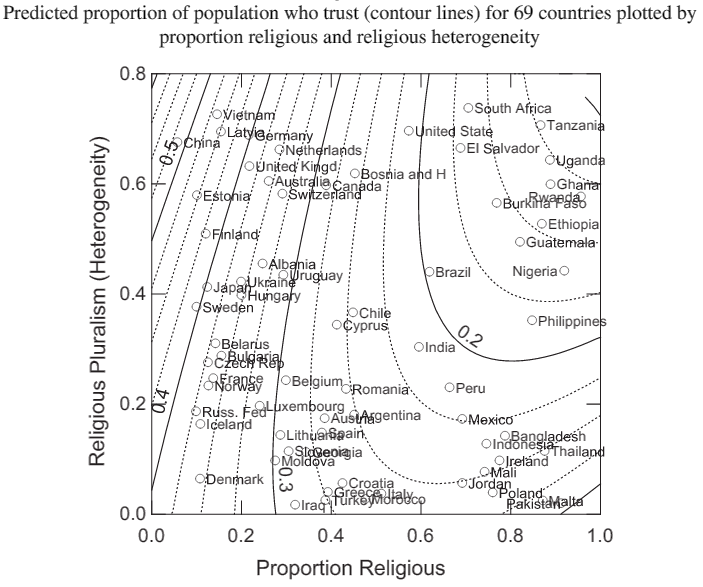
Are some Trump supporters’ political views motivated by race?
One way to find out is to see whether the typical Trump supporter is less likely to support policies when they are subtly influenced to think that they are helping black versus white people. This was the root of a study by political scientists Christopher Federico, Matthew Luttig, and Howard Lavine.
Prior to the election, they asked 746 white respondents to complete an internet survey. Each person was randomly assigned to see one of two pictures at the beginning of the survey: a white man standing next to a foreclosure sign or the exact same photograph featuring a black man. Respondents were also asked whether they supported Trump. (Non-white people were left out of the analysis because there were too few Trump supporters among them to run meaningful comparative statistics.)
The first graph shows that white Trump supporters were eight percentage points more likely to oppose mortgage relief if they had seen a “black cue” (the picture featuring a black man) than a “white cue.” The opposite was true for white Trump opponents.
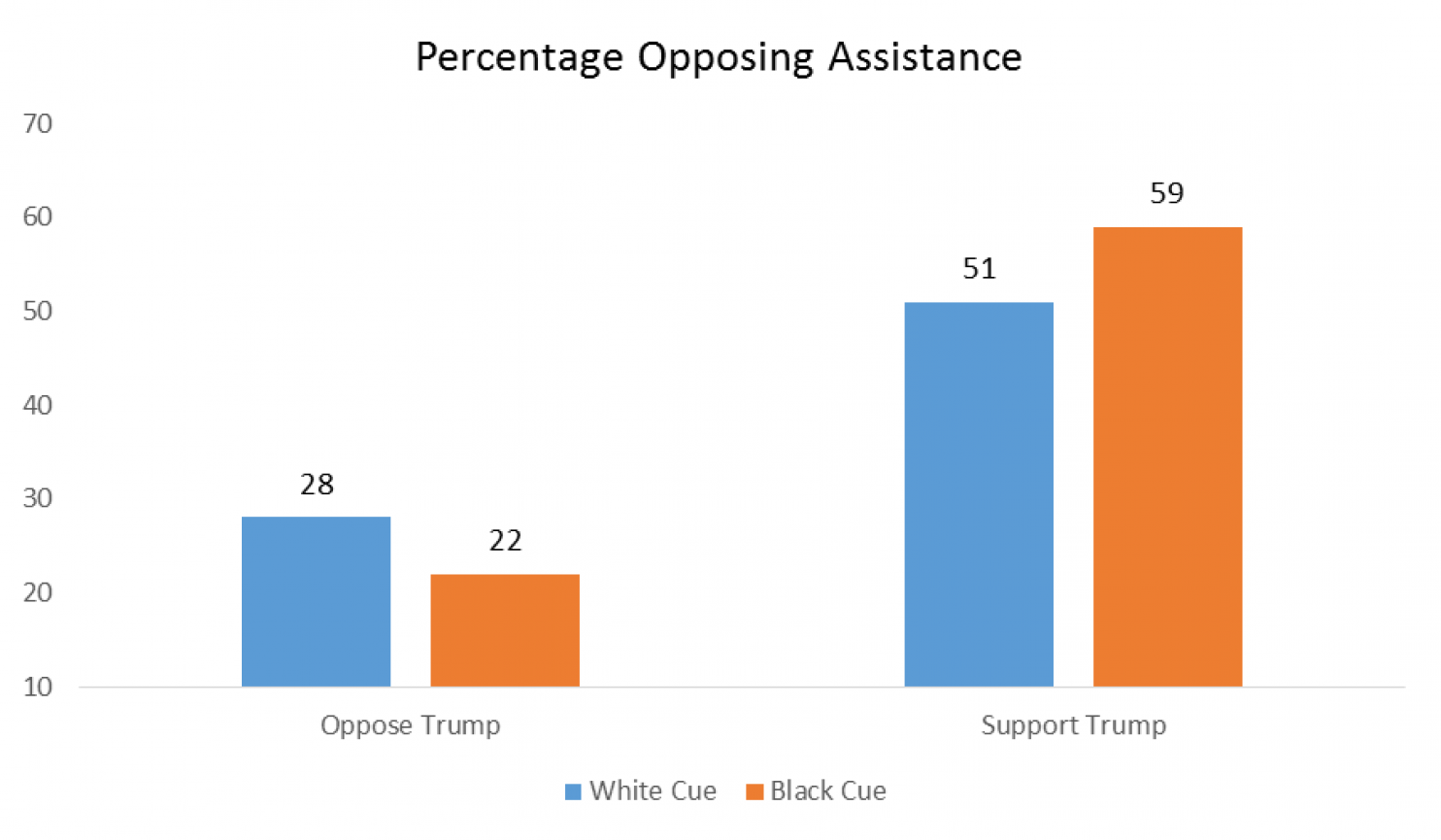
When asked if they were “somewhat angry” about the assistance, the same pattern held:
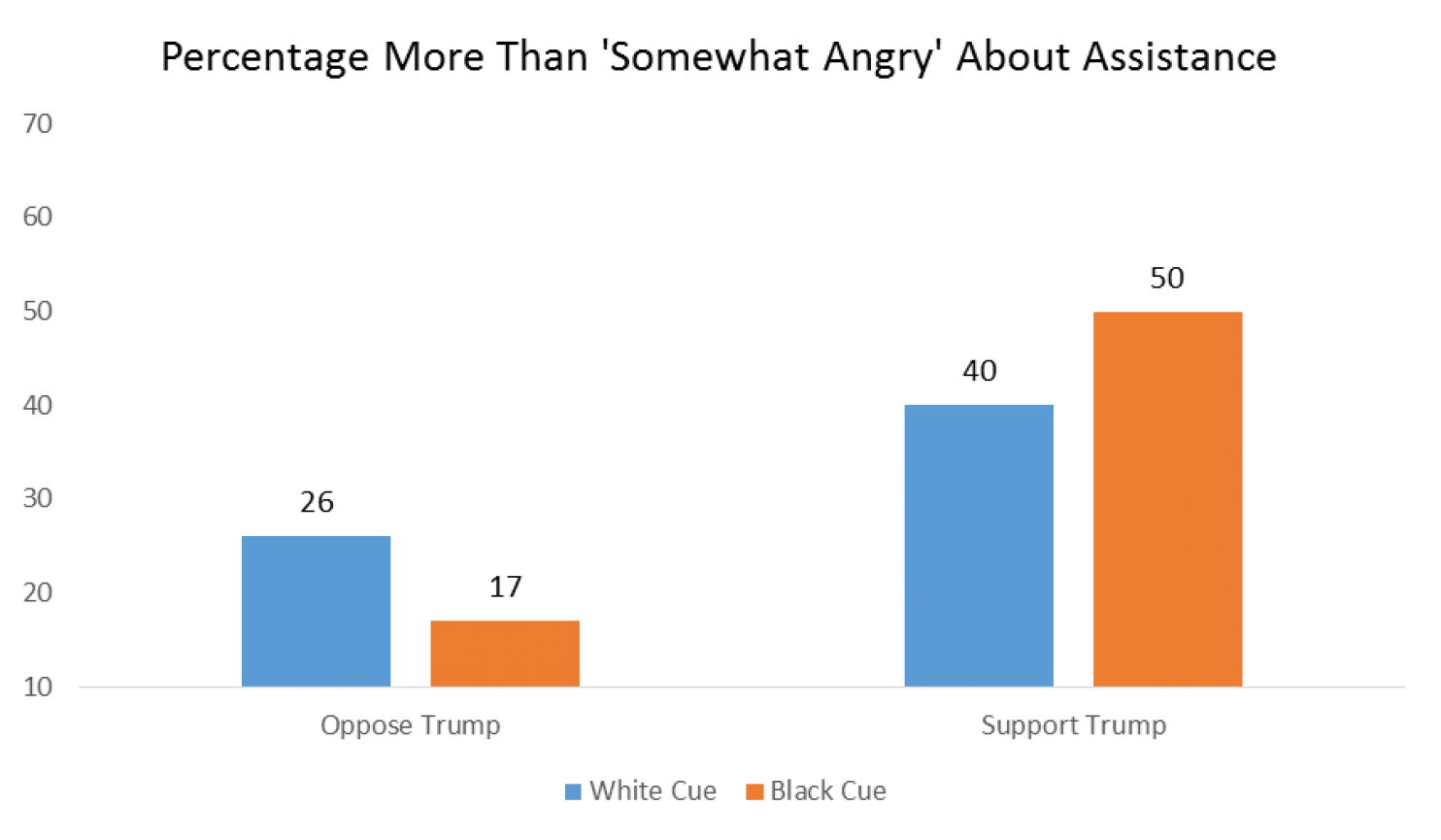
And likewise when asked if the beneficiaries of mortgage assistance were at least “somewhat to blame” for their situation:
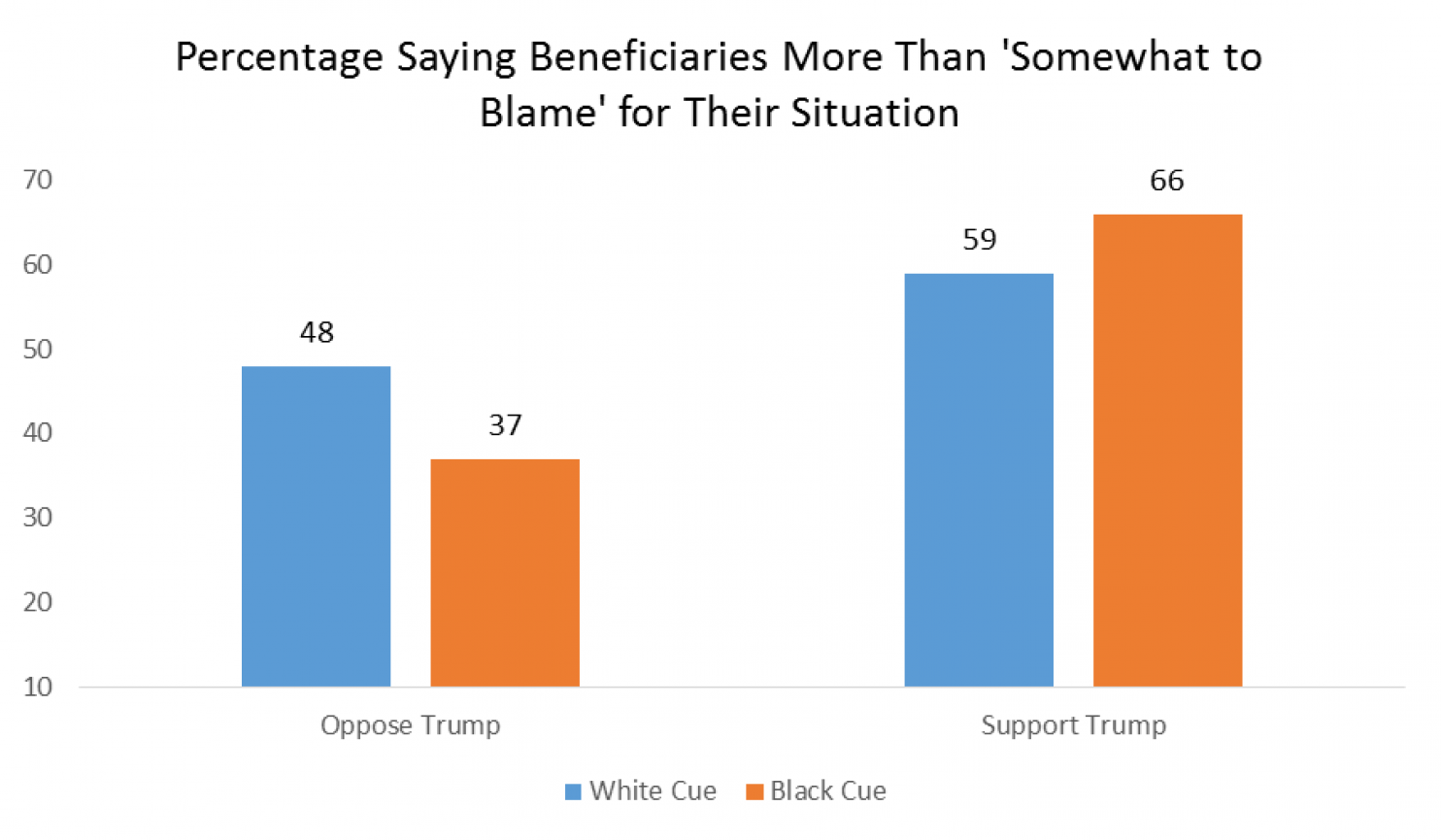
Findings held when the researchers controlled for possible confounding variables.
These findings aren’t particularly surprising. Others have also found that priming respondents to think of black people tends to make them tougher on crime and advocate for less generous social programs, like in this study on attitudes toward CA’s three-strikes law. What’s new here is the difference between Trump supporters and opponents. For opponents of Trump, priming made them more sympathetic toward mortgage holders; for supporters, priming made them less. This speaks to a real divide among Americans. Some of us feel real hostility toward African Americans. Others definitely do not.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.