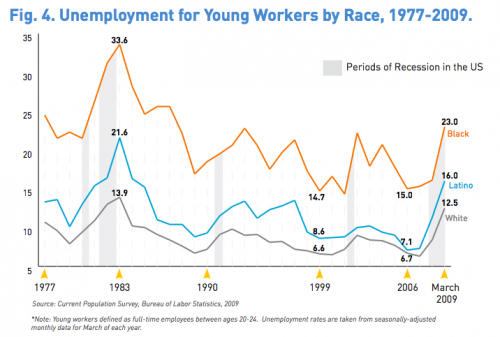
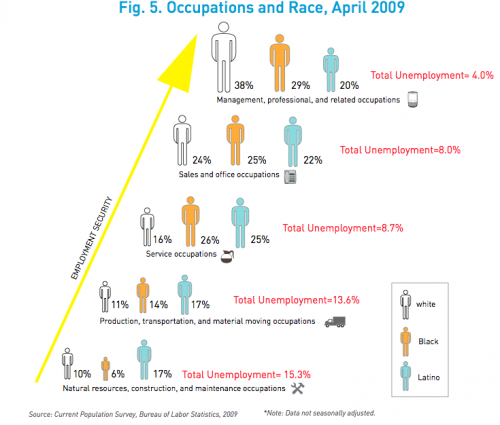
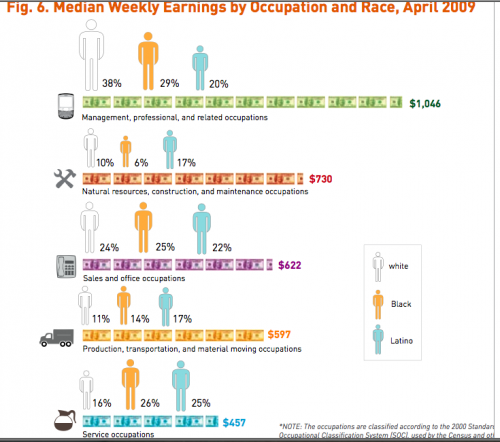
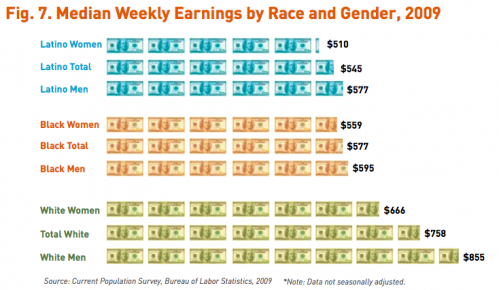
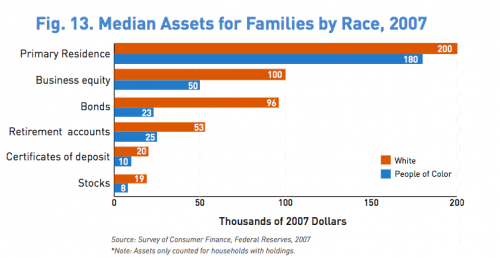
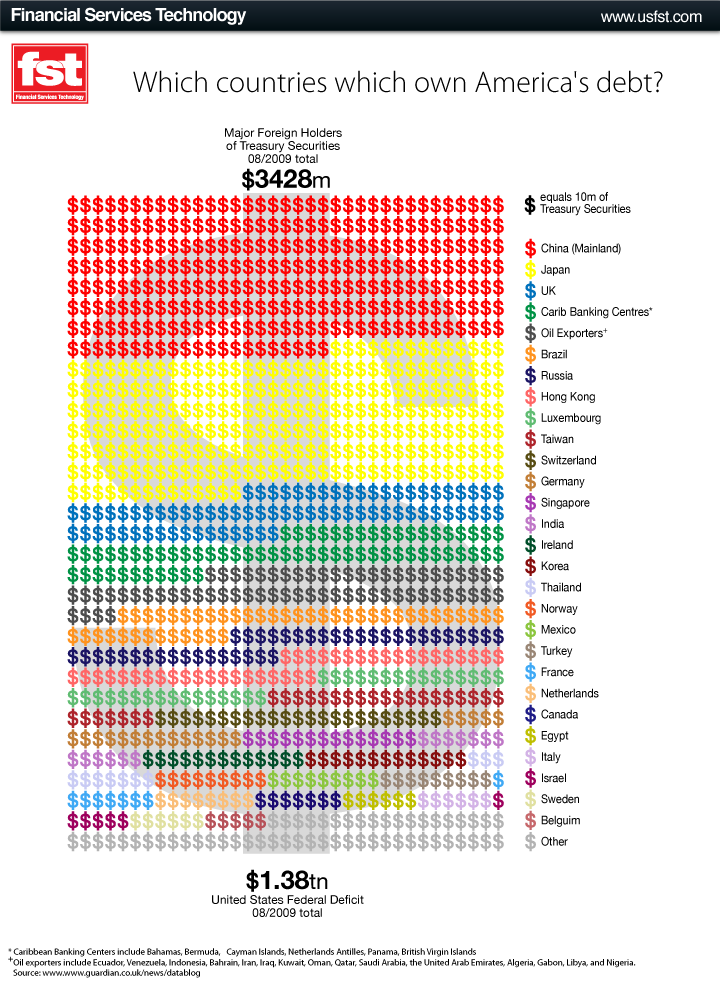
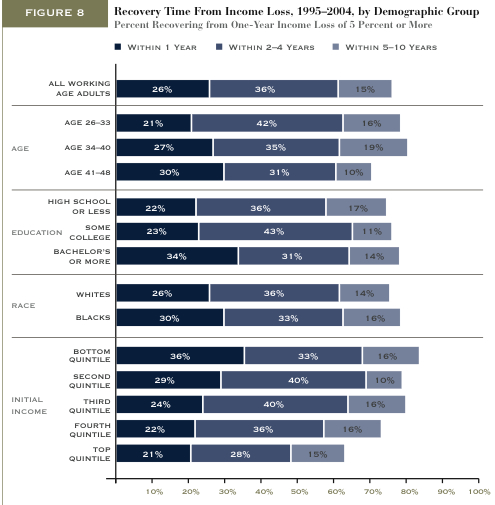
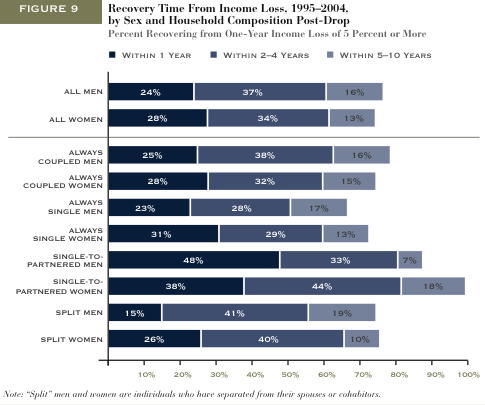
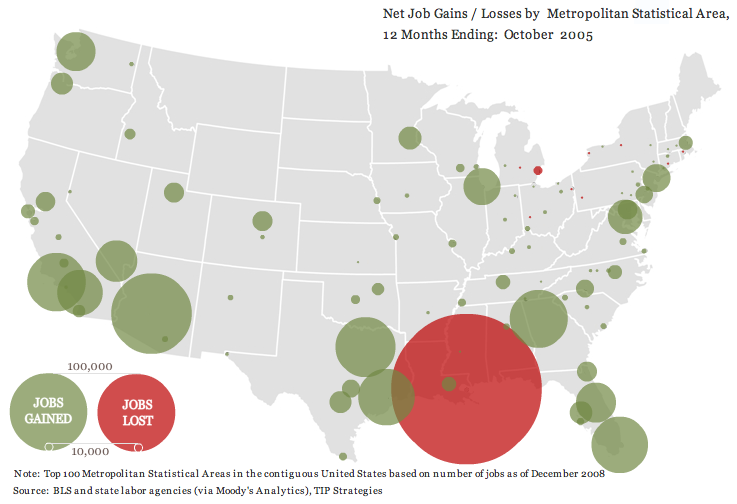
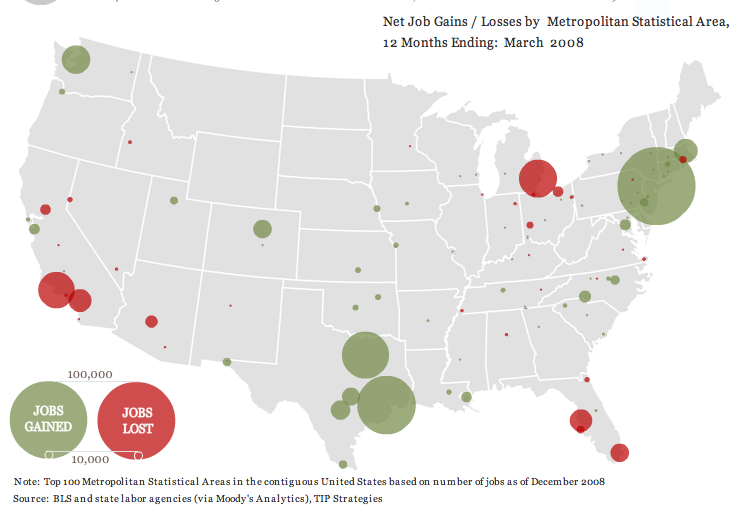
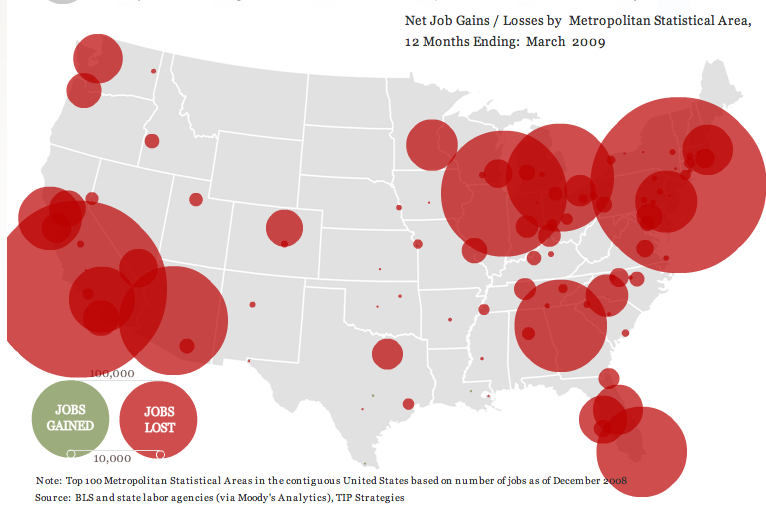
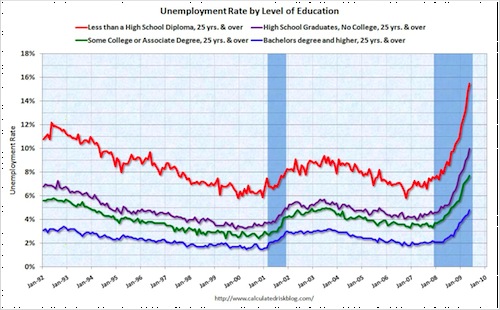
This week the New York Times featured a story about joblessness rates among black and white men and women. As the figures below show, black men and women always face higher levels of unemployment compared to whites of the same education level; for men, the disparity increases as education level increases; and for black women, that pattern holds at least for 2009.
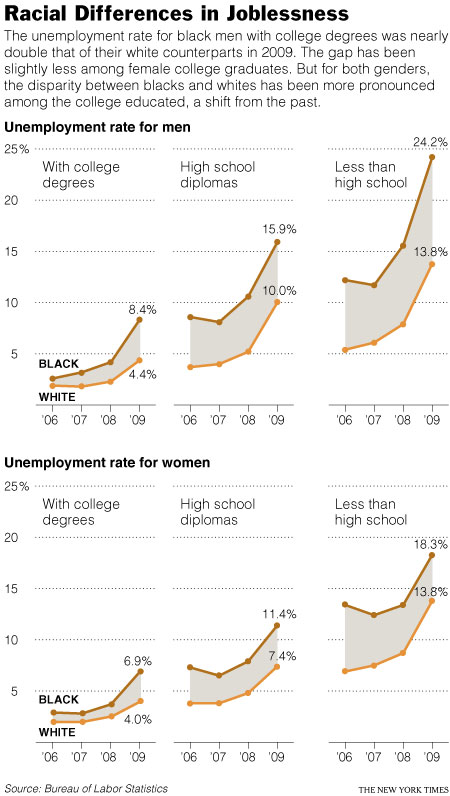
For more detailed data on this phenomenon, see our posts on race and the economic downturn, the intersection of race and criminal record, and education and unemployment.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.