On Saturday, October 17th, 2015, the Minneapolis Film Society screened Pretty Village at St. Anthony Main theater, a documentary depicting the experience of Kemal Pevranic and his village during the war in Bosnia (1992-95). Pevranic, the main subject of the film, is also the producer and a human rights activist who works to raise awareness and to rebuild his community in Bosnia by working on reconciliation efforts, particularly with young people of all three ethnicities in Bosnia. The Center for Holocaust and Genocide Studies co-sponsored the film screening event, in which I participated as the moderator of the post-screening discussion. more...
A few things have been happening in Burundi this year. The president, Pierre Nkuruzinza circumvented the constitution and ran for a third term. The result of this has been on-going conflict from April. Burundi was not a surprise though. Journalists I spoke to earlier this year all stated that regional coverage of Burundi had pointed to something being afoot as early as last year. None-the-less, here we are, with yet another unfolding atrocity, several deaths, an ever growing numbers of displaced and plenty of hand-wringing by the international community.
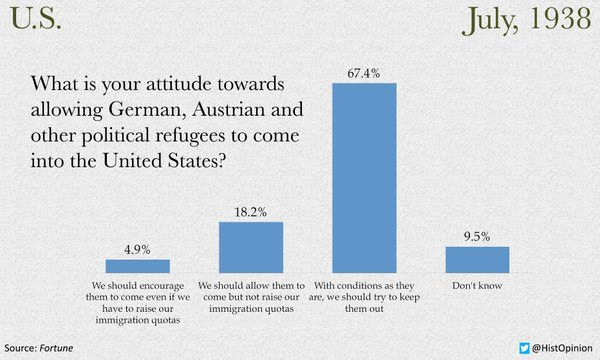 The Twitter account @HistOpinion recently reminded us of the prevailing opinion on raising the immigrant quota for refugees who were fleeing Nazi Germany. Two-thirds of the respondents polled by Gallup’s American Institute of Public Opinion in July 1938 agreed with the proposition that “with conditions as they are we should try to keep them out.”
The Twitter account @HistOpinion recently reminded us of the prevailing opinion on raising the immigrant quota for refugees who were fleeing Nazi Germany. Two-thirds of the respondents polled by Gallup’s American Institute of Public Opinion in July 1938 agreed with the proposition that “with conditions as they are we should try to keep them out.”
The Spirit of the Laws: The Plunder of Wealth in the Armenian Genocide
Taner Akçam and Umit Kurt, Translated by Aram Arkun
 Pertinent to contemporary demands for reparations from Turkey is the relationship between law and property in connection with the Armenian Genocide. This book examines the confiscation of Armenian properties during the genocide and subsequent attempts to retain seized Armenian wealth. Through the close analysis of laws and treaties, it reveals that decrees issued during the genocide constitute central pillars of the Turkish system of property rights, retaining their legal validity, and although Turkey has acceded through international agreements to return Armenian properties, it continues to refuse to do so. The book demonstrates that genocides do not depend on the abolition of the legal system and elimination of rights, but that, on the contrary, the perpetrators of genocide manipulate the legal system to facilitate their plans.
Pertinent to contemporary demands for reparations from Turkey is the relationship between law and property in connection with the Armenian Genocide. This book examines the confiscation of Armenian properties during the genocide and subsequent attempts to retain seized Armenian wealth. Through the close analysis of laws and treaties, it reveals that decrees issued during the genocide constitute central pillars of the Turkish system of property rights, retaining their legal validity, and although Turkey has acceded through international agreements to return Armenian properties, it continues to refuse to do so. The book demonstrates that genocides do not depend on the abolition of the legal system and elimination of rights, but that, on the contrary, the perpetrators of genocide manipulate the legal system to facilitate their plans.
Taner Akçam holds the Kaloosdian and Mugar Chair of Armenian Genocide Studies at Clark University. He is the author of many books, including: The Young Turks’ Crime Against Humanity: The Armenian Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing in the Ottoman Empire (Princeton University Press, 2012), which received the Middle East Studies Association’s Hourani Book Prize and was listed by Foreign Affairs as “Best International Relations Books of 2012.”
Umit Kurt is a Ph.D. Candidate in the History Department of Clark University. He is the author of The Great, Hopeless Turkish Race: Fundamentals of Turkish Nationalism in the Turkish Homeland 1911-1916 (Iletisim Publishing House, 2012).
The Great Fire: One American’s Mission to Rescue Victims of the 20th Century’s First Genocide
By Lou Ureneck

The harrowing story of a Methodist Minister and a principled American naval officer who helped rescue more than 250,000 refugees during the genocide of Armenian and Greek Christians-a tale of bravery, morality, and politics, published to coincide with the genocide’s centennial.
Professor Ureneck (Journalism, Boston University) conducted much of his research in writing the book in the U of M Library’s extensive Kautz Family YMCA Archives, highlighting the University’s unique ability to place historic events in context, and provide primary sources for study and scholarship.
Recently I laid over at Amsterdam’s Schiphol Airport, at which the Delta Airlines security agent checked my U.S. passport prior to boarding the plane to Minneapolis. Upon seeing my name and place of birth (Bosnia and Herzegovina), he asked in Serbian if I spoke “our language.” I responded with a “yes, of course,” and he completed the rest of the security procedure in ‘our language,’ revealing that he is a Serb who escaped to the Netherlands in 1991 because he did not want to have to fight the Bosniaks (Bosnian Muslims) or the Croats, as they are all “my people, our people.” more...
Representing Mass Violence: Conflicting Responses to Human Rights Violations in Darfur
By Joachim Salvesberg
 How do interventions by the UN Security Council and the International Criminal Court influence representations of mass violence? What images arise instead from the humanitarianism and diplomacy fields? How are these competing perspectives communicated to the public via mass media? Zooming in on the case of Darfur, Joachim J. Savelsberg analyzes more than three thousand news reports and opinion pieces and interviews leading newspaper correspondents, NGO experts, and foreign ministry officials from eight countries to show the dramatic differences in the framing of mass violence around the world and across social fields.
How do interventions by the UN Security Council and the International Criminal Court influence representations of mass violence? What images arise instead from the humanitarianism and diplomacy fields? How are these competing perspectives communicated to the public via mass media? Zooming in on the case of Darfur, Joachim J. Savelsberg analyzes more than three thousand news reports and opinion pieces and interviews leading newspaper correspondents, NGO experts, and foreign ministry officials from eight countries to show the dramatic differences in the framing of mass violence around the world and across social fields.
The book is hot off the presses and is also available in its entirety online.
Professor Joachim Savelsberg is a professor of sociology at the University of Minnesota, the Arsham and Charlotte Ohanessian Chair, and affiliate faculty to the Center for Holocaust and Genocide Studies.
Wahutu Siguru sat down with Dr. Joachim Salvesberg from the University’s Sociology Department to discuss his new book, Representing Mass Violence: Conflicting Responses to Human Rights Violations in Darfur for the September edition of “Eye on Africa.”
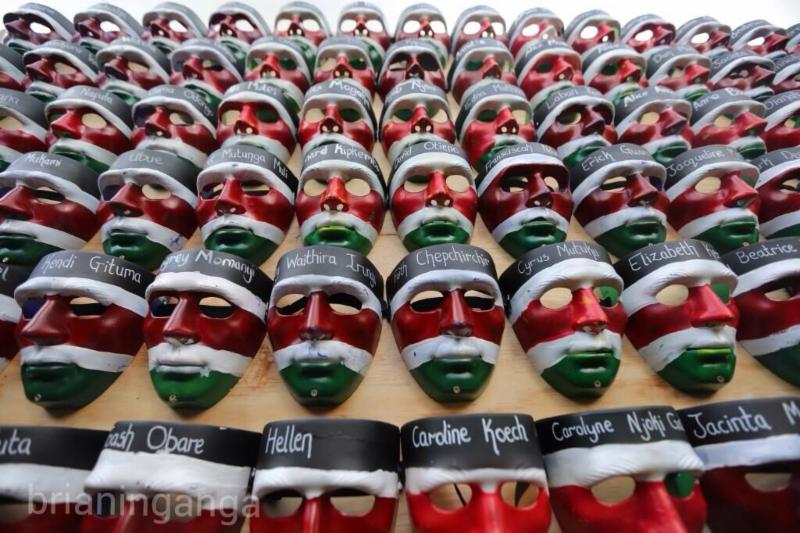 On the 2nd of April my home country, Kenya, suffered its bloodiest terrorist attack in recent history. The attack by Al-Shabaab was at a university in the town of Garissa, close to the Kenya-Somali border. While it would be tempting to rant and rave about the causes of the attack, the lapse in Kenya’s security forces, or even the almost non-existence of an official government response — not only to the attack but the victims’ and their families’ plight and suffering — I will not. Instead this month’s article is on the 147 students that died, the almost equal number of students considered missing, and the hundreds more that survived and will always have these scars.
On the 2nd of April my home country, Kenya, suffered its bloodiest terrorist attack in recent history. The attack by Al-Shabaab was at a university in the town of Garissa, close to the Kenya-Somali border. While it would be tempting to rant and rave about the causes of the attack, the lapse in Kenya’s security forces, or even the almost non-existence of an official government response — not only to the attack but the victims’ and their families’ plight and suffering — I will not. Instead this month’s article is on the 147 students that died, the almost equal number of students considered missing, and the hundreds more that survived and will always have these scars.
 Six decades after he first coined the term genocide, Raphael Lemkin’s life has made it to the silver screen. In Watchers of the Sky director Edet Belzberg takes viewers through the efforts of Lemkin to get the crime of genocide recognized by the international community and the United Nations.
Six decades after he first coined the term genocide, Raphael Lemkin’s life has made it to the silver screen. In Watchers of the Sky director Edet Belzberg takes viewers through the efforts of Lemkin to get the crime of genocide recognized by the international community and the United Nations.
Throughout the movie, activists, scholars and experts share their reflections on the legacy of Lemkin’s tireless dedication to pursuing justice for victims of atrocities around the world. Among those interviewed is Samantha Power, U.S. Ambassador to the UN and author of A Problem from Hell, which served as an inspiration for the documentary. more...
