This is the first of a two-part series dedicated to answering the question “Do we need a new World’s Fair?” It is an honest question that I do not have an answer to. What I aim to do here is share my thoughts on the subject and present historical data on what these sorts of events have done in the past. In the first part, I explore what previous World Fairs have accomplished and what we must certainly avoid. The second part will investigate what a new 21st century fair might look like, and how it would help our economy. Part 1 is here.

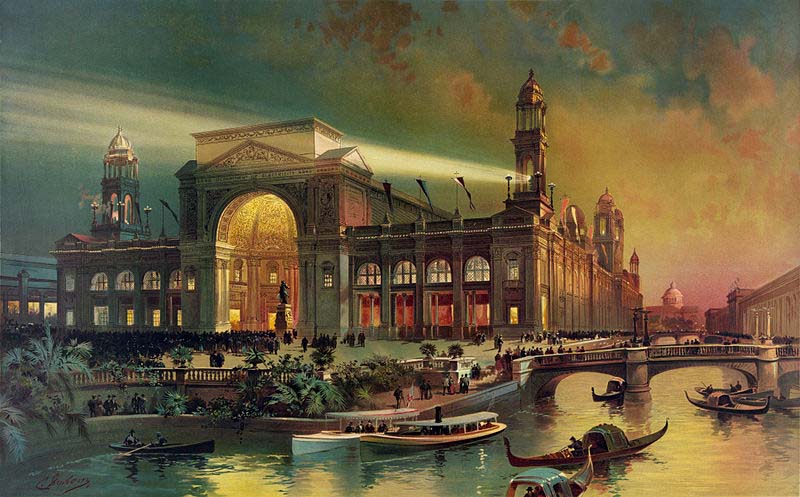
Yesterday we looked at the last few World Fairs that were held in the United States. Those 20th century fairs demonstrated technologies that today we take for granted as common-place. Everything from Juicy Fruit gum to fluorescent lighting has been introduced to the world through these massive fairs. World Expos still take place, but are now found in China, Japan and South Korea. The 2012 expo will be held in Seoul, South Korea. The latest World’s Fair, Expo 2010, was held in Shanghai, China and set historic records as the largest and most well-attended expo. But the success of the Shanghai Expo doesn’t quite translate to America’s shores. As The Atlantic’s Adam Minter wrote last year:
To American ears, the concept of a World’s Fair sounds archaic, and when applied to Shanghai, a contemporary symbol of all that is new, vibrant, and even threatening, it’s disconcerting. But in Shanghai, where the future is an obsession, this reported $46 billion hat-tip to the past makes perfect sense: just as New York once announced its global pre-eminence via World’s Fairs in 1939 and, again, in 1964, the organizers of Expo 2010 view the six month event as nothing less than Shanghai’s coronation as the next great world city. more...