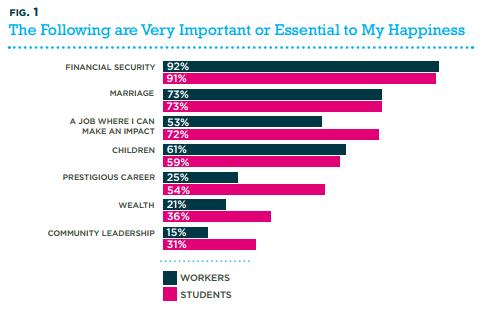
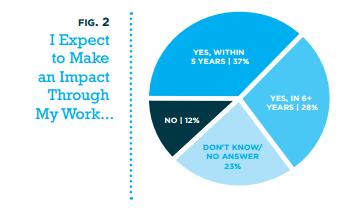
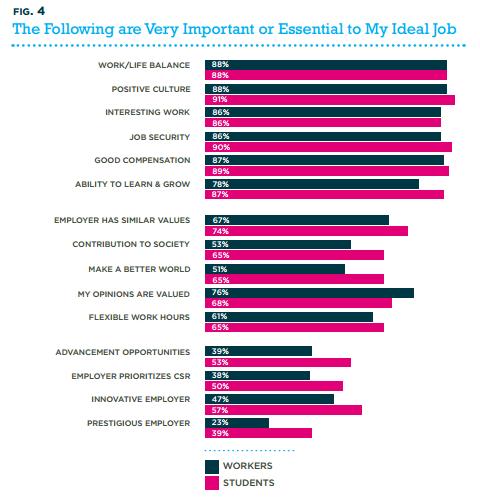
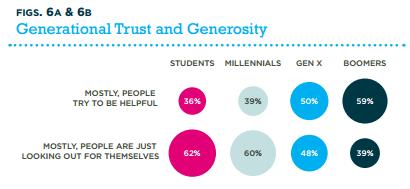
Course Guide for
FAMILIES AND SOCIETY
(last updated 9/2013)
Developed by Marcie Hambrick, MSW
Georgia State University
Defining Contemporary Family
- How do we define a family?
- U.S. trends in marriage, divorce, and cohabitation
- Why I’m not married
- Less marriage and more cohabitation in Los Angeles
- “Traditional” marriage
- Marriage is over: “Live with it”
- Recession, resilience, divorce?
- Is marriage changing?
- Considering the meaning of marriage equality
- Global attitudes toward homosexuality
- Americans underestimate how many other Americans support same sex marriage
- Why are people changing their minds about same-sex marriage?
- Nearly one-in-five adults still living with their parents
Partnering
Childless Families
Parenting
- The cost of in-vitro fertilization
- Representing transracial adoptions
- Discourses on adoption in Once Upon a Time
- Teenage pregnancy as moral panic
Socialization of Children
- Babies learn how to have a conversation
- Baby worshipper: An example of religious socialization
- On children and socialization
- Hasbro teaches girls to be good housewives
- Boys, social control, and school dress codes
- Halloween costumes
Extended Family
Gendered Roles
- Most women would rather divorce than be a housewife
- The power of pork: Who needs feminism?
- The relationship between patriarchy and the denigration of men
Work and Family
- The “motherhood penalty”
- Both sexes increasingly value both career and family
- Gender and family time
- Why did married mothers go to work?
- Class privilege and parental leave
- Relax, “breadwinner moms” do not portend a coming matriarchy
- Single mother, meet jobless man
- Gender and the dual career academic couple
Race and Family
- Framing children’s deviance
- Failing to understand when non-white people distrust the police
- Does positive stereotyping explain Asian academic success?
Social Class and Family
- Social class and the college choices of high school valedictorians
- Poverty poses a bigger risk to pregnancy than age
Family Violence