This has been a hard week. Another young, unarmed black man was killed by police. The Root added Michael Brown’s face to a slideshow of such incidents, started after a black man named Eric Garner died after being put in a chokehold by officers less than one month ago. This week’s guilty verdict in the trial of the man who shot Renisha McBride left me feeling numb. Nothing good could come of it, but at least I didn’t feel worse.
The shooting of Michael Brown, however, is still undergoing trial by media and the verdict is swayed by the choices made by producers and directors as to how to portray him. When Marc Duggan was killed by police earlier this year, they often featured pictures in which he looked menacing, including ones that had been cropped in ways that enhanced that impression.
Left: Photo of Duggan frequently used by media; right: uncropped photo in which he holds a plaque commemorating his deceased daughter.
As the media coverage of Brown’s death heated up, the image that first circulated of Brown was this:
Reports state that this was his current Facebook profile picture, with the implication that media actors just picked the first or most prominent picture they saw. Or, even, that somehow it’s Brown’s fault that this is the image they used.
Using the image above, though, is not neutrality. At best, it’s laziness; they simply decided not to make a conscious, careful choice. It’s their job to pick a photograph and I don’t know exactly what the guidelines are but “pick the first one you see” or “whatever his Facebook profile pic was on the day he died” is probably not among them.
There are consequential choices to be made. As an example, here are two photos that have circulated since criticism of his portrayal began — the top more obviously sympathetic and the bottom more neutral:
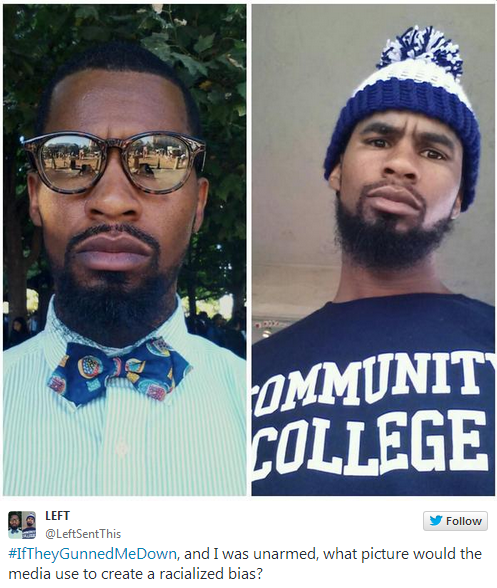
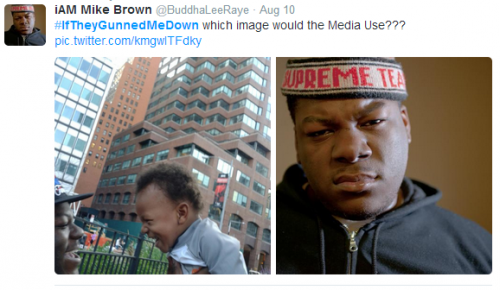
Commenting on this phenomenon, Twitter user @CJ_musick_lawya released two photos of himself, hashtagged with #iftheygunnedmedown, and asked readers which photo they thought media actors would choose.
Top: Wearing a cap and gown with former President Clinton; bottom: in sunglasses posing with a bottle and a microphone.
The juxtaposition brilliantly revealed how easy it is to demonize a person, especially if they are a member of a social group stereotyped as violence-prone, and how important representation is. It caught on and the imagery was repeated to powerful effect. A summary at The Root featured examples like these:
The New York Times reports that the hashtag has been used more than 168,000 times as of August 12th. I want to believe that conversations like these will educate and put pressure on those with the power to represent black men and all marginalized peoples to make more responsible and thoughtful decisions.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.