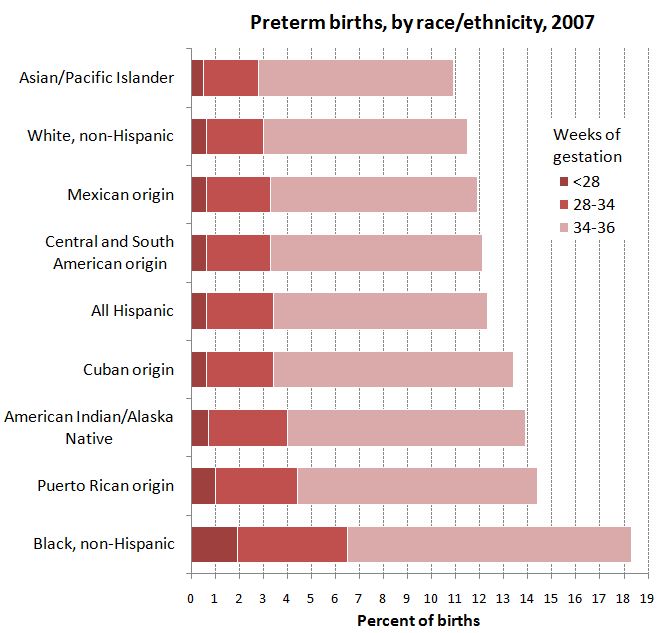
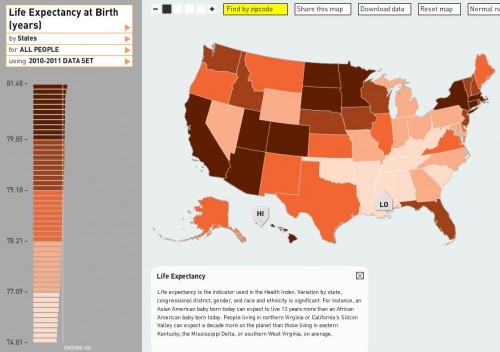
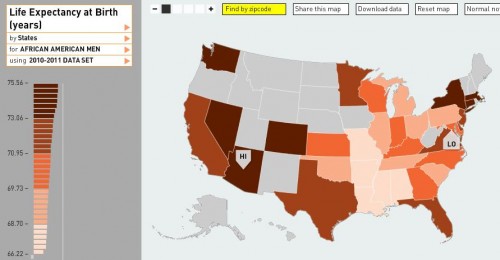
The CDC has just released a Health Disparities and Inequalities Report with new numbers detailing the uneven mortality and morbidity in the U.S. Family Inequality‘s Philip Cohen highlighted the data on pre-term birth among whites, blacks, Asians/Pacific Islanders, Hispanics, and some Hispanic subgroups. It’s nice to see data that includes more than just whites and blacks; studies often do not report data on Hispanics, Asian/Pacific Islanders, and especially American Indians because the number of respondents is considered too low (and they do not over sample these groups). More, breaking out the different Hispanic sub-groups is also rare. As Cohen said, it’d be nice to see such detail for other groups as well (though it’s tough to do so for black Americans because those who arrived in the slave trade have often lost track of their national/ethnic origin).
In any case, the data both confirm previous findings and offer an important insight. In the confirmatory case, it shows that Asians and whites are less likely to give birth to pre-term babies than other groups, with blacks suffering the worst outcomes. As for the interesting finding: notice the wide range of outcomes for Hispanics of different origin. Reporting only “All Hispanic” hides important variation. We can be assured that that variation is true for the other racial groups as well.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.