Health care providers who perform abortions routinely use ultrasound scans to confirm their patients’ pregnancies, check for multiple gestations, and determine the stage of the pregnancies. But it is far from standard – and not at all medically necessary – for women about to have abortions to view their ultrasounds. Ultrasound viewing by patients has no clinical purpose: it does not affect the woman’s condition or the decisions health providers make. Nevertheless, ultrasound viewing has become central to the hotly contested politics of abortion.
Believing that viewing ultrasounds will change minds, opponents of abortion – spearheaded by the advocacy group Americans United for Life – have pushed for state laws to require such viewing. So far, eighteen states require that women be offered the opportunity to view their pre-abortion ultrasound images, and five states actually go so far as to legally require women to view their ultrasound images before obtaining an abortion (although the women are permitted to avert their eyes). In two of the five states that have passed such mandatory viewing laws, courts have permanently enjoined the laws, keeping them from going into effect.
States that allow/require ultrasounds before abortion (vocative):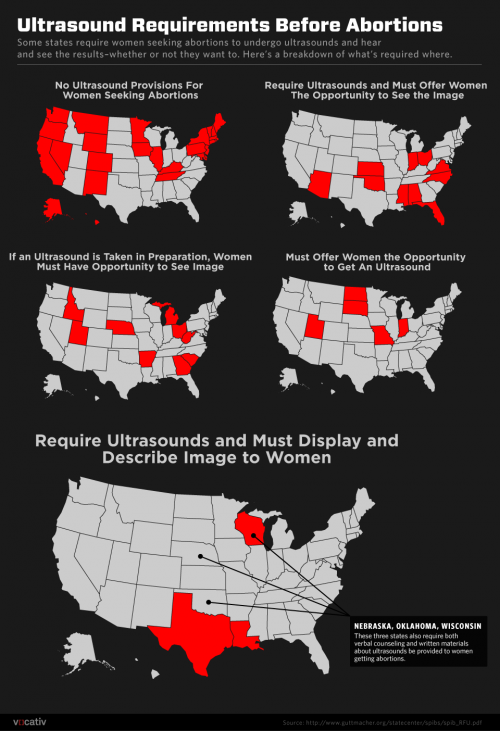
As the debates continue to rage, both sides assume that what matters for an abortion patient is the content of the ultrasound image. Abortion opponents believe the image will demonstrate to the woman that she is carrying a baby – a revelation they think will make her want to continue her pregnancy. Ironically, supporters of abortion rights also argue that seeing the image of the fetus will make a difference. They say this experience will be emotionally distressing and make abortions more difficult. Paradoxically, such arguments from rights advocates reinforce assumptions that fetuses are persons and perpetuate stigma about abortion procedures.
Does viewing change women’s minds – or cause trauma?
What is missing from all of this is research on a crucial question: How do women planning abortions actually react to voluntary or coerced viewing of ultrasounds? As it turns out, seeing the ultrasound images as such does little to change women’s minds about abortion. What matters is how women scheduled for abortions already feel. Viewing an ultrasound can matter for women who are not fully certain about their plans to have an abortion.
My colleagues and I analyzed medical records from over 15,000 abortion visits during 2011 to a large, urban abortion provider. This provider has a policy of offering every patient the voluntary opportunity to view her ultrasound image. In her intake paperwork, the patient can check a box saying she wants to view; then, when she’s in the ultrasound room, the technician provides her with the opportunity to see the image. Over 42% of incoming abortion patients chose to view their ultrasound images, and the substantial majority (99%) of all 15,000 pregnancies ended in abortion.
Our research team looked at whether viewing the ultrasound image was associated with deciding to continue with the pregnancy instead of proceeding with the abortion. We took into account factors such as the age, race, and poverty level of the women involved, as well as how far along their pregnancies were, the presence of multiple fetuses, and how certain women said they were about their abortion decision.
As it became clear that certainty mattered, we looked more closely. Among women who were highly certain, viewing their ultrasound did not change minds. However, among the small fraction (7.4%) of women who were not very certain or only moderately certain, viewing slightly increased the odds that they would forego their planned abortion and continue with their pregnancy. Nonetheless, this effect was very small and most did proceed to abortion.
Our findings make sense, because some women who are unsure about their abortion decision may seek experiences such as ultrasound viewing to help them make a final choice. Nevertheless, many previous studies have documented that women’s reasons for abortion are complex and unlikely to be negated simply by viewing an ultrasound image. Our study analyzed a situation where viewing ultrasounds was voluntary, but there is no reason to think that mandatory viewing would change more minds. Forcing women to view their ultrasounds could, however, affect patient satisfaction and sense of autonomy.
Apart from whether minds are changed, many people imagine that viewing an ultrasound for an unwanted pregnancy is distressing; and in interviews with 26 staff members at an abortion facility that offers pre-abortion ultrasounds, my colleague and I discovered that many staffers believed viewing the image caused relief for women early in their pregnancies but was traumatic for those at later stages.
However, when my colleagues and I asked 212 women throughout the United States about their reactions to viewing pre-abortion ultrasounds, we found no evidence that viewing was broadly distressing or that emotions depended on the gestational stage. All interviewees said their minds were not changed about proceeding with abortions. Just over one in five reported that viewing provoked negative reactions of guilt, depression, or sadness; one in ten reported positive feelings such as happiness; and the largest group, just over a third, said they felt “fine,” “okay,” or even “nothing.” This common response that viewing did not matter was a surprise given the intensity surrounding political debates.
Our research questions the wisdom of state laws that force women scheduled to have abortions to view their ultrasounds prior to the procedure. Fewer than half of abortion patients want to view their ultrasounds, and there is no clinical benefit. More to the point, abortion providers already offer patients the opportunity to view their ultrasounds – and never turn down women’s requests to look at these images. When women already feel uncertain about proceeding with an abortion, viewing the image of the fetus may make a difference. But for the vast majority whose minds are made up, viewing does not matter – and trying to force this to happen in every case merely adds costs and indignities to the abortion process.
Originally posted at Scholars Strategy Network. Read more at:
- Constructing the Meaning of Ultrasound Viewing in Abortion Care
- Women’s Interest in and Emotional Response to Viewing Their Ultrasound Image in Abortion Care
- Relationship between Ultrasound Viewing and Proceeding to Abortion
Katrina Kimport, PhD is an assistant professor in the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences and a research sociologist with the Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health program at the University of California, San Francisco.









