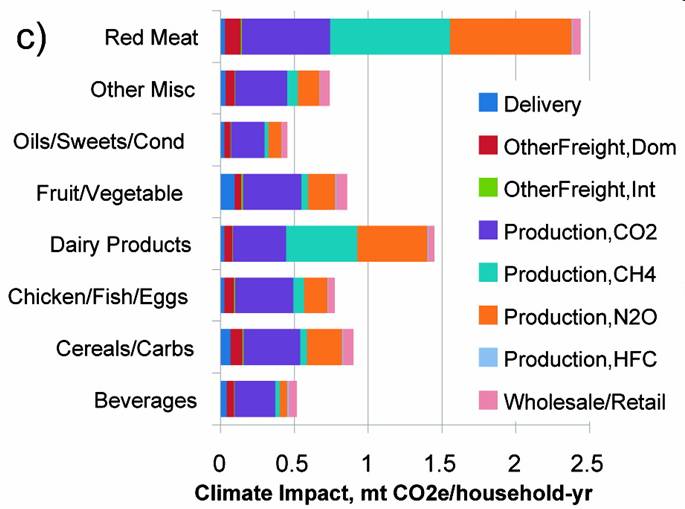
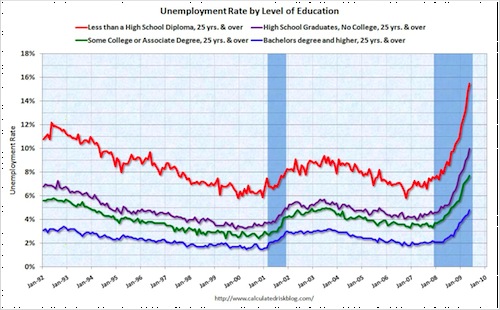
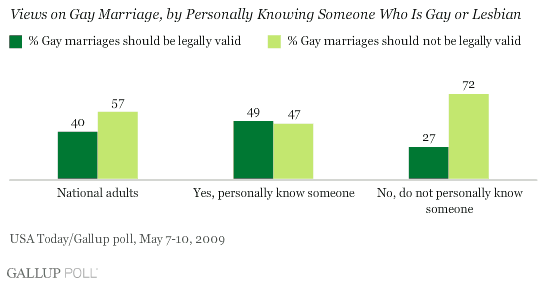Teresa C. sent in a link to a benefit in Raleigh, NC, for a women’s center. The benefit was called Walk for Women and included a mile-long walk in high heels (though apparently the high heels are optional):

I get what they’re trying to do. Really, I do: an attention-getting way of raising money for what I’m sure is a worthy cause. And having worked or volunteered in many social-service jobs, I know fundraising can be hard (especially in an economic downturn) and you can end up doing some sort of weird stuff if you think it will bring in donations. (I once helped out at a dog blessing at an animal shelter. People brought in their dogs and had them blessed by an Episcopalian preacher [priest? I’m not sure of the terminology] and received a little medal with the image of some saint who apparently is the patron saint of animals, and who I am too lazy to look up right now, to hang on the dog’s collar. Also, there was wine, which in small-town Kansas was the source of some controversy.)
[NOTE: When I originally wrote this post, I had no idea that blessing animals is something some Episcopalians and Catholics do fairly often. I thought it was just something a sweet but kind of flaky volunteer thought up. I apologize if the comments about the animal blessing ceremony seemed disrespectful–I truly didn’t know that it’s a common religious ceremony. I decided to leave that section in but cross through it rather than delete it entirely, as it seemed dishonest to just erase it and pretend it hadn’t happened. I messed up, and I know it.]
So I know where people are coming from when they organize such things. But it still kind of bugs me that organizing walks in high heels has become a common fundraising technique for organizations that serve (primarily) women–women’s centers, domestic violence shelters, rape crisis centers, and so on. And I can’t help but think that walking around in heels is, ultimately, an odd way to help women. At least in this case, participants are apparently raising money. But several times I’ve seen high-heeled walks that are simply to “raise awareness,” with no particular emphasis on donations. The ones I saw all had men wearing high heels. And the thing is, I can’t figure out what on earth the point is. What type of awareness is it raising? Is walking around in high heels supposed to increase a person’s understanding of some of the problems women face? What are bystanders supposed to get out of it?
The Raleigh Walk for Women organizers also had a Beauty Blitz at a local salon, where people could drop in, register for the walk, and get discounts on salon services from a person who was a contestant on “Biggest Loser.” And also have a cocktail. So the event is this strange mixture of helping women by using the trappings of femininity (high heels, beauty care). And I just find it kind of odd.