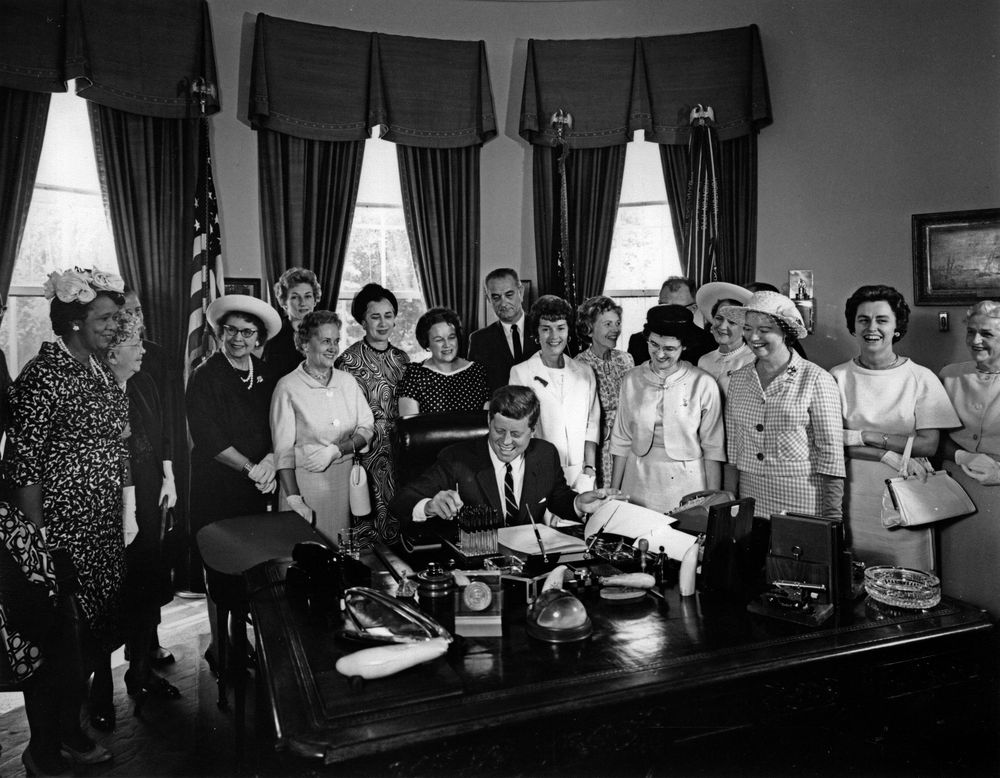
People often think of social change in the lives of American children since the 1950s as a movement in one direction – from children being raised in married, male-breadwinner families to a new norm of children being raised by working mothers, many of them unmarried. Instead, we can better understand this transformation as an explosion of diversity, a fanning out from a compact center along many different pathways.
The dramatic rearrangement of children’s living situations since the 1950s
At the end of the 1950s, if you chose 100 children under age 15 to represent all children, 65 would have been living in a family with married parents, with the father employed and the mother out of the labor force. Only 18 would have had married parents who were both employed. As for other types of family arrangements, you would find only one child in every 350 living with a never-married mother!
Today, among 100 representative children, just 22 live in a married male-breadwinner family, compared to 23 living with a single mother (only half of whom have ever been married). Seven out of every 100 live with a parent who cohabits with an unmarried partner (a category too rare for the Census Bureau to consider counting in 1960) and six with either a single father (3) or with grandparents but no parents (3).The single largest group of children – 34 – live with dual-earner married parents, but that largest group is only a third of the total, so that it is really impossible to point to a “typical” family.
With two-thirds of children being raised in male-breadwinner, married-couple families, it is understandable that people from the early 1960s considered such families to be the norm.* Today, by contrast, there is no single family arrangement that encompasses the majority of children. more...
![By Irangilaneh (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://thesocietypages.org/families/files/2014/08/Back_to_school-150x150.jpg)

