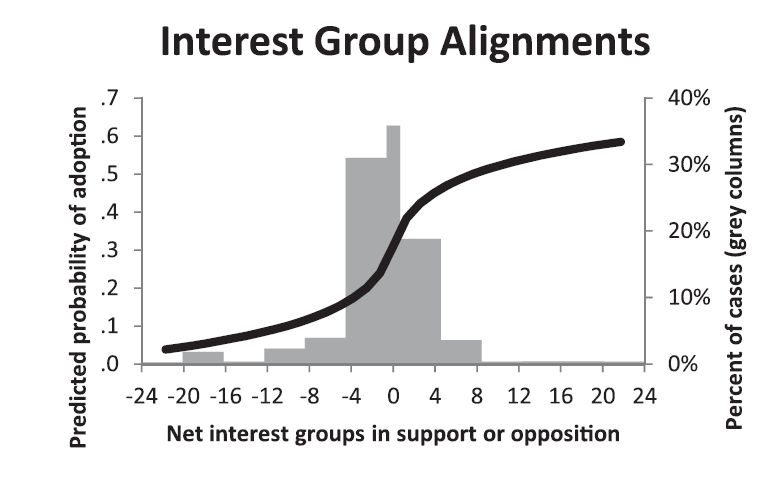
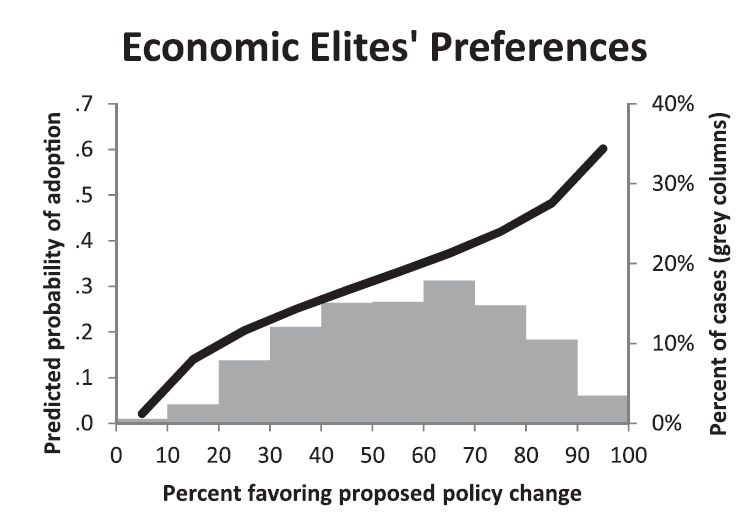
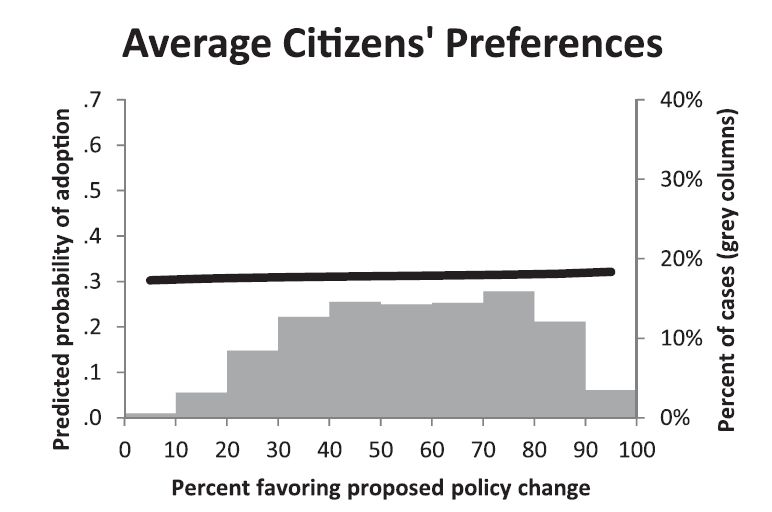
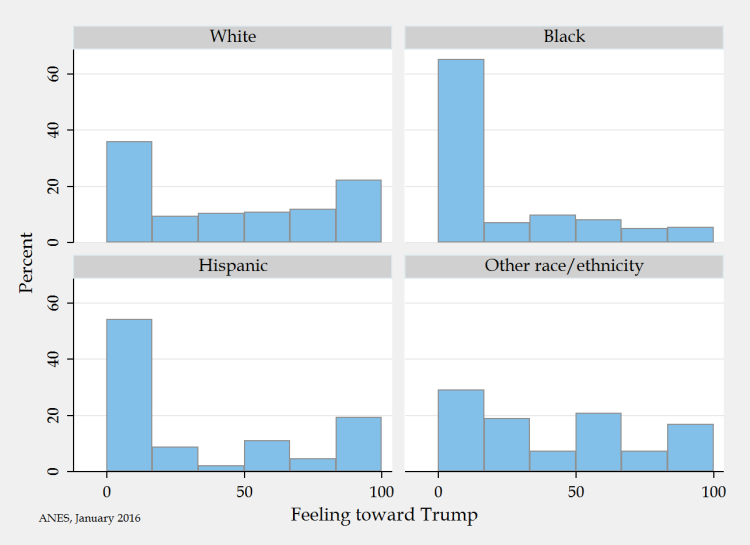
In 1970, the day after National Guard troops killed four unarmed protesters at Kent State University, students at Southern Illinois University went to the local McDonald’s and demanded that the flag be lowered to half staff. The franchise owner complied.
Ray Kroc, the founder of McDonald’s got wind of this and told the franchise owner to raise the flag back up to full staff. When he conplied, the students threatened to burn the place down.
The whipsawed franchise owner phoned McDonald’s CEO Fred Turner asking what to do. If Turner’s response isn’t part of the canon of management courses, it ought to be: “The next delivery truck that arrives, have him back in to the flag pole and knock it down.”
Lands’ End now finds itself in a similar position but with no flagpole and no trucks.
You may have noticed that the most Lands’ End catalogue looks different from the other 273 they’ve sent you this year. Lots of people in a tableau rather than close ups of one model in merch. And palm trees. Palm trees? From Wisconsin? The paper too is less slick, with more of a matte finish. But what has landed Lands’ End in hot water is the four-page interview with Gloria Steinem wearing Lands’ End gear. (The text in the upper right begins, “Introducing the Legend Series, our ode to individuals who have made a difference . . . .”)

Lands’ End is in trouble – profits and sales way down – and the new CEO wanted to change the look of the catalogue if not the clothes. But that was the beginning of more trouble. First, conservatives got word of it and started criticizing Lands’ End for celebrating a woman who not only spoke out in favor of legalized abortion but who had actually had an abortion and said so. Lands’ End responded: “It was never our intention to raise a divisive political or religious issue, so when some of our customers saw the recent promotion that way, we heard them. We sincerely apologize for any offense.”
Besides apologizing, they also wiped the Gloria material from their website. (So far, they haven’t yet asked me to return my catalogue, but who knows?)
Then the pro-Gloria forces took to Facebook and Twitter.
“I don’t intend to teach my children that anyone should do business with a company that is ashamed to even talk about feminism,”
The Washington Post says that Lands’ End, in its attempt to retroactively duck the issue, is tacking away from the trend. Companies, says WaPo, have now become “unapologetic in their stance on social issues.” Big companies –Target, Gap, Visa, Cheerios, etc. – have supported the Supreme Court decision on gay marriage or criticized Trump’s denigration of Latinos. Sears and Wal-Mart came out against the Confederate flag.
The message of these earlier moves seemed to be that the companies were willing to stake out a position they felt strongly about, even if it meant alienating some customers. Lands’ End, it appears, may have a different mindset.
Is it Lands’ End, or is it the issue? After the Charleston Church Massacre of June 2015, retreating from the Confederate flag became the majority view even in the South.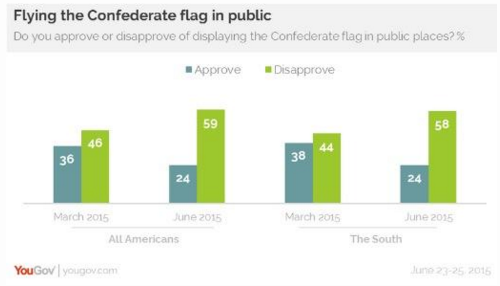
The trend on gay marriage has also made acceptance a safe bet:
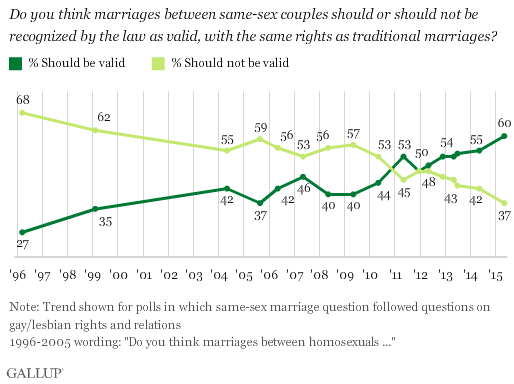
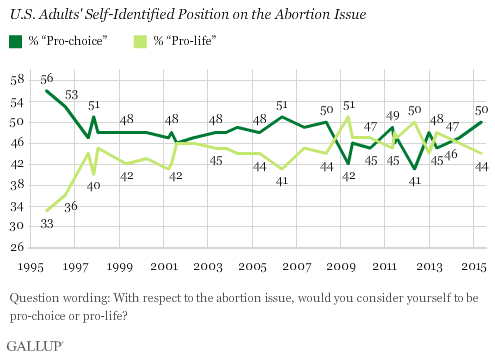
Lands’ End was caught between equally strong opinions. Their dilemma on Gloria reflects their dilemma on clothing and clientele. Lands’ End wants to attract younger shoppers, who lean towards the pro-choice side, but not lose their older customers, who lean the opposite direction.
Here at the SocioBlog, we’re proud to show our colors – a bright orange Lands’ End sweater.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.