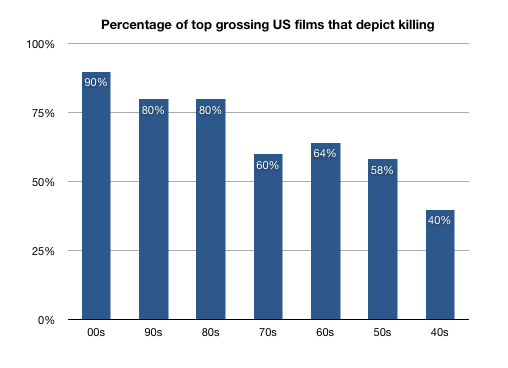
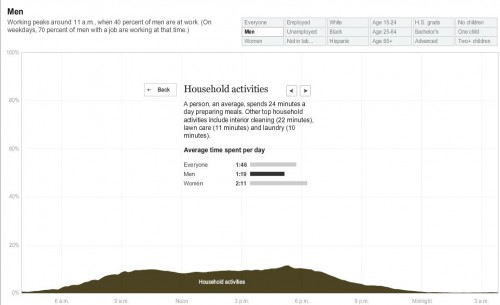
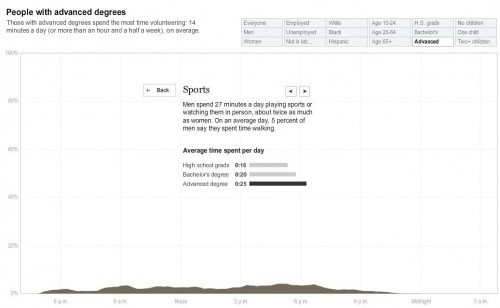
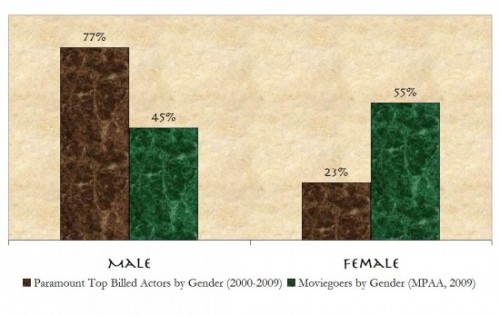
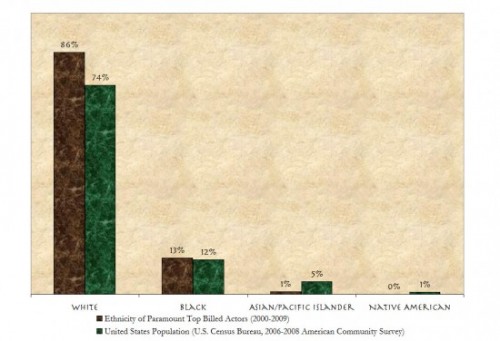
Cross-posted at Jezebel.
Alicia S. sent in an image of the poster for the movie Life as We Know It, featuring Katherine Heigl and Josh Duhamel. Heigl appears to be in her familiar role as responsible, career-oriented, but uptight and ultimately unfulfilled woman who falls for an irresponsible or immature guy. In the movie, the two main characters end up raising a child together after the death of the baby’s parents. The poster pretty much sums up the messages you’re going to get about gender:
Want more? Here’s the trailer:
So women are responsible — they can even get themselves dressed — and nurturing while men are childish boors. Alicia says,
While Heigl is presented as a warm, caring motherly figure, her male costar is likened to a baby: immature and irresponsible, just another child in the family. He reflects the stereotype represented in so many romantic comedies and Monday night sitcoms alike that men are messy, careless, and juvenile.
They’re repeatedly presented as messy, careless, and juvenile…and yet still ultimately get the mature, caring, nurturing, attractive woman.
These stereotypes are offensive to women and men. Women are supposed to settle — to fall in love with the equivalent of a child, and to find that endearing, as opposed to insulting or creepy. That means, of course, she’ll have to be primarily responsible for childcare and running the household, since you can’t trust an immature, careless person to do important things (think of every sitcom or commercial that shows a hapless man messing everything up when he’s left to care for the house on his own).
And men are depicted as ridiculous oafs. I’m always surprised that more men aren’t offended by this representation of manhood: men as incompetent pigs who treat women badly (setting up another date in front of his current one at the beginning of the trailer) who can barely take care of themselves, much less anyone else. Of course, the stereotype does have benefits from those men willing to draw on it: if you are incapable of taking care of children and doing housework without causing a major disaster, you’re relieved from those tasks, or your partner has to fight constantly to get you to do them. So while the gender stereotypes on display here are insulting to both men and women, they reinforce a gendered division of parenting labor that justifies putting the burden of that labor on women rather than men.