I am excited to see that sociologist Linda Blum has come out with a new book, Raising Generation Rx: Mothering Kids with Invisible Disabilities in an Age of Inequality. Here’s a post from the archive highlighting some of her important and powerful findings.
In an article titled Mother-Blame in the Prozac Nation, sociologist Linda Blum describes the lives of women with disabled children. While mothers are held to an essentially impossibly high standard of motherhood in the contemporary U.S. and elsewhere, mothers of disabled children find themselves even more overwhelmed.
The daily care of their child is often more intensive but, in addition to that added responsibility, mothers were actively involved in getting their children needed services and resources. The need for mothers to be proactive about this was exacerbated by the fact that they had to negotiate different social institutions, each with an interest in claiming certain service spheres, but also limited budgets. “While each system claims authoritative expertise,” Blum writes, “either system can reject responsibility, paradoxically, when costs are at issue.” Because they often had to argue with service providers and find ways to beat a system that often tried to keep them at bay, they had to become experts in their child’s disability, of course, but also public policy, learning styles, the medical system, psychology/psychiatry, pharmaceutics, manipulation of jargon and law, and more.
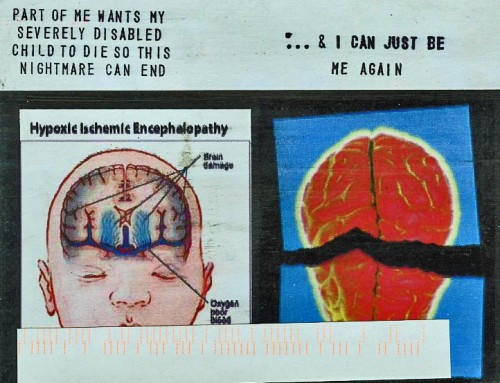
Mothers often felt that they were their child’s only advocate, with his or her health and future dependent on making just one more phone call, getting one more meeting with an expert, or trying one more school. Accordingly, they were simultaneously exhausted and filled with guilt. I wondered, when I came across this Post Secret confession, if this mother was experiencing some of the same things:
Originally posted in 2012.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.