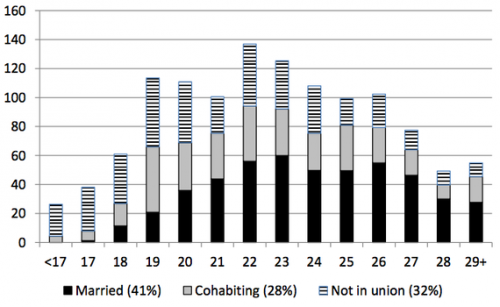
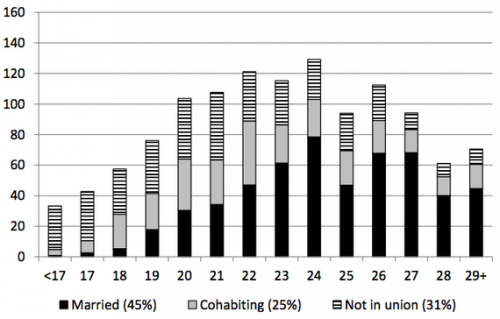
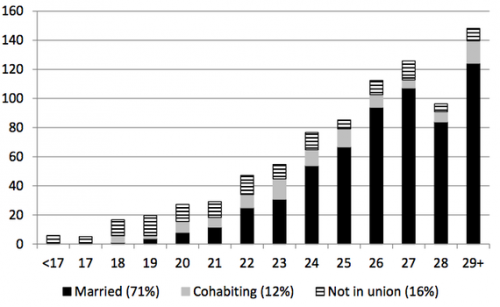
In the aftermath of the revelation that Facebook has been manipulating our emotions – the one that prompted Jenny Davis to write a post titled Newsflash: Facebook Has Always Been Manipulating Your Emotions – the folks at OkCupid admitted that they been doing it, too.
I’ll let you debate the ethics. Here’s what Christian Rudder and his team found out about attractiveness. Let me warn you, it’s not pretty.
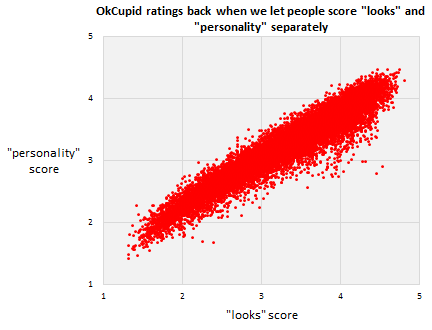
OkCupid originally gave users the opportunity to rate each other twice: once for personality and once for score. The two were strikingly correlated.
Do better looking people have more fabulous personalities? No. Here’s a hint: a woman with a personality rating in the 99th percentile whose profile contained no text at all.
Perhaps people were judging both looks and personality by looks alone. They ran a test. Some people got to see a user’s profile picture and the text and others just saw the picture. Their ratings correlated which means, as Rudder put it: “Your picture is worth that fabled thousand words, but your actual words are worth… almost nothing.”
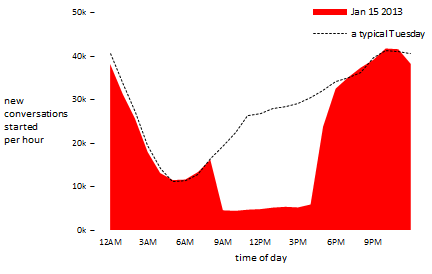
Their second “experiment” involved removing all of the pictures from the site for one full workday. In response, users said something to the effect of hell no. Here’s a graph showing the traffic on that day (in red) compared to a normal Tuesday (the dotted line):
When they put the pictures back up, the conversations that had started petered out much more aggressively than usual. As Rudder put it: “It was like we’d turned on the bright lights at the bar at midnight.” This graph shows that conversations started during the blackout had a shorter life expectancy than conversations normally did.
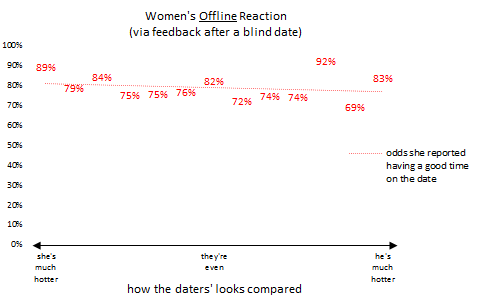
It’s too bad the people are putting such an emphasis on looks, because other data that OkCupid collected suggests that they aren’t as important as we think they are. This figure shows the odds that a woman reported having a good time with someone she was set up with blind. The odds are pretty even whether she and the guy are equally good looking, he’s much better looking, or she is. Rudder says that the results for men are similar.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.