Today is Labor Day in the U.S. Though many think of it mostly as a last long weekend for recreation and shopping before the symbolic end of summer, the federal holiday, officially established in 1894, celebrates the contributions of labor.
Today is Labor Day in the U.S. Though many think of it mostly as a last long weekend for recreation and shopping before the symbolic end of summer, the federal holiday, officially established in 1894, celebrates the contributions of labor.
Here are some SocImages posts on a range of issues related to workers, from the history of the labor movement, to current workplace conditions, to the impacts of the changing economy on workers’ pay:
The Social Construction of Work
- The surprisingly racist reason we don’t tip flight attendants
- Luxury and the consumption of labor
- The unsung heroes of the crash landing in San Francisco
- Why do firefighters take such risky jobs?
- McDonald’s delusional blame-the-victim budget
- Devaluing hospitality workers
- Domestic behavior as both gendered and raced: Who does what for airlines?
- Child labor and the social construction of childhood (pictured)
- Child labor, 1908-1912
- Women are 49% of the workforce, but we still think work is for men
Work in Popular Culture
- Children’s books and segregation in the workplace
- Hurricane Sandy and high fashion: Portraying a class hierarchy
- Whimsical branding obscures Apple’s troubled supply chain
- The “working family” discourse and the invisibility of individuals
- The DJ in American culture: Resonant but misunderstood
- Whiteness and tokenism on the runway
- Forbes’ photostock faux paus (what do women workers look like?)
Unemployment, Underemployment, and the “Class War”
- The “Precariat”: The new working class
- When classes collide: Workers and guests at high end hotels
- Who benefits from government programs?
- Food stamps, public policy, and the working poor
- Can the minimum wage cover average housing costs?
- Discrimination against the long-term unemployed
- Jon Stewart on class warfare
- Mike Rowe defends blue-collar manual labor
Unions and Unionization
- What have unions ever done for us?
- Footage of strikes and protests
- “Is your washroom breeding Bolsheviks?”
- Target’s anti-union video for new employees
- Unemployment and support for unions
- César Chávez and the fight for farmworkers’ rights
- Hiring non-union workers to staff picket lines
- “A woman’s place is in her union!”
Economic Change, Globalization, and the Great Recession
- Prison labor and taxpayer dollars
- The austerity agenda and public employment
- How many PhDs are professors?
- Professors join the “precariat”
- The exploitation of worker productivity
- What kinds of jobs are we gaining in the slow recovery?
- Historical look at changes in types of work
- Two American families trapped in a changing economy
Gender and Work
- Most women would rather divorce than be a housewife
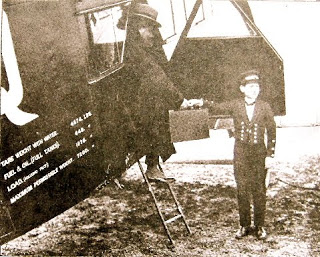
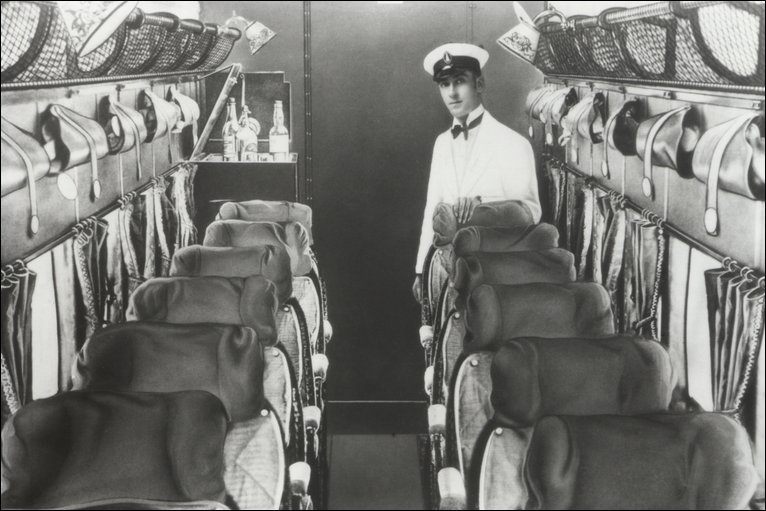
- Before the stewardess, the “steward”: When flight attendants were men
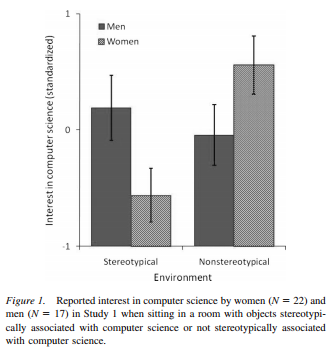
- Star Trek is scaring the ladies: Why women don’t major in computer science
- The dual career academic couple
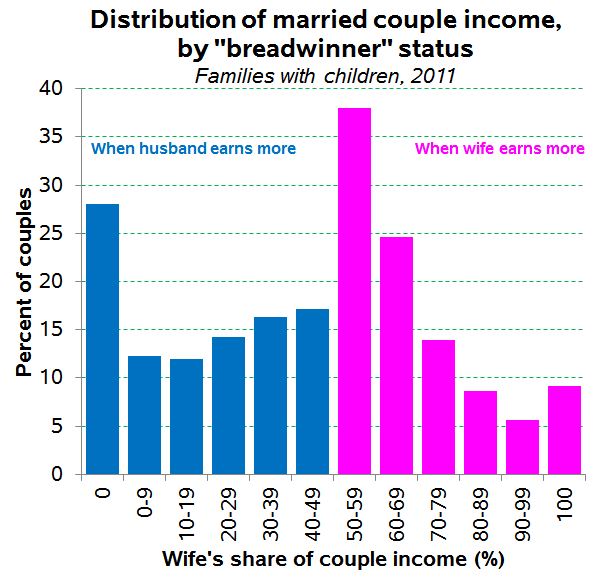
- Why “breadwinner moms” don’t portend a coming matriarchy
- Single mother, meet jobless man
- Gender, work, and family time
- First-time mothers and access to paid work leave
- The role of employer selection in gendered job segregation
The U.S. in International Perspective
- The U.S. is las in paid vacation and holidays
- International comparison of workplace leave policies
- Vacation in international perspective
Just for Fun
- Who is the highest paid employee of your state?
- Secrets of the Internet Adult Film Database
- Two-thirds of college students think they’re going to change the world
Bonus!
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.