New York City’s stop-and-frisk policy has gotten intensified scrutiny recently. A stop and frisk refers to police officers stopping and searching individuals who are out in public. These stops don’t require a warrant; the police officer has to have reasonable cause to believe the person is engaged in criminal activity.
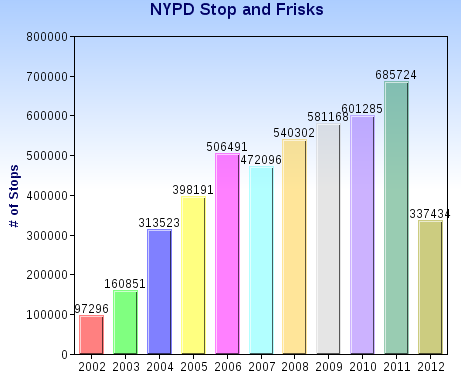
Critics point out that these stops are incredibly inefficient, and that relying on cops’ evaluations of who is suspicious opens the door to widespread racial profiling. The New York Civil Liberties Union analyzed the NYPD’s own data, which they are required to record about all stops. Over the past decade, literally millions of people have been the targets of stop-and-frisks, with steady growth in the use of the program. I made a chart of the data from 2002 through the first 6 months of 2012:
Yet all these stops have led to little discovery of actual crime. Overall, about 87-89% of stops lead to no evidence of wrong-doing.
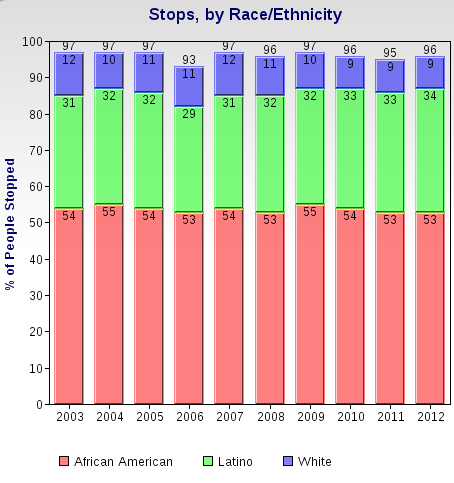
These stops have also disproportionately affected minorities. Here’s a breakdown by race/ethnicity, based on the NYPD data:
You can read more about the data on stop-and-frisks at the NYCLU website.
The Nation recently posted a video that discusses the impacts of stop-and-frisk on the lives of those targeted and on perceptions of the police, as well as police officers discussing the pressure to complete stop-and-frisks. The clip includes an audio recording that a 17-year-old made when he was being targeted for a stop-and-frisk after having just been stopped a couple of blocks earlier. As the video makes clear, these stops are about more than an inconvenience in citizens’ lives; they involve real harassment and fear of violence for those who find themselves the target of police suspicions:

Comments 14
Taryneh — October 15, 2012
There are a few petitions regarding stop and frisk on change.org. This is an awful way to treat our young people. This would never continue if the stops where random or otherwise included those from privileged groups. They would complain and organize, and they would be heard. THese young men should be heard too.
Yrro Simyarin — October 15, 2012
Disgusting abuse of the police state. And then they wonder why people won't cooperate with the police.
Jerry Detry — October 15, 2012
I just read Chris Arnade's account today at about the time you posted yours:
http://arnade.tumblr.com/post/28834272034/how-to-get-a-ticket-if-white-in-hunts-point Since reading his original post it has been updated as of today.
Astralrunner — October 15, 2012
Since middle and upper class crimes are much more likely to be white-collar, wouldn't the equivalent to a stop-and-frisk for them be a random tax audit? It's not like you're going to find some money launderer's tax return in their pockets with sticky notes pointing out all the fraudulent parts for the cop to recognize.
Racial Disparities in the Criminal Justice System | Erin V Echols — October 16, 2012
[...] Racial profiling still continues today, For example, New York Cities Stop-and-Frisk policies allow cops to stop and frisk individuals who are deemed “suspicious,” Police people overwhelmingly stop (and routinely harass) people of color during these stops, yet 87-89% of the... [...]
Food for Thought: Critical Intersections of Law, Race, Gender, and Class | Law and Society@Kwantlen — October 27, 2012
[...] Images has an interesting post on the NYPD ‘stop-and-frisk’ policy. The post includes a link to the video [...]
NYPD’s stop-and-frisk policy and Critical Race Theory | Law and Society@Kwantlen — November 2, 2012
[...] http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/2012/10/15/nypds-stop-and-frisk-policy/ Share this:TwitterFacebookLike this:LikeBe the first to like this. [...]
NYPD and ‘Racial Profiling’ | Law and Society@Kwantlen — November 4, 2012
[...] Sharp, G. (2012, October 15). NYPD’s Stop-and-Frisk Policy. Retrieved from: http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/2012/10/15/nypds-stop-and-frisk-policy. [...]
NYPD Stop & Frisk; Protected Ideology of the Elites | Law and Society@Kwantlen — November 5, 2012
[...] http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/2012/10/15/nypds-stop-and-frisk-policy/ [...]
Say NO to hiring Bratton : #oakmtg ‘Public Safety’ | Occupy Oakland Calendar — January 14, 2013
[...] Bratton was the NYPD Commissioner who led the department into policies including stop & frisk, now deemed unconstitutional by a NYC court, and years of under reporting of crimes in order to [...]
Crime, News Coverage, and Institutional Racism « shouting loudly — July 22, 2013
[...] (y)our hearts; it can be in the mortgage you grant or don’t, the education policies you adopt, or the policing tactics you support. Mayor Bloomberg is obviously comfortable around racial minorities and would surely never dream of [...]
New York City: A Police State | bsfoundinq101 — March 18, 2015
[…] http://thesocietypages.org/socimages/2012/10/15/nypds-stop-and-frisk-policy/ […]