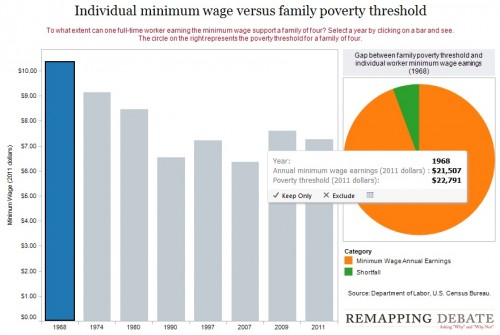
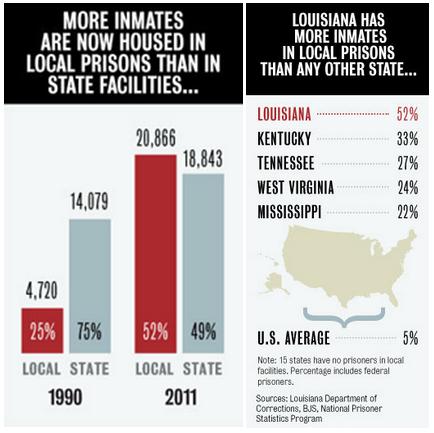
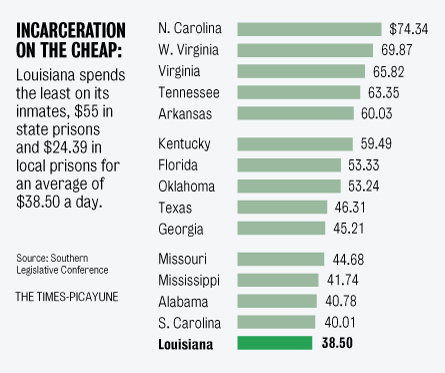
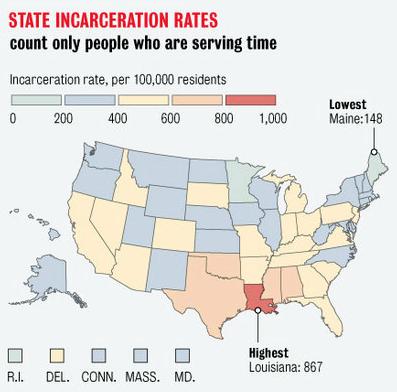
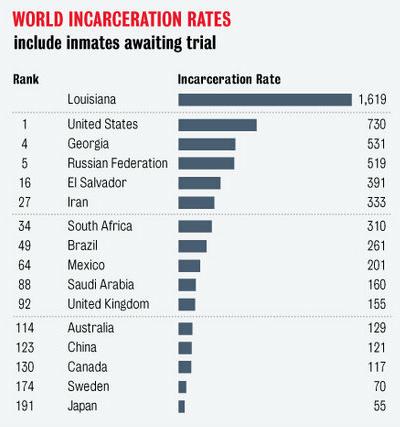
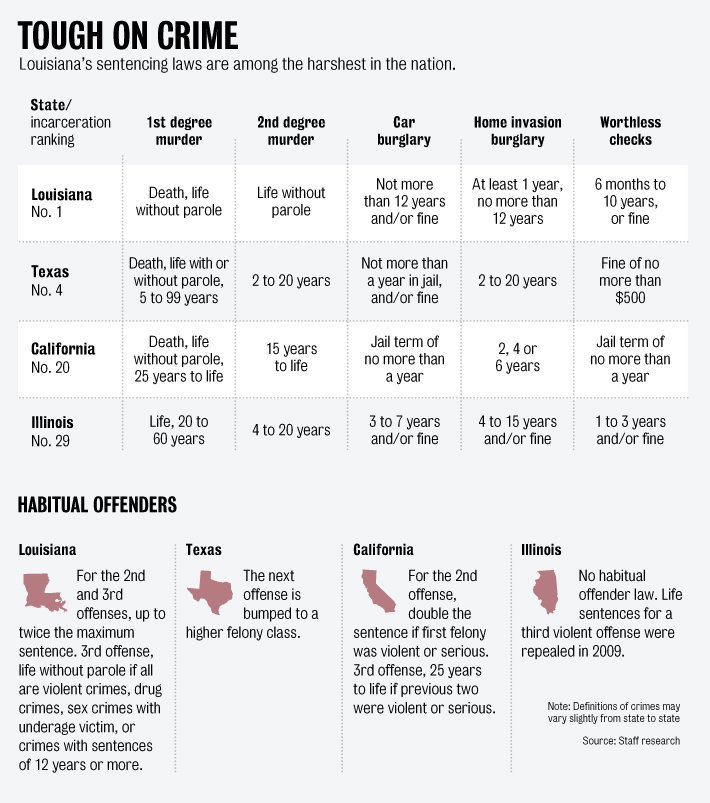
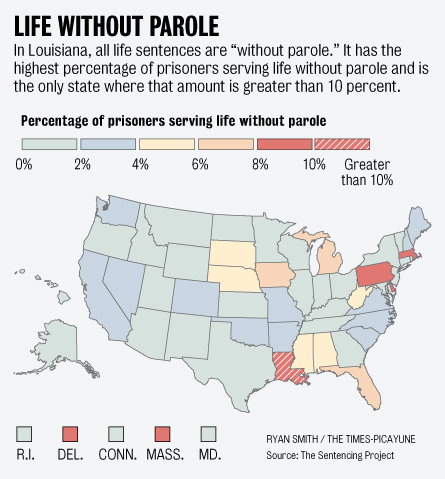
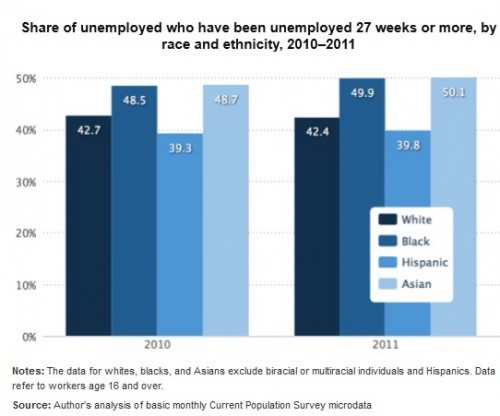
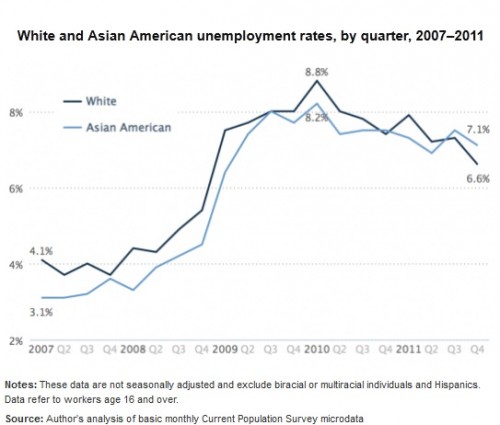
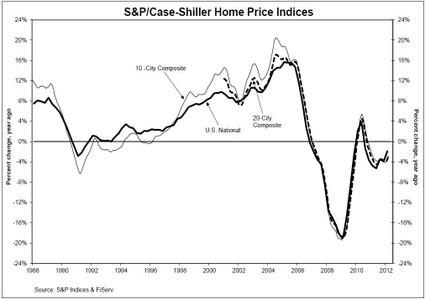
Remapping Debate has posted an interactive graph that lets you look at the decreasing relative value of the federal minimum wage. The graph shows the gap, at various points in time, between the annual income of a full-time worker earning minimum wage and the poverty line for a family of four (all expressed in 2011 dollars; you can see specific historical, unadjusted minimum wage rates here). In 1968, a single minimum-wage earner made about 94% of the federal poverty line for four people:
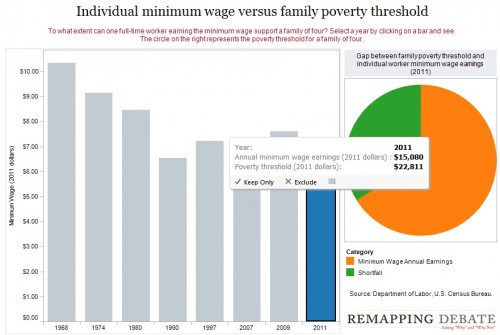
By 2011, the gap had widened significantly; one minimum-wage worker earns about 66% of the poverty threshold for a family of four:
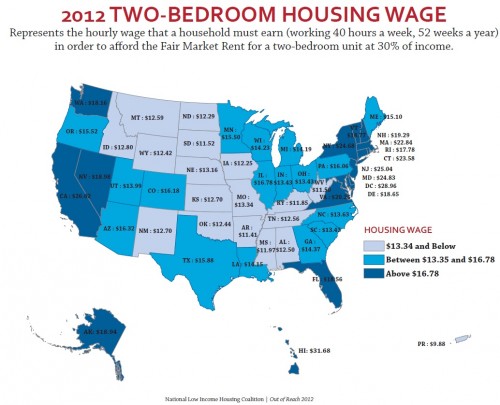
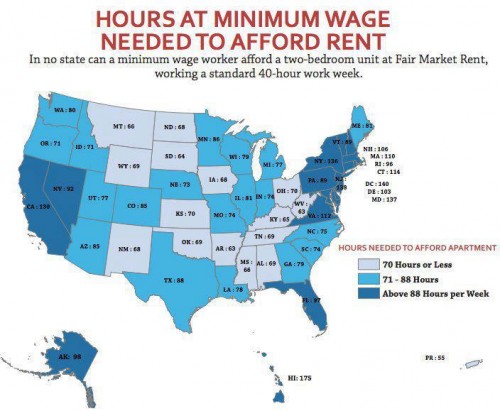
Though the federal minimum wage has gone up over time, its relative value covers less and less of the costs of living in the U.S.