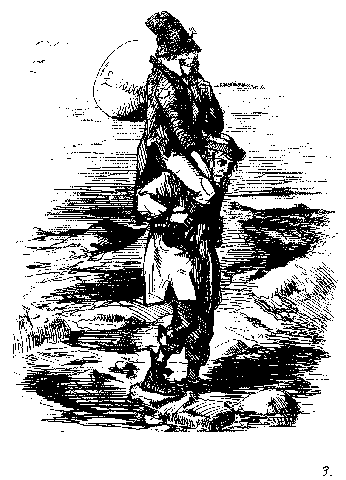
Below are two photos — one of Barack Obama as an adult and one of a young Obama and his Grandfather, Stanley Dunham (found here and here). I tried a little experiment in class. I put up the photo of adult Obama and I had my students make a list of what characteristics made him identifiably Black, in their view. Every one of them put on their list his nose, lips, and hair, and several made comments about his ears or just that “the combination of all his facial features” was “clearly” Black.
Then I brought up the photo of young Obama and his grandfather alongside it:
It led to a really interesting discussion. Because my students think of Obama as Black, they saw all his features through that racial lens. It was obvious to them that he had “Black” facial features. After viewing the photos next to one another, they talked about how the two men look very similar, but their facial features seem “clearly” Black on one person and “clearly” White on the other because we’re used to believing that Blacks and Whites look very different. Because they believe in racial differences, they see them. This activity seemed to really help students grasp what I meant when I talked about the way we identify things as racial differences when they’re really variations that occur in many different groups that we swear are physically distinct from one another.
It’s interesting because I’d halfway expected my students to argue that Obama doesn’t “really” look Black at all — that they would say his skin color and hair, perhaps, were identifiable as African American, but that they would point out that he’s half-White and argue that in fact he doesn’t have stereotypically Black or White features. I mean, that would made sense, right? But I’ve tried this with three classes now, as well as several random individuals I’ve subjected to it to see if it might work as a class activity, and no one has yet failed to identify a number of the facial features Obama and Dunham share as specifically African-American features when they see them on Obama.
What a great example of racialization and the social construction of race.
See also our Pinterest pages: what color is flesh? and the social construction of race.
Gwen Sharp is an associate professor of sociology at Nevada State College. You can follow her on Twitter at @gwensharpnv.