We rounded out the year with 6,850,000 visits and nearly 10,000,000 page views. We are proud and honored to enjoy over 35,000 Facebook friends and 15,000 Twitter followers, plus nearly 10,000 on Pinterest and almost 1,000 on our two-month-old Tumblr page. A huge thank you to everyone for your enthusiasm and support!
Highlights:
- Our 6th birthday.
- A home page.
- A shiny new Tumblr.
- A 5,000th post.
- New Pinterest pages: the social construction of flavor, “women” vs. “people”, marketing feminism, the mean girls meme, and rape culture (see them all here).
- Two new syndication relationships with Business Insider and Policy Mic.
- Tweets from Piper Kerman, Shankar Vedantam, and Amanda Palmer.
- New Course Guides: sociology of work and occupations, family and society, the sociology of Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders and women’s history (see them all here).
- A gig writing for Salon.
Best of 2013!
Over the last week we’ve highlighted our favorite and most loved posts from 2013. Here’s the list in case you missed it!
Reader’s Choice (plus # of Facebook likes before we re-posted)
- From the Mouths of Rapists: The Lyrics of Robin Thicke’s Blurred Lines (174,000)
- The Balancing Act of Being Female; Or Why We Have So Many Clothes (31,000)
- Gender and the Body Language of Power (21,000)
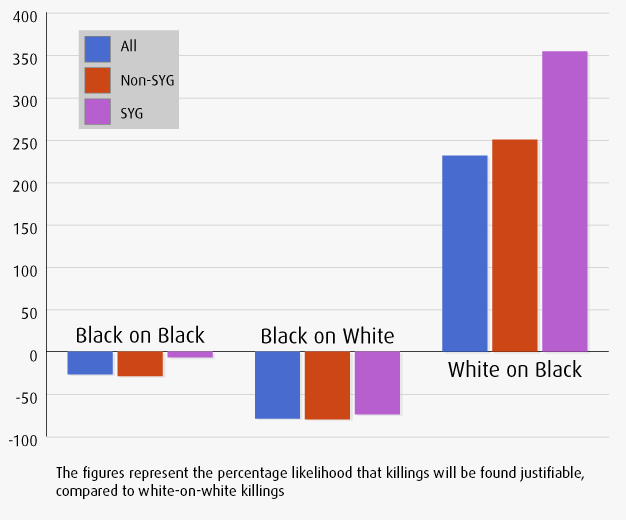
- Stand Your Ground Laws Increase Racial Bias in “Justifiable Homicide” Trials (20,000)
- Surprise! Your Flight Attendants are all Strangers! (16,000)
- My Two Cents on Feminism and Miley Cyrus (15,000)
- Men Feel Bad around Smart, Successful Women (7,500)
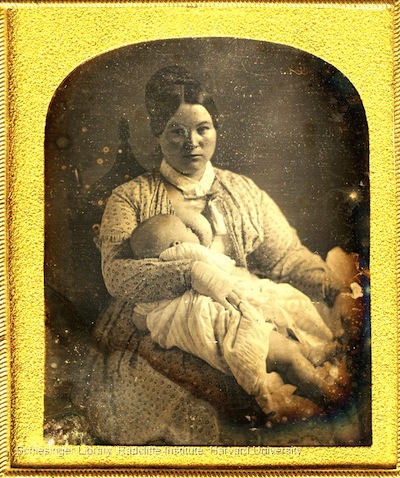
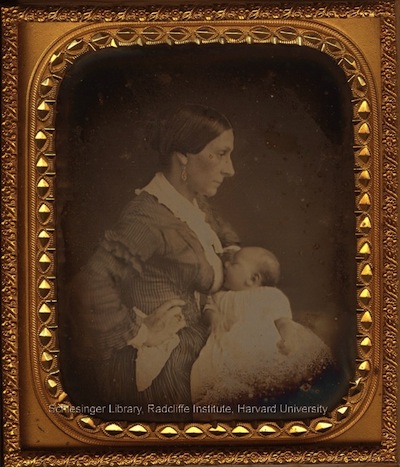
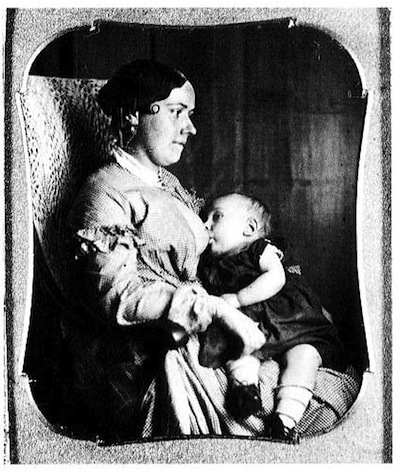
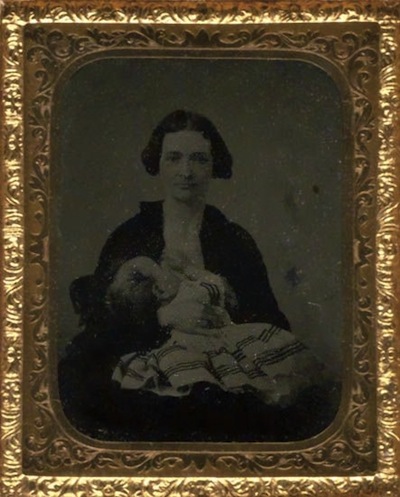
- Shifting Discourses of Motherhood: The Victorian Breastfeeding Photo Fad (7,000)
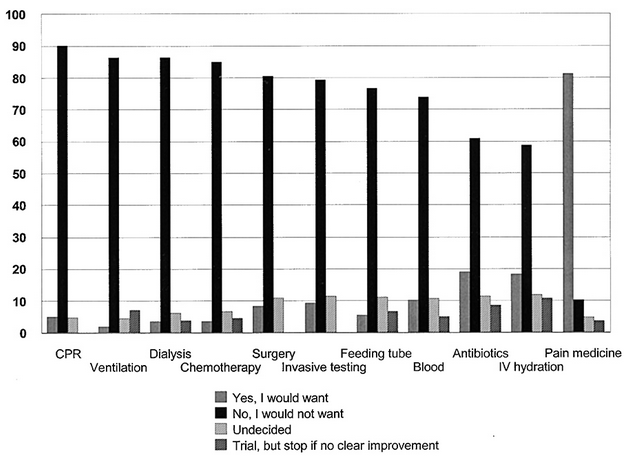
- How Do Physicians and Non-Physicians Want to Die? (5,800)
- Double Standards and Blurred Lines at the VMA Awards (5,400)
- Most Women Would Rather Divorce than be a Housewife (5,100)
- Re-Touching the Consequences of Extreme Thinness (5, 100)
Editor’s Picks
- African-American Travel and Jim Crow Segregation
- Why Are People Changing Their Minds About Same-Sex Marriage
- The Marketing Tactics of Firearm Manufacturers
- Children’s Books and Segregation in the Workplace
- Men and Women Use Uptalk Differently: A Study of Jeopardy
- What are Rappers Really Saying about the Police?
- On the Sexualized Insult (Not for the Faint of Heart)
- The Unsung Heroes of the Crash Landing in San Francisco
And this Happened…
…the fruits of my obsession with flight attendants. If you read these, you might be obsessed too!
- The Surprisingly Racist Reason We Don’t Tip Flight Attendants
- Before the Stewardess, the Steward: When Flight Attendants Were Men
- Domestic Behavior as Both Gendered and Raced: Who Does What for Airlines?
- International Politics and the First African American Flight Attendants
- Are Flights Full? Airline Advertising vs. Real Life
- Hanging onto the Stewardess at Delta Airlines
- Surprise! Your Flight Attendants are all Strangers! (also a reader’s pick)
- The Unsung Heroes of the Crash Landing in San Francisco (also an editor’s pick)
Happy New Year everyone! Here’s to wonderful things in 2014!
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.