Re-posted in honor of Grandparents’ Day.
My Christmas present to my mom one year was time off from childcare. For several days while I was back home, I took over all of her usual duties regarding her grandkids; as she tries to support two daughters who are divorced with kids and struggling to get by, taking care of grandkids had expanded to take up most of her non-working life. She was incredibly excited to have the free time to finally go to the dentist and do other basic errands for herself.
MetLife and Generations United just released the results of a study of grandparents’ contributions to the support and care of their grandkids. It illustrates how grandparents serve as a support system, providing both childcare and financial assistance.
The data come from a national sample of 1,008 grandparents over age 45. A caution: the survey was conducted online, though they say the sample was weighted to be representative of the full population, not just the online population.
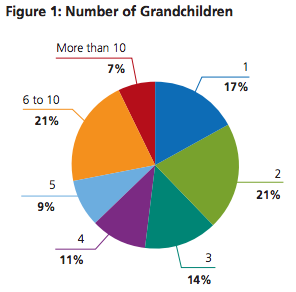
On average, grandparents have 4 grandkids:
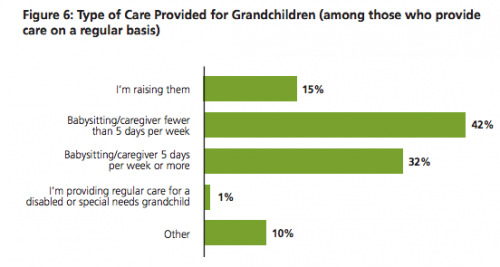
Thirteen percent of the sample reported caring for their grandchildren on a regular basis. Of those, a third watch the grandkids at least 5 days per week, while over 40% babysit less often, and 15% are raising their grandchildren:
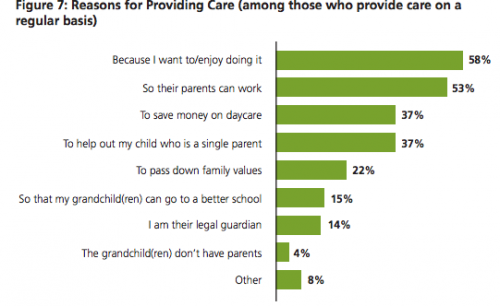
Most grandparents reported that one of the reasons they watch their grandchildren is because they enjoy it, but their answers also make clear that grandparents are playing a key role in filling the gap in care during periods when parents are at work but kids aren’t in school:
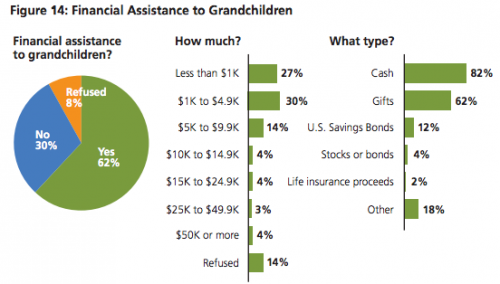
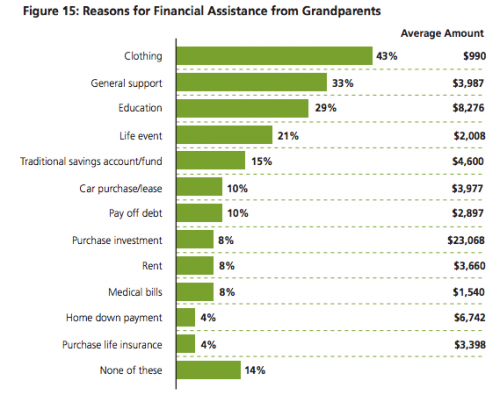
Grandparents also serve as a form of economic safety net. It’s not surprising that grandparents buy stuff for their grandkids; we often depict grandparents as spoiling their grandkids with lots of toys and luxuries. But grandparents also provide more direct support. Of this sample, 62% had provided financial assistance in the past 5 years, and of those, 43% said they are providing more help than they used to because of the economic crisis. These graphs show the amount and type over the past 5 years:
And the money isn’t just going for toys and fun stuff. Clothing, general financial help, and educational expenses are the most common types of assistance, though the biggest average levels of giving are for investments, followed by educational expenses and helping buy a home:
A third (34%) said they continue to provide financial assistance even though they think it’s going to cause problems for their own financial futures.
For another aspect of the essential support grandparents provide, check out Philip Cohen’s earlier post on poverty and the number of kids living with their grandparents.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.