Adrienne K., who posts at Native Appropriations, let us know about the book Make It Work! North American Indians: The Hands-On Approach to History. Her friend Katie found it in the 4th-grade classroom library at the school where she teaches on the Rosebud Sioux Reservation in South Dakota:
As posted on Native Appropriations, Katie said,
The book purports to give a history of Native Americans and a guide to Native crafts, but what it ends up being is a veritable handbook for white kids to “play Indian.” All the photos are of white kids dressed up as Indians! I can’t find one picture (other than the historical ones, of course) of a Native American child. Even more disturbingly, the descriptions make it sound as if these white kids are authentic representations of Indian clothing, etc.
Katie found it particularly odd that this book was in a classroom on a Sioux reservation. Some pages from the book:
The information is often rather vague. For instance, on one page a description of the Seminole tribe says, “The Seminole were a group formed by Creek Indians and other people from different areas.” Um, ok…that’s less than helpful.
In this image, Adrienne points out that children dressed up as a Seminole and a “Plains Warrior” (?) are playing stickball, as though the game was played by all American Indian groups (rather than mostly confined to the Southeastern region of the U.S.):
As Adrienne mentions, throughout the book, only the past tense is used, as though Native Americans are relics of the past, no longer in existence (or at least, no longer interesting).
I have seen lots of books like this. In fact, I was once given a book like this when I was a kid. At the time I thought it was awesome. The books all seem to have a common theme: American Indians are part of history in the same way that, say, the ancient Greeks [note: several readers object that ancient Greeks aren’t gone, either, since there are still Greek people around–see below] are — something to study that is interesting but no longer exists. Native cultures are presented as neat art projects for non-Native kids to create, all under the guise of learning about the history of Native Americans. But as we see here, any educational benefit the books might aim at is undermined by the conflation of many different groups and cultural features into one or two generalized “Indians” who end up combining elements of Native societies that were separated geographically and temporally.
And almost all of these books present the “Plains Warrior,” as though there was a single Plains culture made up entirely of war-lovers decked out in feather headdresses. Even as a kid I wondered what a Plains Indian was, since I’d never heard of a tribe called the Plains.
Part of what is going on here is the romanticization of Native Americans as courageous, noble, but ultimately tragic figures of the past. Modern Native Americans, those living now and wearing blue-jeans and t-shirts and perhaps eating Wonder Bread as often as homemade fry bread, just aren’t interesting. They don’t fit into our romanticized narrative. They aren’t authentic. Authentic American Indians were culturally distinct…and disappeared about the time Geronimo became a member of Buffalo Bill’s Wild West show. And that makes the cultural appropriation acceptable, because it’s referring to people in the past. Creating a “Plains outfit” with burlap and a stapler is no more problematic than using a sheet to create a Roman toga.
UPDATE: As I said above, a number of commenters have asked how it’s any different to dress up like Native Americans than it is to dress up like ancient Greeks, seeing as how there are still Greeks around. I think there is a distinction. When people think about ancient Greek civilization, no one is then making Greeks who live today invisible. We do not imply that Greeks disappeared because a particular Greek society waned in influence. And we certainly don’t imply that ancient Greeks were the same as every other European civilization, with a few sartorial differences here or there. We also don’t suggest that anyone living in Greece today who doesn’t, say, worship Zeus is inauthentic, not a “real” Greek. People living in Greece aren’t stuck in time the way many people who romanticize American Indians see them.
NEW (Apr. ’10)! Jessica S. and Lucia M.M. sent in examples of “teepees” sold for fun.
First, from Jessica, a teepee by Land of Nod (a sister company of Crate and Barrell). The copy reads: “Our roomy teepee is the perfect place for peewees to powwow.”
Second, from Lucia, a teepee sold by Design Within Reach:
—————————–
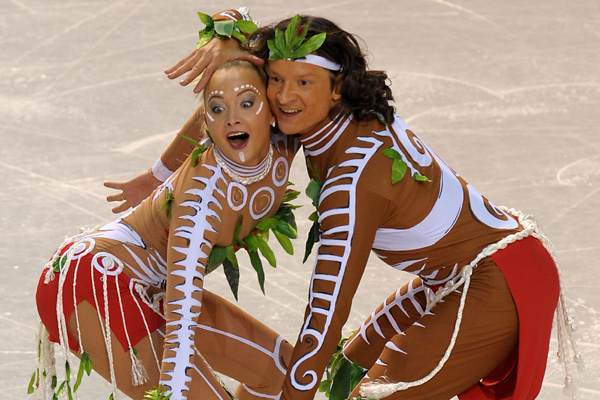
Related posts: racist mascots, Canada’s “indigenous Olympics“, ice skaters dress up like aborigines, indigenous cultures in Avatar (spoiler alert), Halloween costumes, defining “Indian art”, “my skin is dark but my heart is white“, anachronistic images of Native Americans, “My Indian name is…“, the sports mascot Chief Illini, Playmobil’s Native American family, Howe Nissan dealership statue, the “crying Indian” anti-littering PSA, Italian political party uses images of American Indians to oppose immigration, and a Native American toy set.