In this series I have offered five explanations of why people of color are included in advertising. Start with the first in the series and follow the links to the remaining four here.
I am now discussing how they are included. Already I have shown that people of color are often whitewashed and that they tend to be chaperoned. Here I show that, when people of color are included, they are often subordinated through placement and action. That is, they tend to be literally background or arranged so that the focal point (visually or through action) is the white person or people in the ad. You’ll see a lot of this in the previous posts in this series if you go back and look again.
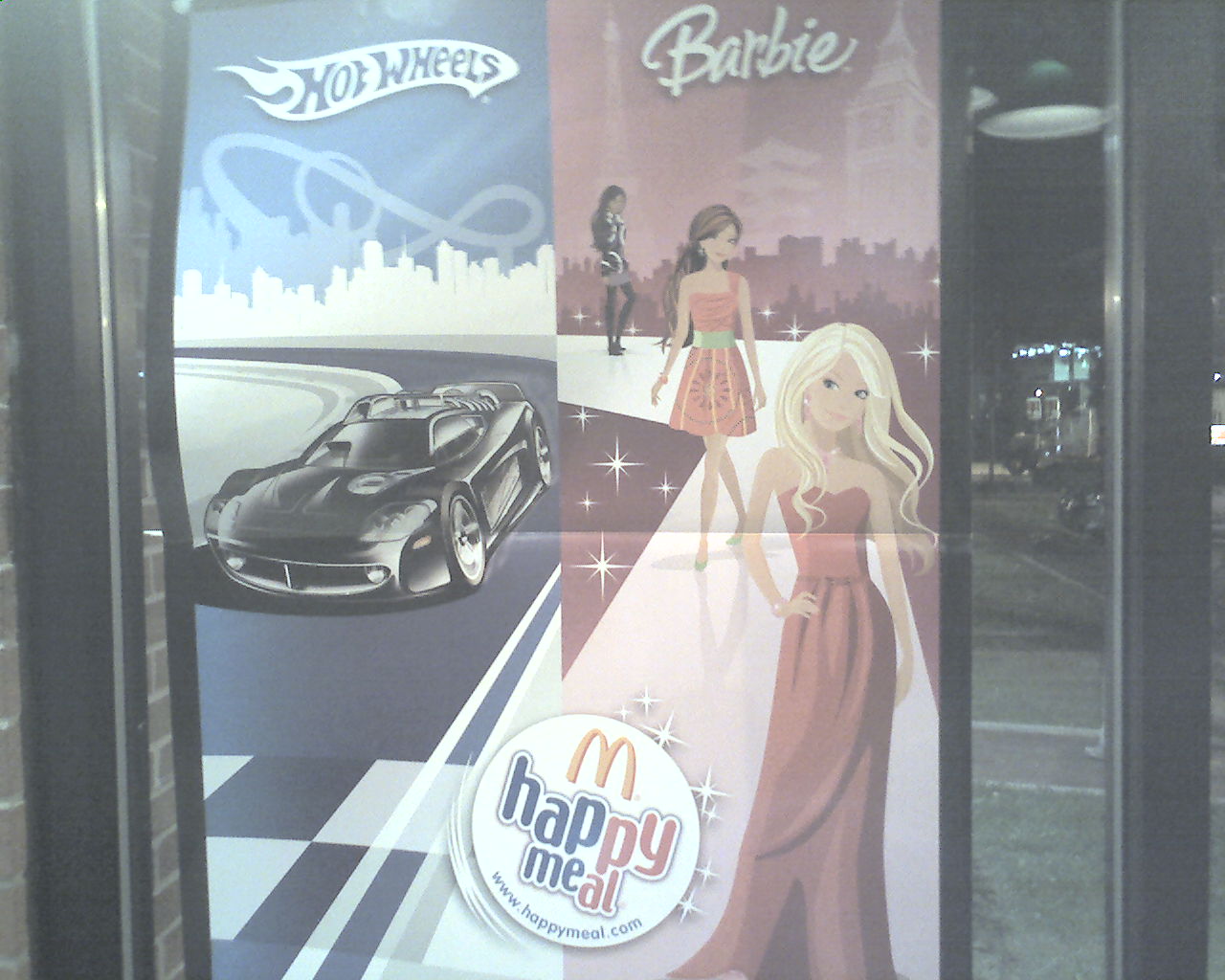
Darin F. sent in this example from a poster for McDonalds Happy Meals. He noted the way in which the women were arranged, closest to furthest, by skin color:
NEW! I found another example of this skin color hierarchy, this time on a CD cover:

More instances in which people of color are background:

In the next two ads, the center of attention–or the action–is where the white woman is: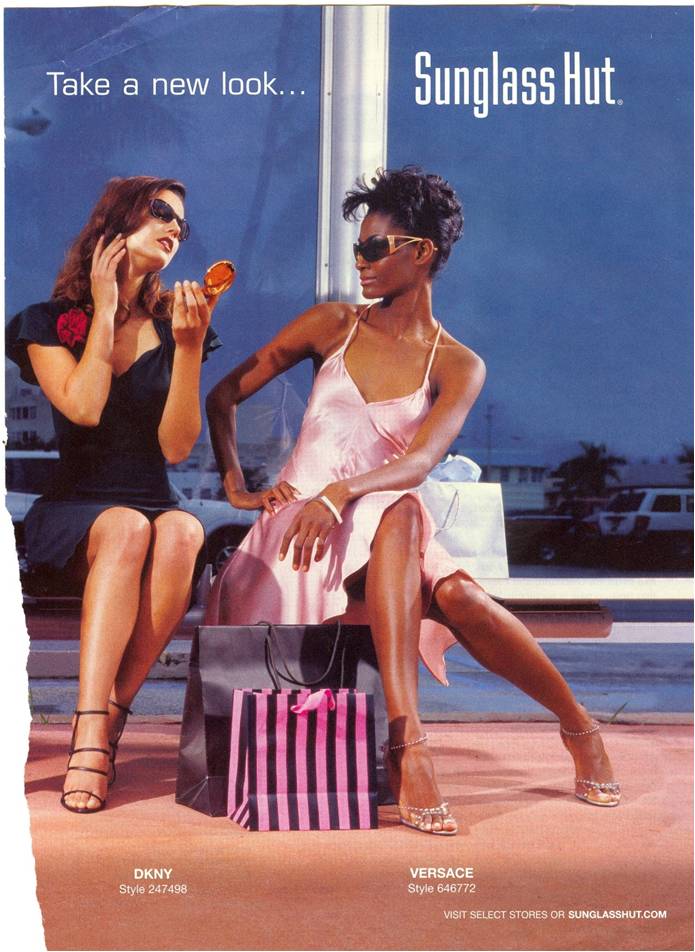 

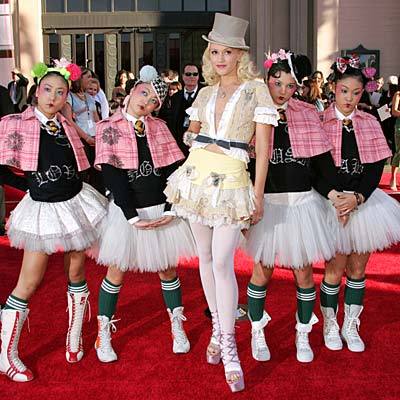
Notice how in this ad, while there are three women of color (an exception to the tendency for people of color to be chaperoned), the woman front-and-center is clearly white:
Something similar is going on in these next two ads:

As Jean Kilbourne points out in her docmentary, Killing Us Softly, this visual representation of racial hierarchy tends to be found unless another axis of hierarchy is at work:

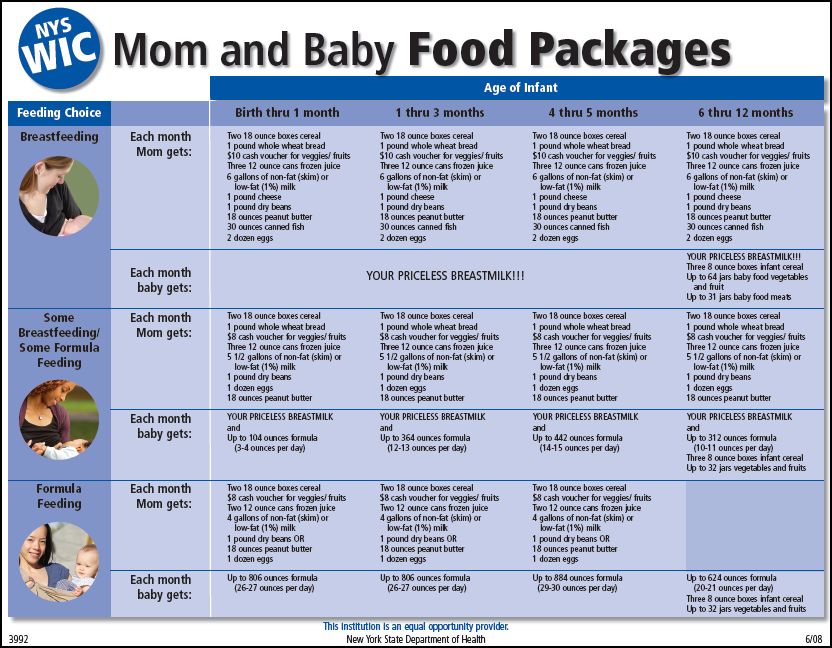
NEW (Mar. ’10)! Anina H. sent in this New York State flier advising mothers on feeding their babies. Notice that the flier includes women of three different races, but the ideal mother (“YOUR PRICELESS BREASTMILK!!!”) is white:
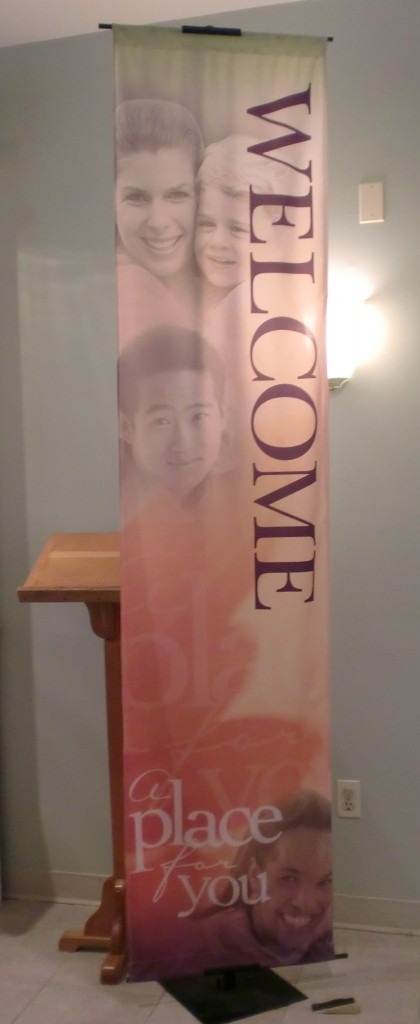
NEW (July ’10)! Naomi D. saw this welcome banner at the entrance of a Methodist Church. Notice how the racial hierarchy is represented on the banner with a White woman and child on the top, an Asian man below her, and a Black woman at the bottom of the banner:
As always, I welcome your comments!
Next up: Interracial dating, the last taboo.
Also in this series:
(1) Including people of color so as to associate the product with the racial stereotype.
(2) Including people of color to invoke (literally) the idea of “color” or “flavor.”
(3) To suggest ideas like “hipness,” “modernity,” and “progress.”
(4) To trigger the idea of human diversity.
(5) To suggest that the company cares about diversity.
How are they included?
(6) They are “white-washed.”
(7) They are “chaperoned.”