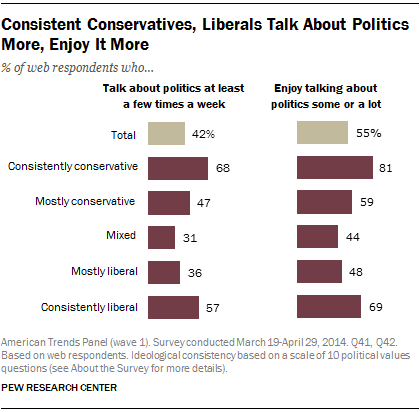
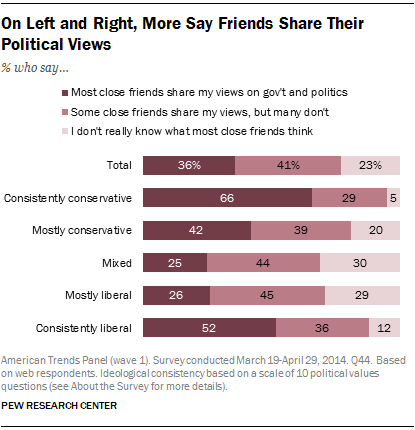
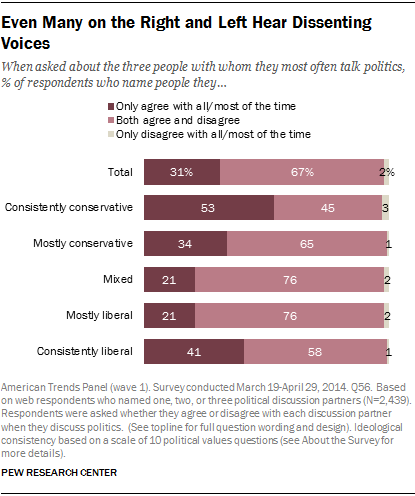
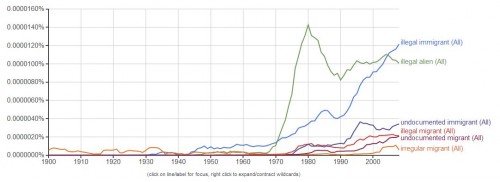
Last month the Pew Research Center released new poll data tracing the conversations Americans have with others about politics. It revealed that the people with the strongest views talk about and enjoy talking about politics the most:
In part because of differences in the importance of politics to people, the political content of friendships varies. Almost a quarter of Americans — mostly moderates — say that they “don’t really know what most [of their] close friends think” about political issues. Just over a third, however — mostly on the tails — report that their close friends agree with them.
Pew is optimistic, reporting that two-thirds of Americans do talk to people with whom they disagree, at least a little.
More from Amy Mitchell and her co-authors at the Pew Research Center.
Cross-posted at Pacific Standard.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.