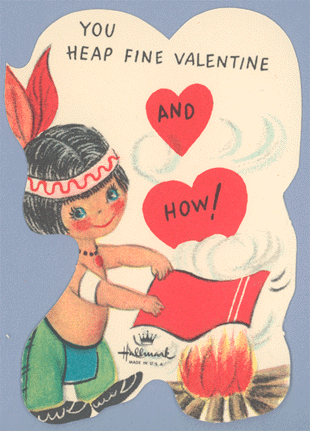Katrin sent us a great example of anachronistic portrayals of Native Americans, this time in a German (?) ad for a muscle pain relief product. The slogan at the end, “Indians do not know pain,” plays on the idea of the stoic native:
race/ethnicity: American Indians/Aboriginals
If you’re interested in cultural representations of Native Americans, I highly recommend the blog Native Appropriations. Recently Adrienne K. posted about an article in a student-government-funded newspaper at Cal State U.-Long Beach that stands out for its disrespectful, hostile tone. The article, titled “Pow Wow Wow Yippee Yo Yippy Yay,” was a “review” of the annual powwow sponsored by the American Indian Student Council. It had never occurred to me that you would review a cultural event as though it were just another form of entertainment, like a new movie, but that’s the least of the issues here. The full article, from the Union Weekly (via OC Weekly):
Some key excerpts:
…it really seemed like a large, Native American themed flea market. Some of the food vendors just seemed to unceremoniously add the word “Indian” to whatever food they were peddling. Indian tacos? What the fuck are Indian tacos?
…like a Mexican pizza from Taco Bell, but shittier. The only experience I have with fry bread is watching a show about how incredibly unhealthy it is to consume, and watching its rapid consumption on campus grounds.
The entire scene felt disingenuous and cheap. Donations are great, and necessary, tossing them unceremoniously on the ground is crass and borderline obscene. Even the homeless have hats and cups.
I flinched several times while reading the article. I grew up in Oklahoma surrounded by Native American cultures, both because I lived in an area where several tribes were very visible and because my mom is part Cherokee herself and several close relatives married people enrolled in other tribes. Even though I know that in most of the U.S. Native Americans are often culturally invisible and most people haven’t gone to tons of powwows or sat around watching the women in the family sewing ribbon shirts in the living room, I still sometimes forget that these things aren’t instantly recognizable and interesting to other people, or that they could see something that I was taught to be respectful and appreciative of and have such a different reaction.
Of course, this article goes beyond being unfamiliar or uninterested. The author, the paper’s campus editor, clearly didn’t want to learn what was going on. I mean, even if you’ve never heard of one before in your life, just a minimal Google search will explain to you than an Indian taco is, more or less, a taco on fry bread (the Osage Nation even has an annual competition). An image of a dancer is used to highlight a mocking, mean-spirited “review,” as though the powwow’s only function was to entertain uneducated outsiders.
The Union Review and the author of the article issued the typical non-apology “apology” statements — we’re just here to let all sides of the debate have a voice! We’re sorry if anyone got themselves all offended, we really didn’t expect this reaction at all! — which is also available at the OC Weekly link above.
As Adrienne points out, though the “Asians in the library ” rant from a UCLA student got a huge amount of attention, there’s been much less about this. It highlights the point Tami made at What Tami Said: overtly disrespectful and/or racist behavior on campuses shouldn’t shock us, if we’re paying attention.
Cross-posted at Racialicious.
We owe many iconic images of American Indians to photographer Edward S. Curtis. Growing up in Wisconsin and Minnesota, Curtis began photographing Indians in 1895 and, in 1906, was offered $75,000 by JP Morgan to continue documenting their lives (wikipedia). The 1,500 resulting photographs inevitably impacted the image of Indians in the American imagination.
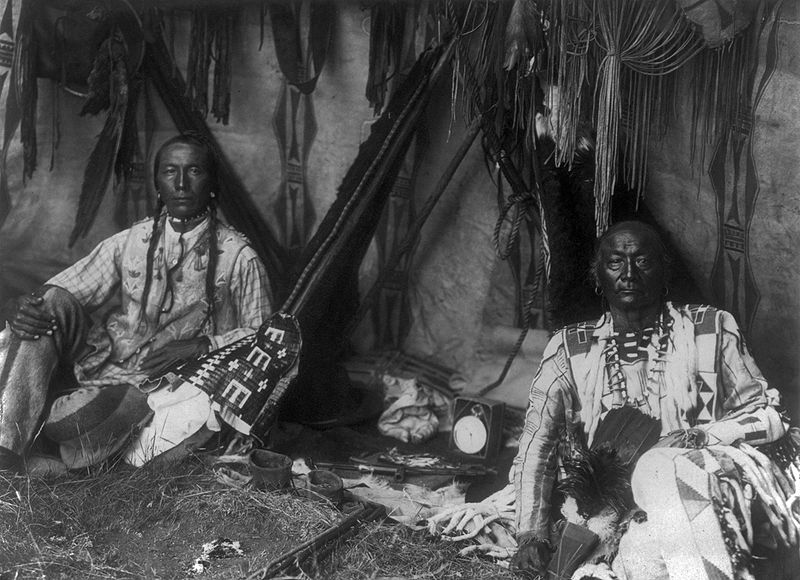
Later it came to light that Curtis’ photographs weren’t exactly pure representations. In some photographs, for example, he erased signs of modernity. The first photograph below, the un-edited version, includes a clock between the two men, whereas the edited version does not.
Curtis also sometimes staged scenes and dressed paid participants in costumes, as in this photograph:
According to Wikipedia contributors:
In Curtis’ picture, Oglala War-Party, the image shows 10 Oglala men wearing feather headdresses, on horseback riding down hill. The photo caption reads, “a group of Sioux warriors as they appeared in the days of inter tribal warfare, carefully making their way down a hillside in the vicinity of the enemy’s camp.” In truth headdresses would have only been worn during special occasions and, in some tribes, only by the chief of the tribe. The photograph was taken in 1907 when natives had been relegated onto reservations and warring between tribes had ended. Curtis paid natives to pose as warriors at a time when they lived with little dignity, rights, and freedoms.
Curtis’ photographs, then, pushed his subjects back into a false past that non-Indian Americans would misrecognize as authentic for a hundred years.
The problem of misrepresentation of groups who have little power to control their own images is a widespread one. Shelby Lee Adams’ work was mired in controversy, with critics suggesting that he contributed to the belief that Appalachians were backward, imbred, and unintelligent. We might apply the same critical eye to representations of marginalized peoples today, like the representation of Arabs in video games and Italian-Americans on Jersey Shore and spin-offs.
Thanks to Dolores R. and Adrienne at Native Appropriations for the post idea.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
I’m still totally geeking out about the Census Bureau starting to release data from the 2010 Census, so today you’re getting another post based on it. Kristina K. let us know that Salon has up maps of the 10 most racially-segregated metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000+, based on analyses from the University of Michigan’s Population Studies Center and available at CensusScope. Note that in the race categories, Hispanic is presented as a separate category; all other racial groups include only members of that race who said they were not of Hispanic origin. The Population Studies Center also has data available broken down by specific races and at the state level, though they don’t have maps for them, just the raw dissimilarity indices.
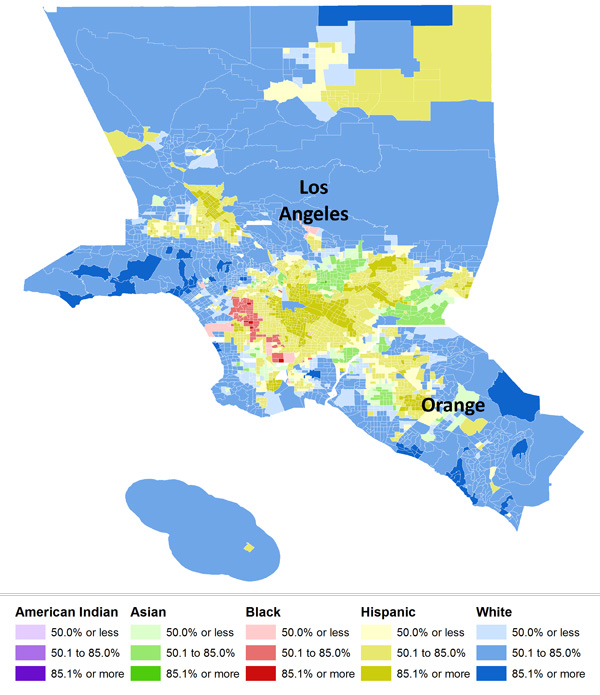
Here’s L.A., at #10:
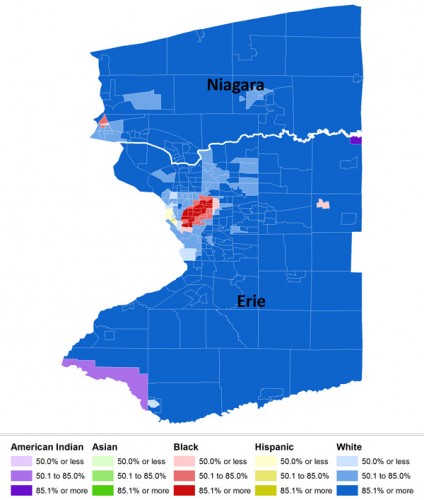
Here, just for my friend Tony, is his hometown of Buffalo, NY, #6 on the list:
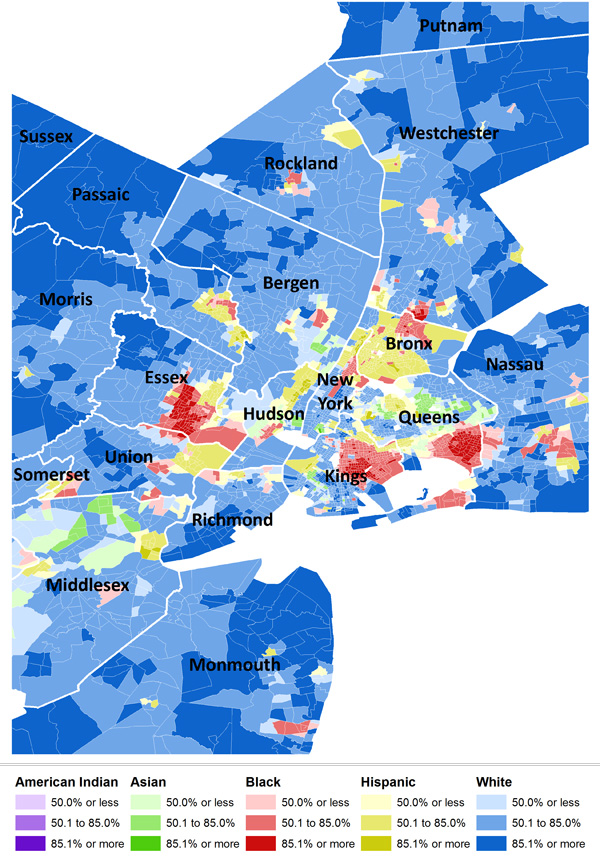
New York comes in second:
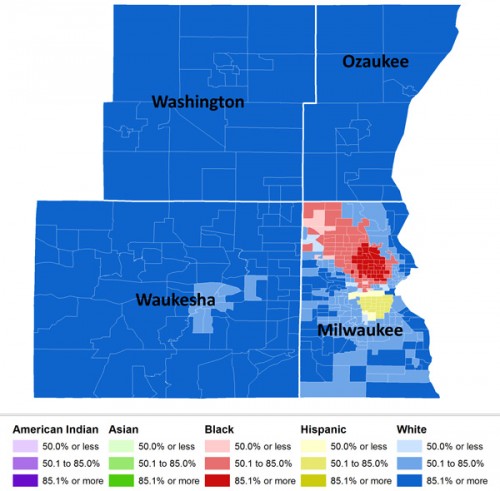
The most segregated 500,000+ metro area in the U.S.? Milwaukee:
Based on the dissimilarity index, over 81% of Milwaukee’s non-White population would have to relocate to be distributed similarly to Whites.
Interestingly, given assumptions many have about race relations in the U.S., the South doesn’t show up here. St. Louis is the most Southern city in the top 10, which is dominated by cities in the old industrial core of the North and upper Midwest/Great Lakes regions.
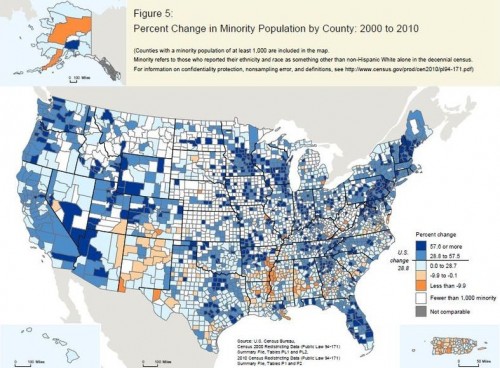
The U.S. Census Bureau has started releasing data from the 2010 Census. This map shows the change in the racial/ethnic minority (i.e., anything other than non-Hispanic White) population over the last decade:
Legend:
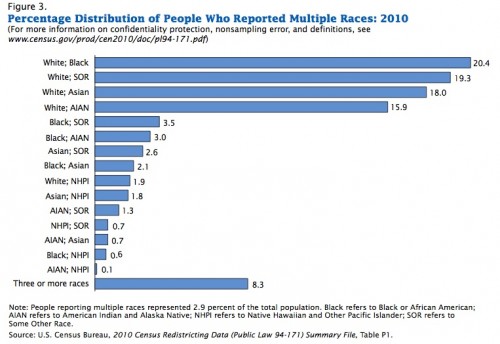
They released a report, An Overview: Race and Hispanic Origin in the 2010 Census (available here), which includes data on those who reported more than one race. Among those who reported more than one race, the vast majority listed two. Here are the most commonly reported combinations:
AIAN = American Indian/Alaska Native, NHPI = Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and SOR = some other race.
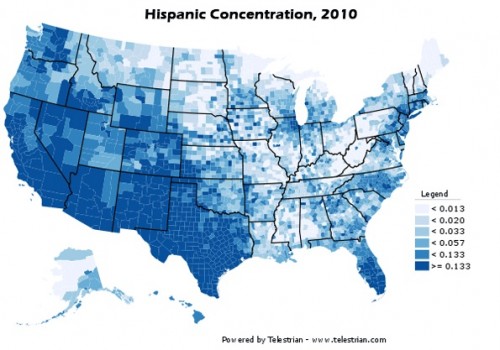
Laura E. pointed out that New Geography posted some maps based on 2010 Census data. Here’s the Hispanic population as a percent of the total population, by county (notice that the legend need to be multiplied by 100 to get the percent):
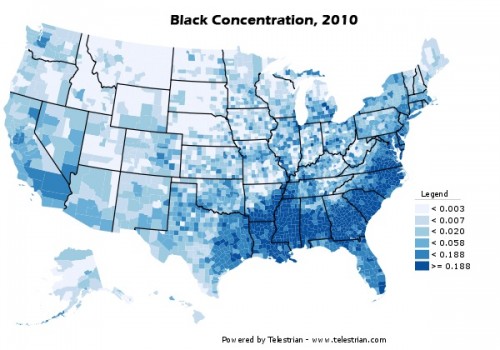
The African American population (alone or in combination with another race, and again, multiply by 100):
Last night I was cold. So cold, in fact, that I had to pull out not one, but two, of my Pendleton blankets to add some extra warmth to my bed. As I shook them out and laid them on my bed, I thought about how special these blankets are to me–one was a graduation gift, the other a thank you gift for serving on a panel about the “Future of Indian Education.” In many Native communities, Pendleton blankets are associated with important events, and have been for hundreds of years. They are given as gifts at graduations, at powwow give-aways, as thank you gifts, in commemoration of births and deaths, you name it. In addition, I’ve always associated the patterns with Native pride — a way for Natives to showcase their heritage in their home decor, coats, purses, etc. There’s something just distinctly Native about Pendleton to me.
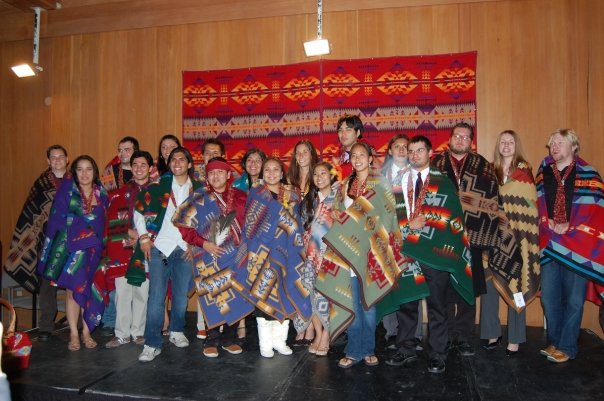
Stanford Native Graduation from a couple years ago:
But recently, Pendleton prints and fabrics have started popping up everywhere. It started with Opening Ceremony’s Pendleton line in 2010, and now Urban Outfitters has started carrying a Pendelton line, celebrities are wearing Pendleton coats, and Native-themed home decor is apparently all the rage. Now Pendleton has announced their newest collaboration, The Portland Collection, which fashion blogs are proclaiming will be the big thing for 2011.
So what’s the problem? I openly admit that a lot of these designs are adorable, and I would fully sport them (that bag! I love!), if I had a spare $1000 or so. I can’t cry straight up cultural appropriation, because…well, it’s complicated.
Pendelton has been supplying Natives with blankets and robes with Indian designs since the late 1800’s, which the “history” section of their website outlines:
A study of the color and design preferences of local and Southwest Native Americans resulted in vivid colors and intricate patterns. Trade expanded from the Nez Perce nation near Pendleton to the Navajo, Hopi and Zuni nations. These Pendleton blankets were used as basic wearing apparel and as a standard of value for trading and credit among Native Americans. The blankets also became prized for ceremonial use.
It’s almost a symbiotic relationship — they saw a market in Native communities, and Native communities stepped up and bought, traded, and sold the blankets, incorporating them into “traditional” cultural activities. Pendleton has also maintained close ties with Native communities and causes, making commemorative blankets for organizations like the National Museum of the American Indian and the National Indian Education Association. They work with Native artists to design the special edition blankets, and even donate some of the proceeds to the causes.
 (NIEA 40th anniversary blanket)
(NIEA 40th anniversary blanket)
But then, on the other hand, they go off and do things like design a $5000 blanket with White Buffalo hair, which many tribes consider extremely sacred and definitely off-limits to commercial sale.
I do appreciate Pendleton’s relationship with Native communities. I love my blankets, and love even more what they represent.
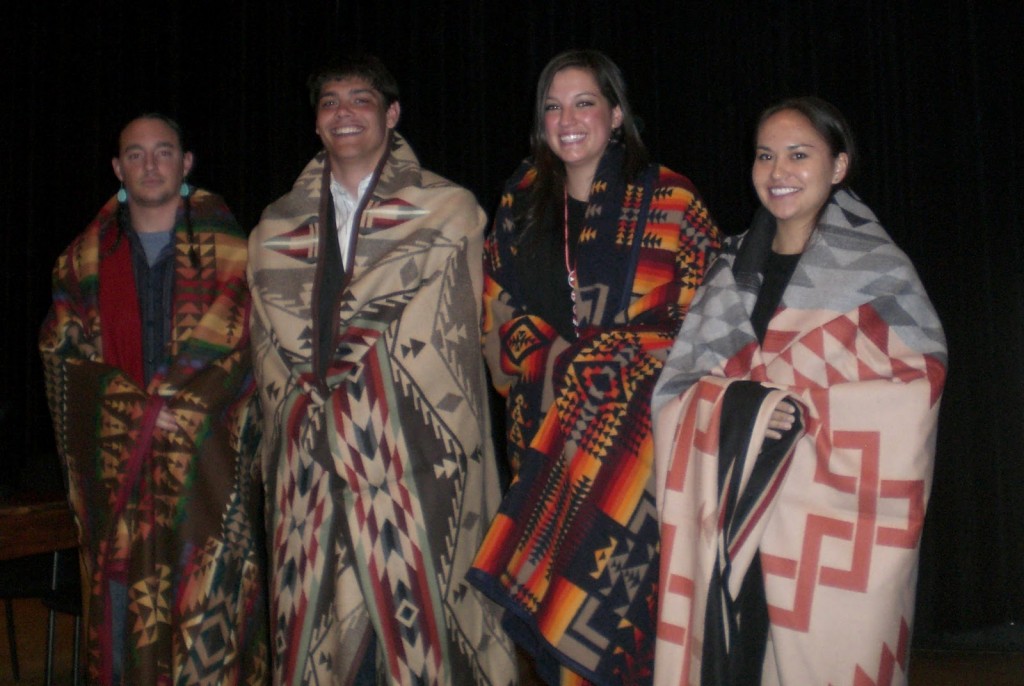
However, seeing hipsters march down the street in Pendleton clothes, seeing these bloggers ooh and ahh over how “cute” these designs are, and seeing non-Native models all wrapped up in Pendleton blankets makes me upset. It’s a complicated feeling, because I feel ownership over these designs as a Native person, but on a rational level I realize that they aren’t necessarily ours to claim. To me, it just feels like one more thing non-Natives can take from us — like our land, our moccasins, our headdresses, our beading, our religions, our names, our cultures weren’t enough? you gotta go and take Pendleton designs too?
Then there’s the whole economic stratification issue of it too, these designs are expensive. The new Portland collection ranges from $48 for a tie to over $700 for a coat, the Opening Ceremony collection was equally, if not more, costly. It almost feels like rubbing salt in the wound, when poverty is rampant in many Native communities, to say “oh we designed this collection based on your culture, but you can’t even afford it!”
So I don’t know. Are all of these designs cultural appropriation? Should I ignore the twinge in my stomach every time I see a Pendleton pattern in the Urban Outfitters window? Should I embrace it as the mainstream fashion scene finally catching up with what we Natives have known since the 1800’s?
Personally, the bottom line is that I would rather associate Pendleton with Native pride and commemorating important events…
…than with hipsters, high fashion, and flash-in-the-pan trends. But I’m obviously conflicted. What do you think? Are these designs and trends ok, or do I have a right to be upset?
(Thanks to Precious for getting me thinking about this!)
Adrienne K. is a member of the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma and a graduate student in Boston, where she studies access to higher education for Native students. In her free time, she blogs about cultural appropriation and use of Indigenous cultures, traditions, languages, and images in popular culture, advertising, and everyday life at Native Appropriations.
Via Native Appropriations, I found a set of vintage Valentines drawing on stereotypes of American Indians at the Vintage Valentine Museum.
“I’d never squaw’k if you’d be my Valentine” (1950s or ’60s):
“I want to be the CHIEF” (1940s or ’50s):
“I’m a straightshoooter Valentine. May I be your BOW” (1930s):
“I’m hunting for you, Valentine” (1941):
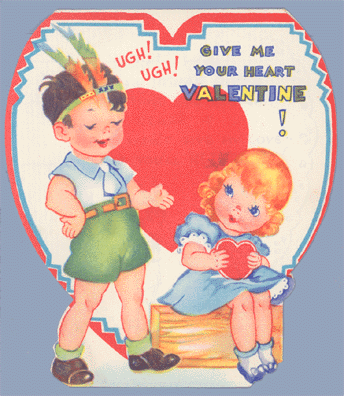
“Ugh! Ugh! I’m an INDIAN GIVER. It’s time you should learn it. For I won’t give my love, unless you’ll RETURN it!” (1940s):
“Ugh! Ugh! Give me your heart Valentine!”:
“You heap fine Valentine AND HOW!” (1950s or ’60s):
“I’m sending this ARROW CHEIFLY to say, let me be your “beau” (1930s or ’40s):
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
We’ve discussed American Indian mascots, advertising featuring anachronistic caricatures of American Indians, the ice skater who appropriated aboriginal culture, the lie at the heart of the famous crying Indian PSA, and the stunning irony that is Avatar, but we’ve never directly addressed the use and appropriation of the idea of the Eskimo. The term refers to the Inuit and Yupik people in Eastern Russia, Alaska, Canada, and Greenland.
Russell Potter, a professor of English at Rhode Island College, collected a few vintage advertisements featuring the idea of the Eskimo. He argues that they fall roughly into two camps: cheerful adorable Eskimo and the Eskimo as primitive and backwards.
These first two for apples and ginger ale fall into the first category:
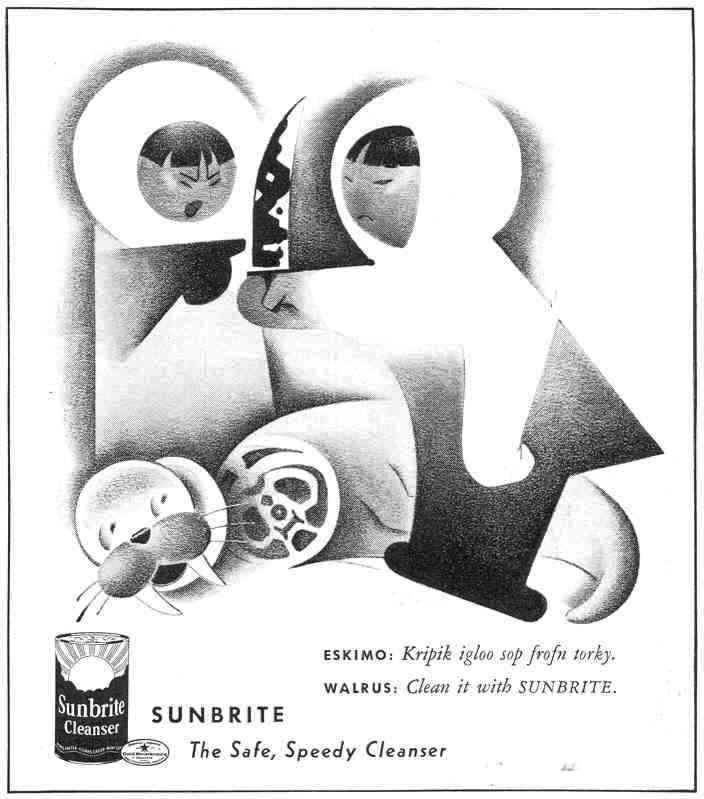
But this ad presents the “Esquimaux” as “dull” and Grape Nuts as civilized:
Building on Potter’s collection, Adrienne at Native Appropriations posted some more contemporary uses of the Eskimo.
Eskimo Joe’s (Stillwater, OK) uses an image of an Eskimo looking downright ridiculous and very much like his dog:
Any child of the ’80s probably remembers the Lisa Frank Eskimo girl (which Adrienne points out looks decidely anglo):
And this ad seems to suggest that even decapitated walruses speak better English than Eskimos:
Here’s another example of the childlike Eskimo, tweeted to us by @Matthew_Kneale:
All of these ads turn Eskimos into (cute but inferior) childlike figures or (deficient and inferior) backwards adults, or some combination of the two. For a population with essentially no contact with the Inuit or the Yupik, the idea that they are real human beings can become lost. When real members of a group are invisible, imaginary representatives can be demonized or romanticized as we see fit.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
If you’re interested in cultural representations of Native Americans, I highly recommend the blog Native Appropriations. Recently Adrienne K. posted about an article in a student-government-funded newspaper at Cal State U.-Long Beach that stands out for its disrespectful, hostile tone. The article, titled “Pow Wow Wow Yippee Yo Yippy Yay,” was a “review” of the annual powwow sponsored by the American Indian Student Council. It had never occurred to me that you would review a cultural event as though it were just another form of entertainment, like a new movie, but that’s the least of the issues here. The full article, from the Union Weekly (via OC Weekly):
Some key excerpts:
…it really seemed like a large, Native American themed flea market. Some of the food vendors just seemed to unceremoniously add the word “Indian” to whatever food they were peddling. Indian tacos? What the fuck are Indian tacos?
…like a Mexican pizza from Taco Bell, but shittier. The only experience I have with fry bread is watching a show about how incredibly unhealthy it is to consume, and watching its rapid consumption on campus grounds.
The entire scene felt disingenuous and cheap. Donations are great, and necessary, tossing them unceremoniously on the ground is crass and borderline obscene. Even the homeless have hats and cups.
I flinched several times while reading the article. I grew up in Oklahoma surrounded by Native American cultures, both because I lived in an area where several tribes were very visible and because my mom is part Cherokee herself and several close relatives married people enrolled in other tribes. Even though I know that in most of the U.S. Native Americans are often culturally invisible and most people haven’t gone to tons of powwows or sat around watching the women in the family sewing ribbon shirts in the living room, I still sometimes forget that these things aren’t instantly recognizable and interesting to other people, or that they could see something that I was taught to be respectful and appreciative of and have such a different reaction.
Of course, this article goes beyond being unfamiliar or uninterested. The author, the paper’s campus editor, clearly didn’t want to learn what was going on. I mean, even if you’ve never heard of one before in your life, just a minimal Google search will explain to you than an Indian taco is, more or less, a taco on fry bread (the Osage Nation even has an annual competition). An image of a dancer is used to highlight a mocking, mean-spirited “review,” as though the powwow’s only function was to entertain uneducated outsiders.
The Union Review and the author of the article issued the typical non-apology “apology” statements — we’re just here to let all sides of the debate have a voice! We’re sorry if anyone got themselves all offended, we really didn’t expect this reaction at all! — which is also available at the OC Weekly link above.
As Adrienne points out, though the “Asians in the library ” rant from a UCLA student got a huge amount of attention, there’s been much less about this. It highlights the point Tami made at What Tami Said: overtly disrespectful and/or racist behavior on campuses shouldn’t shock us, if we’re paying attention.
Cross-posted at Racialicious.
We owe many iconic images of American Indians to photographer Edward S. Curtis. Growing up in Wisconsin and Minnesota, Curtis began photographing Indians in 1895 and, in 1906, was offered $75,000 by JP Morgan to continue documenting their lives (wikipedia). The 1,500 resulting photographs inevitably impacted the image of Indians in the American imagination.
Later it came to light that Curtis’ photographs weren’t exactly pure representations. In some photographs, for example, he erased signs of modernity. The first photograph below, the un-edited version, includes a clock between the two men, whereas the edited version does not.
Curtis also sometimes staged scenes and dressed paid participants in costumes, as in this photograph:
According to Wikipedia contributors:
In Curtis’ picture, Oglala War-Party, the image shows 10 Oglala men wearing feather headdresses, on horseback riding down hill. The photo caption reads, “a group of Sioux warriors as they appeared in the days of inter tribal warfare, carefully making their way down a hillside in the vicinity of the enemy’s camp.” In truth headdresses would have only been worn during special occasions and, in some tribes, only by the chief of the tribe. The photograph was taken in 1907 when natives had been relegated onto reservations and warring between tribes had ended. Curtis paid natives to pose as warriors at a time when they lived with little dignity, rights, and freedoms.
Curtis’ photographs, then, pushed his subjects back into a false past that non-Indian Americans would misrecognize as authentic for a hundred years.
The problem of misrepresentation of groups who have little power to control their own images is a widespread one. Shelby Lee Adams’ work was mired in controversy, with critics suggesting that he contributed to the belief that Appalachians were backward, imbred, and unintelligent. We might apply the same critical eye to representations of marginalized peoples today, like the representation of Arabs in video games and Italian-Americans on Jersey Shore and spin-offs.
Thanks to Dolores R. and Adrienne at Native Appropriations for the post idea.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
I’m still totally geeking out about the Census Bureau starting to release data from the 2010 Census, so today you’re getting another post based on it. Kristina K. let us know that Salon has up maps of the 10 most racially-segregated metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000+, based on analyses from the University of Michigan’s Population Studies Center and available at CensusScope. Note that in the race categories, Hispanic is presented as a separate category; all other racial groups include only members of that race who said they were not of Hispanic origin. The Population Studies Center also has data available broken down by specific races and at the state level, though they don’t have maps for them, just the raw dissimilarity indices.
Here’s L.A., at #10:
Here, just for my friend Tony, is his hometown of Buffalo, NY, #6 on the list:
New York comes in second:
The most segregated 500,000+ metro area in the U.S.? Milwaukee:
Based on the dissimilarity index, over 81% of Milwaukee’s non-White population would have to relocate to be distributed similarly to Whites.
Interestingly, given assumptions many have about race relations in the U.S., the South doesn’t show up here. St. Louis is the most Southern city in the top 10, which is dominated by cities in the old industrial core of the North and upper Midwest/Great Lakes regions.
The U.S. Census Bureau has started releasing data from the 2010 Census. This map shows the change in the racial/ethnic minority (i.e., anything other than non-Hispanic White) population over the last decade:
Legend:
They released a report, An Overview: Race and Hispanic Origin in the 2010 Census (available here), which includes data on those who reported more than one race. Among those who reported more than one race, the vast majority listed two. Here are the most commonly reported combinations:
AIAN = American Indian/Alaska Native, NHPI = Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and SOR = some other race.
Laura E. pointed out that New Geography posted some maps based on 2010 Census data. Here’s the Hispanic population as a percent of the total population, by county (notice that the legend need to be multiplied by 100 to get the percent):
The African American population (alone or in combination with another race, and again, multiply by 100):
Last night I was cold. So cold, in fact, that I had to pull out not one, but two, of my Pendleton blankets to add some extra warmth to my bed. As I shook them out and laid them on my bed, I thought about how special these blankets are to me–one was a graduation gift, the other a thank you gift for serving on a panel about the “Future of Indian Education.” In many Native communities, Pendleton blankets are associated with important events, and have been for hundreds of years. They are given as gifts at graduations, at powwow give-aways, as thank you gifts, in commemoration of births and deaths, you name it. In addition, I’ve always associated the patterns with Native pride — a way for Natives to showcase their heritage in their home decor, coats, purses, etc. There’s something just distinctly Native about Pendleton to me.
Stanford Native Graduation from a couple years ago:
But recently, Pendleton prints and fabrics have started popping up everywhere. It started with Opening Ceremony’s Pendleton line in 2010, and now Urban Outfitters has started carrying a Pendelton line, celebrities are wearing Pendleton coats, and Native-themed home decor is apparently all the rage. Now Pendleton has announced their newest collaboration, The Portland Collection, which fashion blogs are proclaiming will be the big thing for 2011.
So what’s the problem? I openly admit that a lot of these designs are adorable, and I would fully sport them (that bag! I love!), if I had a spare $1000 or so. I can’t cry straight up cultural appropriation, because…well, it’s complicated.
Pendelton has been supplying Natives with blankets and robes with Indian designs since the late 1800’s, which the “history” section of their website outlines:
A study of the color and design preferences of local and Southwest Native Americans resulted in vivid colors and intricate patterns. Trade expanded from the Nez Perce nation near Pendleton to the Navajo, Hopi and Zuni nations. These Pendleton blankets were used as basic wearing apparel and as a standard of value for trading and credit among Native Americans. The blankets also became prized for ceremonial use.
It’s almost a symbiotic relationship — they saw a market in Native communities, and Native communities stepped up and bought, traded, and sold the blankets, incorporating them into “traditional” cultural activities. Pendleton has also maintained close ties with Native communities and causes, making commemorative blankets for organizations like the National Museum of the American Indian and the National Indian Education Association. They work with Native artists to design the special edition blankets, and even donate some of the proceeds to the causes.
 (NIEA 40th anniversary blanket)
(NIEA 40th anniversary blanket)
But then, on the other hand, they go off and do things like design a $5000 blanket with White Buffalo hair, which many tribes consider extremely sacred and definitely off-limits to commercial sale.
I do appreciate Pendleton’s relationship with Native communities. I love my blankets, and love even more what they represent.
However, seeing hipsters march down the street in Pendleton clothes, seeing these bloggers ooh and ahh over how “cute” these designs are, and seeing non-Native models all wrapped up in Pendleton blankets makes me upset. It’s a complicated feeling, because I feel ownership over these designs as a Native person, but on a rational level I realize that they aren’t necessarily ours to claim. To me, it just feels like one more thing non-Natives can take from us — like our land, our moccasins, our headdresses, our beading, our religions, our names, our cultures weren’t enough? you gotta go and take Pendleton designs too?
Then there’s the whole economic stratification issue of it too, these designs are expensive. The new Portland collection ranges from $48 for a tie to over $700 for a coat, the Opening Ceremony collection was equally, if not more, costly. It almost feels like rubbing salt in the wound, when poverty is rampant in many Native communities, to say “oh we designed this collection based on your culture, but you can’t even afford it!”
Personally, the bottom line is that I would rather associate Pendleton with Native pride and commemorating important events…
…than with hipsters, high fashion, and flash-in-the-pan trends. But I’m obviously conflicted. What do you think? Are these designs and trends ok, or do I have a right to be upset?
Via Native Appropriations, I found a set of vintage Valentines drawing on stereotypes of American Indians at the Vintage Valentine Museum.
“I’d never squaw’k if you’d be my Valentine” (1950s or ’60s):
“I want to be the CHIEF” (1940s or ’50s):
“I’m a straightshoooter Valentine. May I be your BOW” (1930s):
“I’m hunting for you, Valentine” (1941):
“Ugh! Ugh! I’m an INDIAN GIVER. It’s time you should learn it. For I won’t give my love, unless you’ll RETURN it!” (1940s):
“Ugh! Ugh! Give me your heart Valentine!”:
“You heap fine Valentine AND HOW!” (1950s or ’60s):
“I’m sending this ARROW CHEIFLY to say, let me be your “beau” (1930s or ’40s):
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
We’ve discussed American Indian mascots, advertising featuring anachronistic caricatures of American Indians, the ice skater who appropriated aboriginal culture, the lie at the heart of the famous crying Indian PSA, and the stunning irony that is Avatar, but we’ve never directly addressed the use and appropriation of the idea of the Eskimo. The term refers to the Inuit and Yupik people in Eastern Russia, Alaska, Canada, and Greenland.
Russell Potter, a professor of English at Rhode Island College, collected a few vintage advertisements featuring the idea of the Eskimo. He argues that they fall roughly into two camps: cheerful adorable Eskimo and the Eskimo as primitive and backwards.
These first two for apples and ginger ale fall into the first category:
But this ad presents the “Esquimaux” as “dull” and Grape Nuts as civilized:
Building on Potter’s collection, Adrienne at Native Appropriations posted some more contemporary uses of the Eskimo.
Eskimo Joe’s (Stillwater, OK) uses an image of an Eskimo looking downright ridiculous and very much like his dog:
Any child of the ’80s probably remembers the Lisa Frank Eskimo girl (which Adrienne points out looks decidely anglo):
And this ad seems to suggest that even decapitated walruses speak better English than Eskimos:
Here’s another example of the childlike Eskimo, tweeted to us by @Matthew_Kneale:
All of these ads turn Eskimos into (cute but inferior) childlike figures or (deficient and inferior) backwards adults, or some combination of the two. For a population with essentially no contact with the Inuit or the Yupik, the idea that they are real human beings can become lost. When real members of a group are invisible, imaginary representatives can be demonized or romanticized as we see fit.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.