organizations like the FAO have been portraying this as positive, they tend to discount the challenge of participating in a demanding global market. Within-country inequality, skewed export/import dynamics, and capitalist trade practices that remain in the favor of the powerful player in these dynamics – the core consumer – cause new and difficult problems for Bolivian farmers, like not being able to afford to buy the food they have traditionally depended upon.
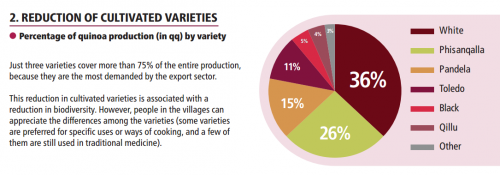
Meanwhile, growing such large amounts of quinoa has been degrading the Andean soil: even the FAO outlines concerns for biodiversity, while otherwise touting the phenomenon.
While efforts have been put in place by farmer unions, cooperatives and development initiatives to mitigate some negative effects on the primary producers of quinoa, they have not been enough to protect the food security of these Andean farmers. Increased consumer consciousness is therefore essential in ensuring that these farmers don’t continue to suffer because of Western dietary fads.
Cross-posted at Sociology Lens.
Aarushi Bhandari is a doctoral student at Stony Brook University interested in globalization and the impact of neoliberal policies on the developing world. She wants to study global food security within a global neoliberal framework and the world systems perspective.