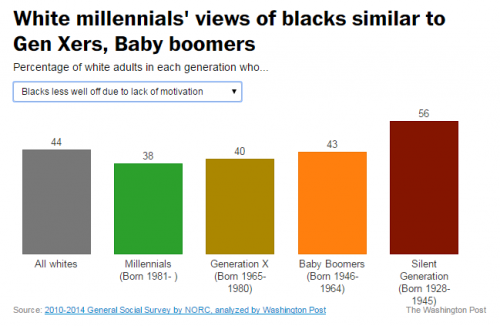
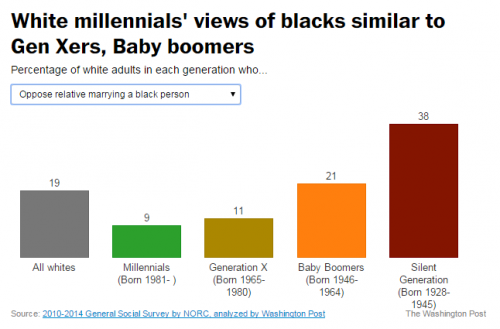
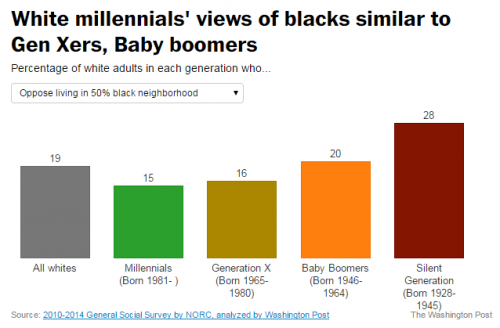
I was on jury duty this week, and the greatest challenge for me was the “David Brooks temptation” to use the experience to expound on the differences in generations and the great changes in culture and character that technology and history have brought.
I did my first tour of duty in the 1970s. Back then you were called for two weeks. Even if you served on a jury, after that trial ended, you went back to the main jury room. If you were lucky, you might be released after a week and a half. Now it’s two days.
What most struck me most this time was the atmosphere in the main room. Now, nobody talks. You’re in a large room with maybe two hundred people, and it’s quieter than a library. Some are reading newspapers or books, but most are on their latops, tablets, and phones. In the 1970s, it wasn’t just that there was no wi-fi, there was no air conditioning. Remember “12 Angry Men”? We’re in the same building. Then, you tried to find others to talk to. Now you try to find a seat near an electric outlet to connect your charger.
I started to feel nostalgic for the old system. People nowadays – all in their own narrow, solipsistic worlds, nearly incapable of ordinary face-to-face sociability. And so on.
But the explanation was much simpler. It was the two-day hitch. In the old system, social ties didn’t grow from strangers seeking out others in the main jury room. It happened when you went to a courtroom for voir dire. You were called down in groups of forty. The judge sketched out the case, and the lawyers interviewed the prospective jurors. From their questions, you learned more about the case, and you learned about your fellow jurors – neighborhood, occupation, family, education, hobbies. You heard what crimes they’d been a victim of. When judge called a break for bathroom or lunch or some legal matter, you could find the people you had something in common with. And you could talk with anyone about the case, trying to guess what the trial would bring. If you weren’t selected for the jury, you went back to the main jury room, and you continued the conversations there. You formed a social circle that others could join.
This time, on my first day, there were only two calls for voir dire, the clerk as bingo-master spinning the drum with the name cards and calling out the names one by one. My second day, there were no calls. And that was it. I went home having had no conversations at all with any of my fellow jurors. (A woman seated behind me did say, “Can you watch my laptop for a second?” when she went to the bathroom, but I don’t count that as a conversation.)
I would love to have written 800 words here on how New York character had changed since the 1970s. No more schmoozing. Instead we have iPads and iPhones and MacBooks destroying New York jury room culture – Apple taking over the Apple. People unable or afraid to talk to one another because of some subtle shift in our morals and manners. Maybe I’d even go for the full Brooks and add a few paragraphs telling you what’s really important in life.
But it was really a change in the structure. New York expanded the jury pool by eliminating most exemptions. Doctors, lawyers, politicians, judges – they all have to show up. As a result, jury service is two days instead of two weeks, and if you actually are called to a trial, once you are rejected for the jury or after the trial is over, you go home.
The old system was sort of like the pre-all-volunteer army. You get called up, and you’re thrown together with many kinds of people you’d never otherwise meet. It takes a chunk of time out of your life, but you wind up with some good stories to tell. Maybe we’ve lost something. But if we have lost valuable experiences, it’s because of a change in the rules, in the structure of how the institution is run, not a because of a change in our culture and character.
Cross-posted at Montclair Socioblog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.