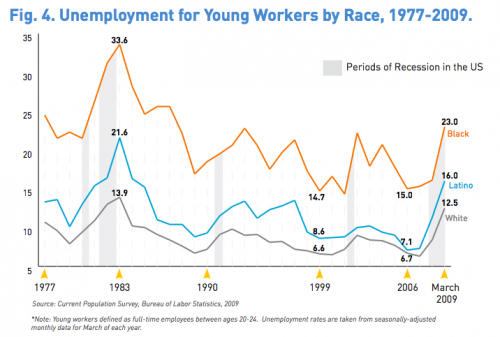
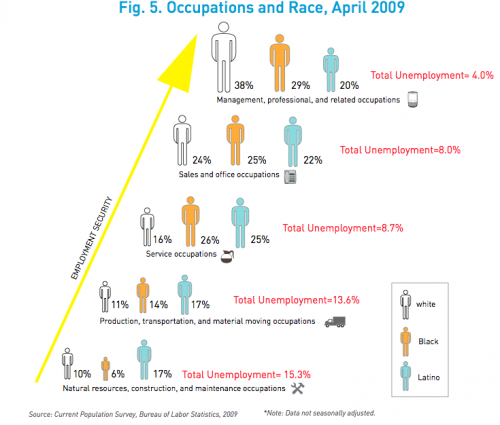
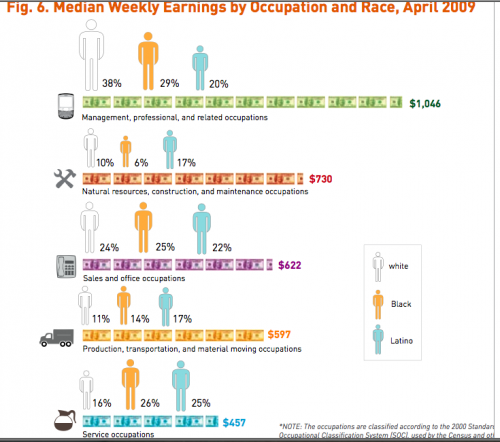
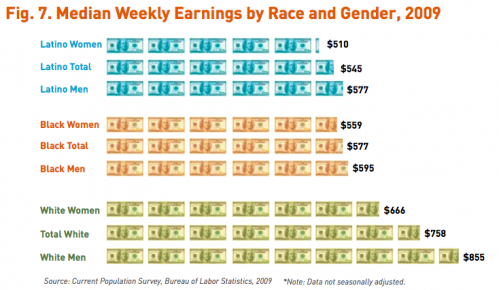
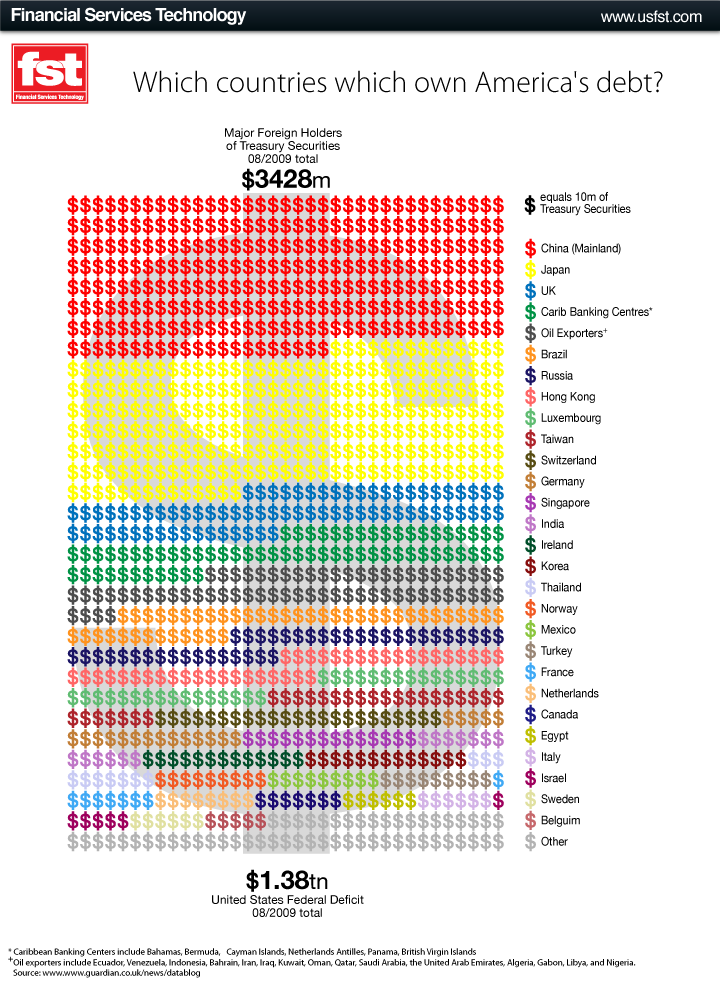
Farrah F. sent us a link to an article on the website for Forward, a newspaper aimed at the American Jewish community. The article looks at the gender gap in pay at Jewish community organizations. According to the article,
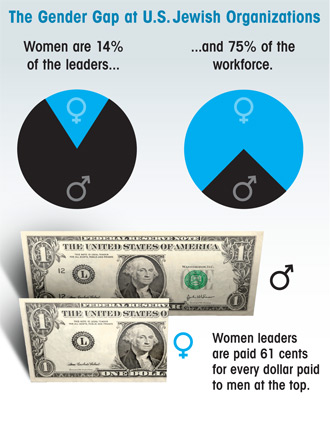
…a Forward survey of 75 major American Jewish communal organizations found that fewer than one in six are run by women, and those women are paid 61 cents to every dollar earned by male leaders.
Incomes of leaders of the organizations they surveyed (data is from 2008 unless otherwise specified, and women are highlighted in blue):

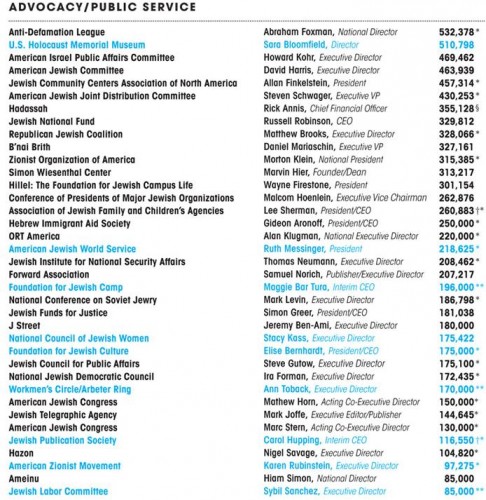

The Forward’s survey was drawn from the most recent public records or, if that information wasn’t available, from the organization itself. The median salary for men was $287,702, while the median for women was $175,211, amounting to a ratio of 61 cents to one dollar.
More from the article:
Women comprise about 75% of those employed by federations, advocacy and social service organizations, and religious and educational institutions, but occupy only 14.3% of the top positions. Of the 11 female leaders identified in this survey, three are in interim roles.
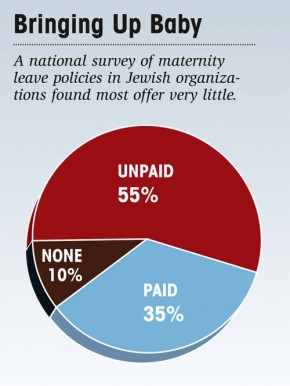
In another article, Forward discusses family leave policies at Jewish organizations, finding that relatively few offer paid leave:
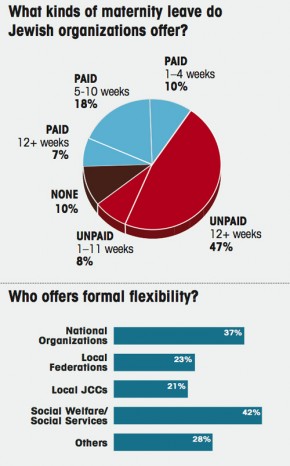
UPDATE: A few people have asked why I chose to post about these particular organizations. The short answer is: because that’s what I had. My interest here wasn’t in the religious aspect, but in the gender disparities in volunteer/community organizations; I suspect these same trends occur in a lot of similar organizations, not just Jewish ones. I wish I had info on a more general set, but I so far haven’t been able to find a study like this one, but for a wider array of organizations. If anyone knows of one, I’d love to post it.