Reprinted from Council on Contemporary Families Brief Report published on May 3, 2023
When we talk about domestic labor, we often talk about the physical activities of doing work around the house and caring for family members. But running a household is more than cooking, cleaning, and transporting kids to practice; it’s also monitoring the pantry to know when groceries are getting low, weighing options about (and deciding on) which vacuum cleaner to buy, and remembering that little league signups are the last week of March and that cleats typically go on sale the week prior to the season.
Domestic labor therefore is not just the physical activities of doing housework and caregiving, but also anticipating and monitoring family needs, organizing and planning, and making decisions on which courses of action to pursue. These sorts of activities, known as cognitive labor, are often hidden (i.e., a parent might be planning their children’s schedules in their head while doing other tasks) and are never-ending as there are always things to think about and plan.
Most research on housework and childcare focuses on routine physical tasks but does not account for hidden cognitive labor. This is problematic because mothers perform more physical domestic labor than fathers, and this disparity contributes to negative consequences such as to the gender pay gap as well as to greater stress and less leisure time for mothers compared to fathers. Yet, mothers also perform more cognitive labor than fathers, and the constant need to anticipate and monitor family needs may be a significant source of additional stress for mothers. In sum, the lack of attention to cognitive labor may mean that the enduring gender gap in domestic labor—and subsequent inequalities in well-being—may be even larger than often estimated.
Our new study recently published in Society and Mental Health focuses on the division of cognitive labor between mothers and fathers during the pandemic, and the implications of this division for parents’ psychological well-being.
Using data from the Study on Parents’ Divisions of Labor During COVID-19 (SPDLC) on 1,765 partnered parents, we examined parents’ time in, and division of, cognitive labor in Fall 2020. Popular press articles illustrate how mothers are increasingly overwhelmed and experiencing burnout due to the sheer volume of things they are trying to juggle. Results from our study provide some empirical support for these colloquial ideas. Among parents in the SPDLC, mothers spent over twice as much time per week performing cognitive labor (5 hours) compared to fathers (2 hours). When asked how cognitive labor was divided between themselves and their partners, mothers reported that they did more of this labor. In addition, mothers reported that the division of cognitive labor was more unequal than the division of housework and childcare—suggesting that the gender gap in domestic labor may indeed be even larger than we commonly think it is.
In addition to understanding how cognitive labor was divided among parents, we also wanted to know if there were consequences of performing this hidden labor. The results were striking; being primarily responsible for cognitive labor was associated with psychological consequences for mothers. Specifically, mothers who were more responsible for cognitive labor reported being more stressed and more depressed. The combination of mothers being primarily responsible for all of these hidden tasks and spending more time doing them means that cognitive labor may act as a chronic stressor that increases mothers’ risk of experiencing psychological distress.
But what about fathers? Do fathers who perform cognitive labor also report negative psychological consequences? Based on our study, the simple answer is no. Our findings show that when fathers perform more of the cognitive labor in families, they actually experience lower stress and fewer depressive symptoms. Similarly, mothers’ stress and depressive symptoms were also lower when fathers took on more of the responsibility for cognitive labor. Thus, whereas mothers’ involvement in cognitive labor may reduce their well-being, fathers’ involvement in cognitive labor appears to benefit both their own and their partners’ well-being.
Research on stress shows that the effects of stressors vary by context, and we find that gender conditions the effect of cognitive labor on parents’ psychological well-being. Fathers are not expected to manage the household and constantly monitor family needs. While fathers increasingly desire to be more engaged parents, they do not face strong social pressures to perform domestic tasks. Consequently, fathers may receive praise and positive reinforcement for performing cognitive labor as they are seen as going above and beyond what is expected of them. In contrast, mothers are expected to be primarily responsible for household tasks and may be penalized and judged if they do not meet these expectations. This makes mothers uniquely susceptible to the hidden, enduring burdens of cognitive labor.
Overall, our new findings suggest that gender inequality in housework and childcare extends to hidden domestic tasks, and also that performance of these tasks likely contributes to inequality in well-being between mothers and fathers. As long as gendered norms of care and the parenting double standard persist, gender inequality in domestic labor and well-being will continue. We need to change our cultural expectations about caregiving and provide more structural opportunities for fathers to be more engaged at home (e.g., remote work, paid leave) to reduce the burdens on mothers, reduce mothers’ stress, and promote greater gender equality at home. Increased opportunities for engagement will likely increase fathers’ awareness of family needs and empower them to take ownership in sharing both physical tasks as well as the hidden cognitive labor.
A briefing paper prepared for the Council on Contemporary Families by Richard Petts, Professor, Department of Sociology, Ball State University, and Daniel L. Carlson, Associate Professor, Department of Family and Consumer Studies, University of Utah.


 Stephanie Coontz offers reflections on the Council on Contemporary Families brief,
Stephanie Coontz offers reflections on the Council on Contemporary Families brief, 

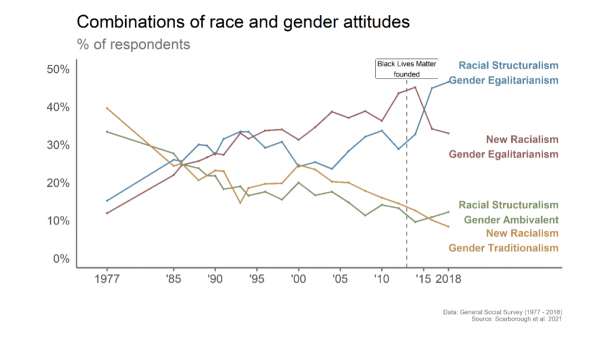
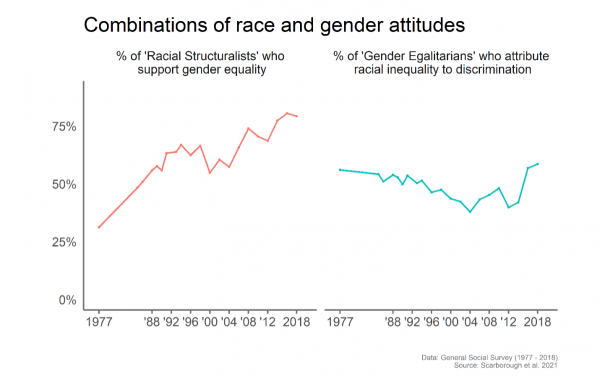
 Will Meghan Markle be welcomed in the royal family? The recent wedding of Markle, a biracial woman of Black and White heritage, and Prince Harry, a White male member of the British royal family, marks a social milestone. More than fifty years out from the Supreme court decision that legalized interracial marriages across all 50 states in the U.S., this wedding has inspired a new conversation about racial inclusivity infusing
Will Meghan Markle be welcomed in the royal family? The recent wedding of Markle, a biracial woman of Black and White heritage, and Prince Harry, a White male member of the British royal family, marks a social milestone. More than fifty years out from the Supreme court decision that legalized interracial marriages across all 50 states in the U.S., this wedding has inspired a new conversation about racial inclusivity infusing 
 Jessica McCrory Calarco is an Assistant Professor of Sociology at Indiana University at Bloomington and recently published the book
Jessica McCrory Calarco is an Assistant Professor of Sociology at Indiana University at Bloomington and recently published the book