In Buying In: What We Buy and Who We Are, Rob Walker discusses the “mysterious return of PBR.” When I was an undergrad in Oklahoma in the late ’90s, PBR had very distinct connotations: it was a crappy, cheap beer you only drank if you didn’t have the money to buy better beer. I know this in large part because I had a number of friends who weren’t in college and lived on low incomes for various reasons, including some who were in bands and kept crappy day jobs just until they got their big record deal. [Just FYI: a punk-influenced song about Schrodinger’s cat can be quite catchy and informative, but it may not be the key to fame and fortune.]
I digress. The point is, they often drank PBR because it was cheap. As far as I could tell, they didn’t do so out of a sense that PBR was good or cool, but because they could buy larger quantities of it than other beer (I was never a beer drinker, so I wasn’t directly engaged in the decision-making process about which brand to buy). It was the beer version of ramen noodles: not necessarily exciting, but it’ll suffice if it’s all you can buy. And at various times I would overhear other people make nasty comments about PBR. It, and its drinkers, were, to put it bluntly, considered trashy by a lot of people.
But as Walker describes, PBR has become hip in a lot of places. Walker describes its resurgence since about 2002, when sales, which had dropped precipitously over the last twenty years, suddenly rose 5%. Portland, OR, seems to be the epicenter of the rediscovery of PBR, though it soon spread to other cities, with trendy bars adding it to their menu.
PBR, surprised by this, set about finding out what was going on. They eventually decided that PBR had become a “protest brand,” the non-hyped underdog beer that hipsters chose because it was non-mainstream and wasn’t constantly pushed at them by a PR machine. As a result, PBR rejected a lot of standard marketing tactics (though they did pay to have the beer placed in the 2009 movie Whip It, among others). Instead, they chose to focus on sponsoring events that the new customer base attended or participated in, but in a relatively quiet, non-intrusive way. Here’s a post for an event PBR is sponsoring this Saturday in Atlanta:
Part of PBR’s image, and attraction to people who consider themselves outsiders, is its association with what Walker calls a “blue-collar, honest-workingman, vaguely anticapitalist image” (p. 113). It’s old-school, blue-collar, salt-of-the-earth beer from the days of Milwaukee’s manufacturing and beer-producing glory. When you buy PBR, it lists a P.O. Box in Milwaukee, and the website lists Milwaukee at the bottom of the page.
Except…not so much. PBR is no longer headquartered in Milwaukee. In 1985 PBR was purchased by a man who was buying up a lot of low-market-share beer companies. He moved the headquarters to San Antonio (in May of this year he announced he sold PBR to another company; the headquarters are now in a suburb of Chicago). The move put about 250 people in Milwaukee out of work, including a lot of the blue-collar workers the beer is associated with.
On top of that, PBR doesn’t actually make beer anymore. Miller brews beer for the company, which then packages it in PBR cans. PBR is no longer a producer of beer; it’s a name and logo attached to beer made by a company many of the people drinking PBR would probably dislike.
On the one hand, PBR is a case that shows how consumers make decisions and can affect the marketplace independent of advertising campaigns; PBR certainly wasn’t spending a lot of money trying to woo this new demographic and didn’t initially know quite what to make of it. A group of consumers identified with PBR. That is, they saw the company as like them. They dislike in-your-face marketing, the feeling that companies are trying to manipulate them. They’re outsiders who see themselves as dissenters from a lot of mainstream culture. And PBR fits well with this identity; it’s the underdog, old-school beer company that isn’t actively trying to win over consumers. No TV commercials, no PBR babes in bikinis giving away free samples at bars. And it has working-class cachet.
But much of this is symbolic. Buying PBR makes money for Miller, a company that uses the loud marketing techniques hipsters express disdain for. At this point, you could argue that PBR is simply a beer fashion label. And while it might have associations with the working-class, the process of outsourcing its beer to Miller and moving headquarters to a different state left quite a few members of that class out of work. Walker argues that this indicates a new form of solidarity with blue-collar workers. It isn’t about making sure you’re buying from companies that pay a living wage or fighting for better working conditions. Symbolic solidarity — paying a nod to the working class by buying products (beer, clothing, etc.) — is often seen as sufficient. By drinking PBR you’re identifying with blue-collar workers in spirit, if not in any specific, concrete way.
PBR capitalizes on the perceptions of the brand while engaging in or working companies who engage in many of the practices that those who repopularized it were rejecting when they switched to PBR in the first place.
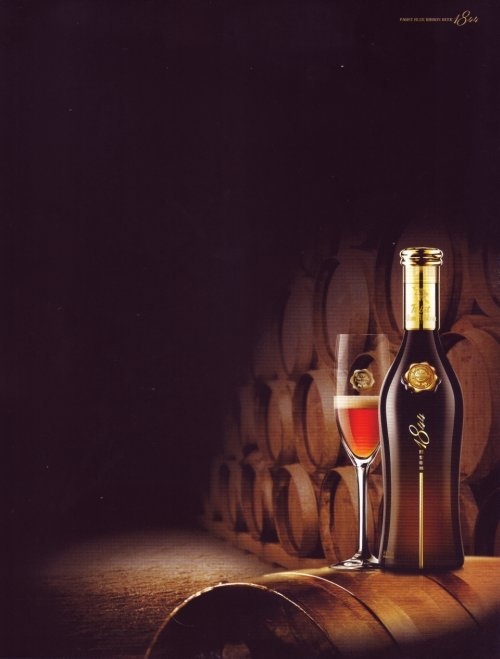
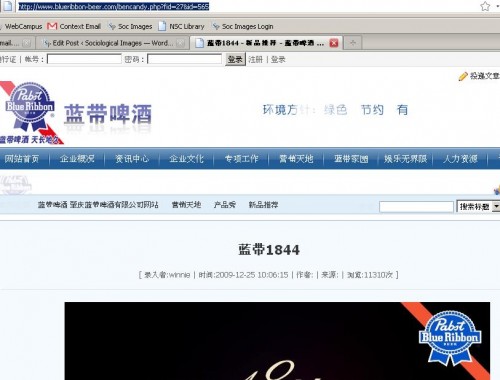
And, just to add one more twist to the story…in China, PBR sells a specialty beer called Blue Ribbon 1844:
How much does the beer sold by the cheap, working-class company cost in China? Why, $44 a bottle. A PBR executive who oversees the Asian market explains, “There’s the nouveau riche, and in China, perception is everything—look at me, I’m rich.” Not exactly the bike-messenger hipster crowd.
So there you go…the long, bizarre, contradictory story of PBR.
————————–
UPDATE: I got an email from an employee of PBR, who says this in defense of the brand:
I just want clear up a huge misunderstanding…We actually are independent American Company, not owned by Miller Brewing. Pabst itself contracts out all its production to other breweries, and has become, in effect, a “virtual brewery.” This keeps our beer fresh and saves us the cost of shipping large distances. It saves the earth, and helps us keep cost low. Many brand do this, also a few micro brands, you be surprised. We are 100% American Company. We also have NOTHING to do with the China Brand. They are a totally separate company just to let you know.
I thought it was only fair to share his viewpoint. However, I don’t know that there’s really a misunderstanding there. I know PBR isn’t owned by Miller, but rather that the company outsources production of their beer, and I *think* my discussion made that distinction. I apologize if anyone was confused by that. As for my assertion that buying PBR makes money for Miller, it’s not because Miller directly owns them, but because they get money for the outsourcing, which common sense indicates they profit from or they wouldn’t keep doing it.
I’m more skeptical about the claim that PBR has nothing to do with the China beer. The Chinese website for the beer has the regular PBR logo prominently displayed on both the site itself and the poster for the beer:
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.