Dylan Matthews, blogging in the Washington Post, discusses a very interesting paper that provides evidence showing that politicians seriously underestimate the progressivity of their constituents.
David Broockman and Christopher Skovron, the authors of the paper, “surveyed every candidate for state legislative office in the United States in 2012 [shortly before the November election] and probed candidates’ own positions and their perceptions of their constituents’ positions on universal health care, same-sex marriage, and federal welfare programs, three of the most publicly salient issues in both national-level and state-level American politics during the past several years.” They then matched the results with estimates of the actual district- and issue-specific opinions of those residing in the candidates’ districts using a data set of almost 100,000 Americans.
Here is what they found:
Politicians consistently and substantially overestimate support for conservative positions among their constituents on these issues. The differences we discover in this regard are exceptionally large among conservative politicians: across both issues we examine, conservative politicians appear to overestimate support for conservative policy views among their constituents by over 20 percentage points on average… Comparable figures for liberal politicians also show a slight conservative bias: in fact, about 70% of liberal office holders typically underestimate support for liberal positions on these issues among their constituents.
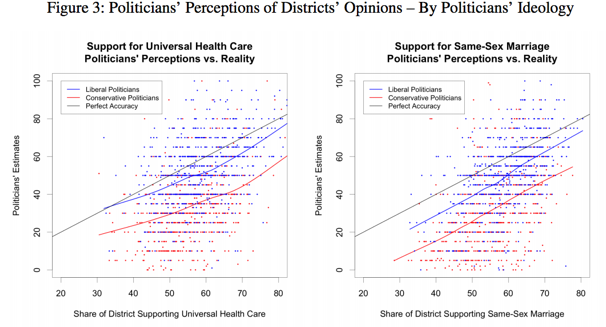
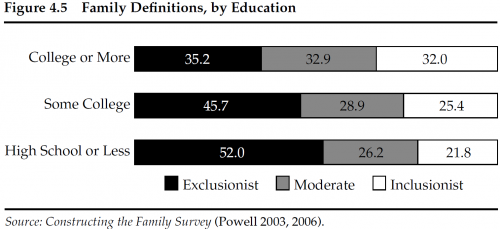
The following two charts illustrate this bias when it comes to universal health care and same sex marriage.
As Matthews explain:
The X axis is the district’s actual views, and the Y axis their legislators’ estimates of their views. The thin black line is perfect accuracy, the response you’d get from a legislator totally in tune with his constituents. Lines above it would signify the politicians think the district more liberal than it actually is; if they’re below it, that means the legislators are overestimating their constituents’ conservatism. Liberal legislators consistently overestimate opposition to same-sex marriage and universal health care, but only mildly. Conservative politicians are not even in the right ballpark.
The authors found a similar bias regarding support for welfare programs. Perhaps even more unsettling, the authors found no correlation between the amount of time candidates spent meeting and talking to people in their districts while campaigning for office and the accuracy of their perceptions of the political positions of those living in their districts.
One consequence of this disconnect is that office holders, even those with progressive views, are reluctant to take progressive positions. More generally, these results speak to a real breakdown in “the ability of constituencies to control the laws that their representatives make on their behalf.”
Martin Hart-Landsberg is a professor of economics at Lewis and Clark College. You can follow him at Reports from the Economic Front.