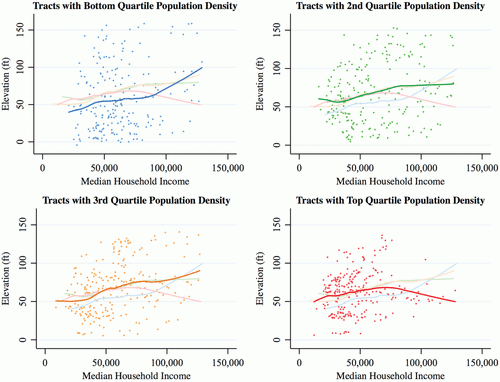
The pictures, of course, went viral. Donald Trump serving fast food, still in the box, to the college champion Clemson University football team. The cardboard containers and paper wrappers were artfully stacked on silver platters alongside ornate candelabras and embossed napkins and served on a formal table beneath a gold-framed portrait of Abraham Lincoln.

Sure the juxtaposition was glaring, and the media, the twitterverse, and the late night talk shows had a field day poking fun at the President’s seeming lack of class. The Washington Post headline quoted Patrick Guaschino, who accused the president of turning the “white house into a White Castle.” Comedian W. Kamau Bell joked that a white house staffer, “choking through tears [would say] ‘I guess we could use the Lincoln gravy boats for the McNugget sauces.’” My personal favorite meme photoshopped Ronald McDonald in place of the president.
These reactions also teach us something important about social class and “good taste.” Pierre Bourdieu famously wrote that “taste classifies the classifier (1984, 6),” and this insight has become essential to understanding contemporary American food cultures. In Discriminating Taste (2017), S. Margo Finn argues that the increasing fascination with “good food,” including trends toward the local, organic and artisanal, and the condemnation of fast and processed foods, are way for people to perform elite status. In a similar take on Foodies, Joseé Johnston and Shylo Baumann write that many foodies enjoy everything from high brow cuisine to street food, but often only enjoy fast food ironically (2010, 2012). And Julie Guthman (2011) and Charlotte Biltekoff (2013) offer contemporary and historical accounts of the ways that more affluent Americans have looked down on the food cultures and (always constrained) food choices of working class and immigrant groups as a way to boost their own cultural status and displace their own cultural anxieties.

Trump isn’t the only person who highlights our assumptions about food and social class. In an article that was just published in American Studies, media scholar Emily J. H. Contois examines Guy Fieri’s take on American food culture, arguing that he uses “unpretentious” foods, as well as his own bleach-tipped, tattooed presentation of self, to create a populist image that “speaks directly to eaters who oppose culinary elites and who experience a sense of disenfranchisement regarding their own sociocultural status.” Examining Fieri’s work offers a “method for considering the most recent rise of populist sentiment in the United States” (2018, 156). Her analysis aligns nicely with comedian Seth Meyers’ Late Night joke, which, playing on the fact that Trump said Burger Kings (plural) that, “had he lost the election, The Burger Kings would have been the name of the food show he would have co-hosted with Guy Fieri.”
Despite his own elite background, Trump has something of a masterful ability to appeal to white working class tastes, and to mobilize that group in opposition to political progressives who might actually work to improve their lives and livelihoods. Working class foods like burgers are part of the habitus through which these sort of Trump voters define themselves. To those who love fast food, serving it to football players might read like an embrace of their ways of being over the so-called cultural elites who (they believe) look down on them. Mocking Trump for this lends credence to this belief.
There is no shortage of reasons to object to fast food— land use and environmental degradation, worker exploitation, low pay, and the concentration of wealth in fewer and fewer hands—and, of course, there are no shortage of reasons to object to Trump’s behavior. But when we mock fast food culture out of context, we ignore the fact that many people have cultural attachments to these foods, and through them, tell themselves stories about who they are and what they believe in. As sociologists, I hope we can hear and empathize with those stories, rather than dismiss them.
Recommended Readings:
Baumann, Shyon and Joseé Johnston. 2012. “Democracy vs. Distinction in Omnivorous Food Culture. Sociologica. 2: 1-12.
Biltekoff, Charlotte. 2013. Eating Right in America. Chapel Hill, NC: Duke.
Bordieu, Pierre. 1987. Distinction: A Social Critique of the Judgement of Taste. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Contois, Emily J. H. 2018. “Welcome to Flavortown: Guy Fieri’s Populist American Food Culture.” American Studies. 57(3): 143-157.
Guthman, Julie. 2011. Weighing In. Berkeley: UC Press.
Johnston, Josee and Shyon Baumann. Foodies. NY: Routledge.
Alison Hope Alkon is associate professor of sociology and food studies at University of the Pacific. Check out her Ted talk, Food as Radical Empathy