This is one of our favorite Christmas-themed posts from the archive. We hope you don’t mind the re-post!
White privilege refers to the many, many benefits of being white in a society dominated, both culturally and materially, by other white people. The notion was popularized by Peggy McIntosh in a 1989 an essay titled White Privilege: Unpacking the Invisible Knapsack. One benefit is that most fictional characters, unless otherwise specified (and sometimes even so), are assumed to be white. Growing up non-white in a white-dominated world, then, means that most of the mythological figures of your childhood do not look like you in one important way.
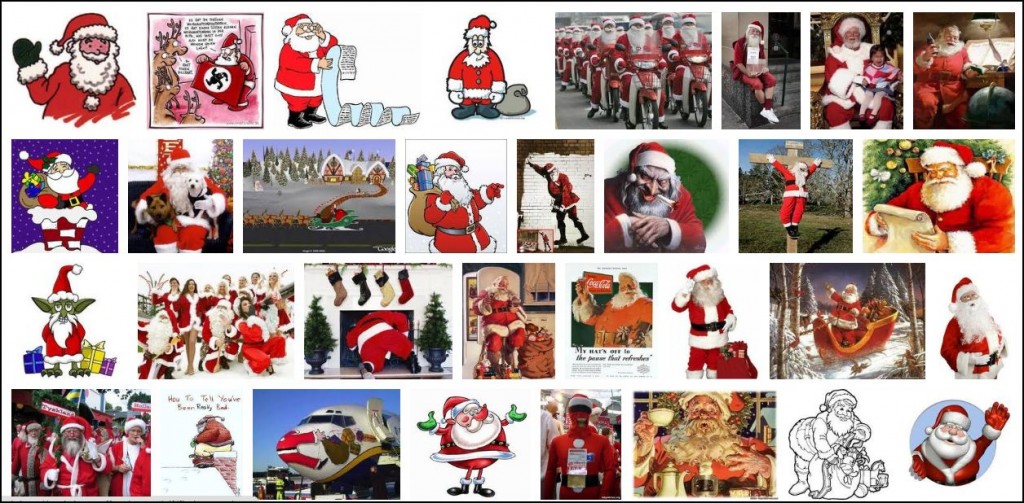
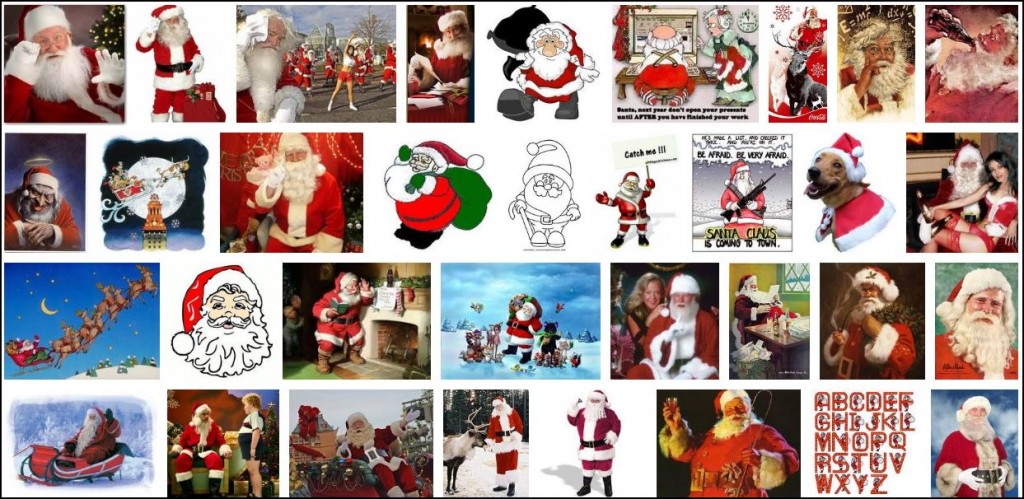
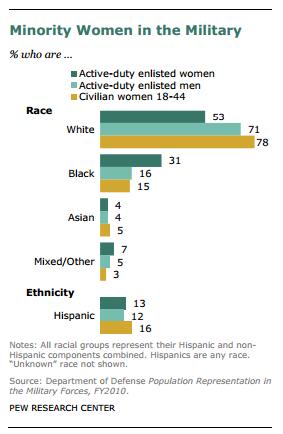
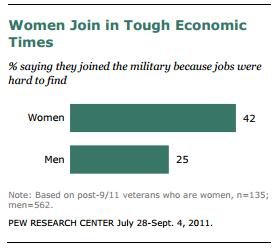
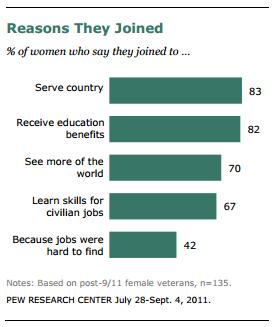
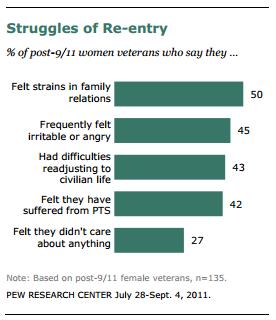
Santa, of course, is a fictional figure whose appearance is invented. Theoretically anyone could be Santa. Yet, while we may see the occasional non-white Santa at the mall or in novelty holiday stories, he is unbearably and overwhelmingly white in our (google-able) imagination: The first three pages of a google image search for “Santa”:
For more examples, see all of our posts about white privilege. Thanks for Martha Pitts as Ms. for this post idea.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.