Log onto any website where men who have sex with men (MSM) go to meet partners, and a key classification is whether a man is a “top,” a “bottom,” or “versatile.” These terms to refer to whether, when having anal sex with men, a man prefers to penetrate, to be penetrated, or is open to both. But are these durable roles?
We examined how much college MSM specialize as tops or bottoms. We find that, among college men who have ever had anal sex with a man, most have been both a top and a bottom sometime, most have done both across the course of their most recent relationship, and some have done both within a single date or hookup.
We use the Online College Social Life Survey (OCSLS) that surveyed more than 20,000 US students in 21 colleges and universities between 2005 and 2011. We use data from all 493 men who have had sexual interaction with men, and on the 826 events with men on which these men reported. The types of events respondents were asked to report on were their most recent hookup, their most recent date, and the most recent time they had sex within their most recent (or current) relationship of at least 6 months.
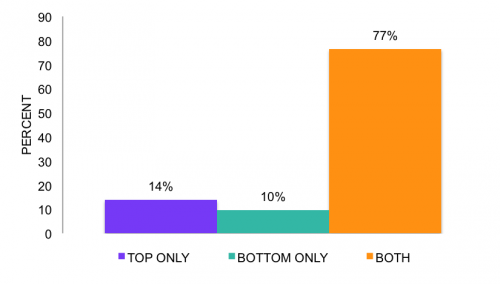
First, we found that only a small minority have only topped or bottomed. Of the men who have ever had anal sex with a man, 14% said they had only topped, 10% said they had only bottomed, and the vast majority, 77%, said they had done both.
Among MSM who have ever had anal sex, percent who have only topped, only bottomed, or done both
While the graph above shows that most MSM have tried both roles at least once, it is still possible that men tend to take only one role within any given relationship. In fact, this is true for 30% of men whose last relationship of at least 6 months in duration was with a man. But a large majority, 70%, played both roles with their partner sometime during the relationship – that is, they were both top and bottom at some point in that relationship.
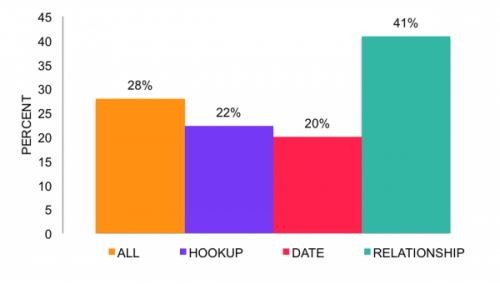
Our most striking finding is shown in the next graph: often men are both top and bottom within a single event. In MSM events that involved anal sex, over 25% entailed both partners being top and bottom in that event. Men did both in about 20% of hookups and dates. They were even more likely to have been top and bottom the last time they had sex in their most recent relationship — 41% of the time. Thus, combining the previous graph with this one, we see that 70% of MSM relationships involved the man doing both sometime across the duration of the relationship, and 41% of specific times they had sex with relationship partners involved doing both.
Among MSM events involving anal sex, percent in which men both top and bottom, by type of event
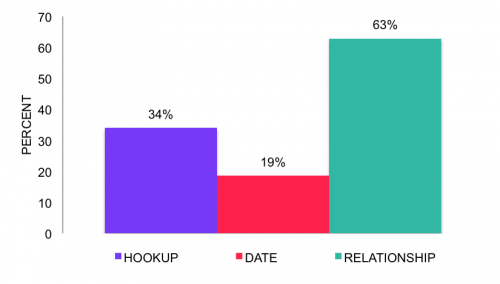
Everything we have shown above is limited to events involving anal sex, or men who have had anal sex with men. But how common is anal sex among college MSM? The graph below shows how often it occurred in specific events. Only about a fifth (19%) of events men labeled dates involved anal sex, compared to about a third (34%) of hookups (that difference is statistically significant). So most college MSM hookups and dates don’t involve anal sex at all. They generally involve oral sex (results not shown). But a majority of times when men have sex with a male relationship-partner, they do have anal sex — in 63% of cases. These findings bear some similarity to what we find for heterosexual students — that students are more likely to have intercourse in hookups than dates, but most likely to do so in relationships.
Percent of MSM events that involve anal sex, in hookups, dates, and relationships
 In sum, the clear message of our analysis is that being versatile is common among college MSM — most men have been both tops and bottoms sometime, most relationships involve switching between roles, and a significant minority of single events involve both, especially when the event occurs within a relationship.
In sum, the clear message of our analysis is that being versatile is common among college MSM — most men have been both tops and bottoms sometime, most relationships involve switching between roles, and a significant minority of single events involve both, especially when the event occurs within a relationship.
Methodological details included at Contexts, where this post originally appeared.
Eliza Brown is a PhD student at NYU with interests in the sociologies of knowledge, health, and sexuality. Also at NYU, Paula England is a professor of sociology, the Director of Graduate Studies, and the principal investigator for the Online College Social Life Survey. If you are a researcher and would like to have the OCSLS data for analysis, contact Dr. England for information.