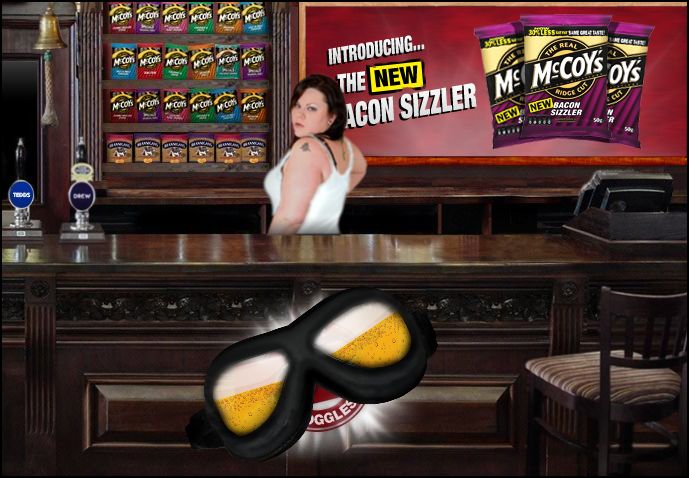
Anna sent in another example of a brand marketing itself as for-manly-men-only. Add this one, featuring McCoy Crisps, to some of our other examples: Dockers, Klondike Bar, Alpo, Oberto beef jerky, and Ketel One.
The first thing that the McCoy Crisps Pub site requires is that you tell it what kind of shoes you’re wearing:
If you answer “incorrectly,” the website says: “No, not right. Get inside and learn how to be a real man.”
When you enter the online pub, the first thing you see is a woman that you are supposed to be disgusted by. Immediately a set of beer goggles flies up onto your face (because you wouldn’t want to look at her for more than a split second, apparently):
Then you see this (phew! that was close!):
Alongside playing darts, drinking games, and playing manly trivia, you can get tips on how to be more manly. Such as “How Not to Look Like a Girl Watching TV” and “How to Get Away with Not Ironing”:
And you can also take a manly quiz to find out how manly you are. The quiz nicely tells you exactly how you are allowed to behave and what you are allowed to like. Some examples of questions:


So being a guy means manipulating women with puppies, making fun of your brother-in-law for being a good husband and father, making women cook for you, eschewing personal grooming and healthy eating as much as possible, objectifying women, and enjoying the Pirelli company calender.
Oh, and, if you haven’t seen the Pirelli calendar, you really, really, really don’t want to click here (NSFW; trigger warning).
So there you have it: another marketing campaign that assumes that men are stupid, shallow, sexist, sport-o-holics. I don’t understand why men tolerate it.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.