Dalton Conley’s newest animated video provides an overview of the social construction of race: the categories we define as race aren’t based in biology, yet they’re incredibly important factors that influence our opportunities, constraints, and life outcomes.
race/ethnicity: Blacks/Africans
Cross-posted at Racialicious.
Frances Stead Sellers at the Washington Post has a fascinating account of the differences in Black and White American sign language. Sellers profiles a 15-year-old girl named Carolyn who in 1968 was transferred from the Alabama School for the Negro Deaf and Blind to an integrated school, only to learn that she couldn’t understand much of what was being signed in class.
White American sign language used more one-handed signs, a smaller signing space, stayed generally lower, and included less repetition. Some of the signs were subtlety different, while others were significantly different.
As is typical, the White students in the class did not adapt to Carolyn’s vernacular; she had to learn theirs. So she became bilingual. Sellers explains:
She learned entirely new signs for such common nouns as “shoe” and “school.” She began to communicate words such as “why” and “don’t know” with one hand instead of two as she and her black friends had always done. She copied the white students who lowered their hands to make the signs for “what for” and “know” closer to their chins than to their foreheads. And she imitated the way white students mouthed words at the same time as they made manual signs for them.
Whenever she went home, [Carolyn] carefully switched back to her old way of communicating.
These distinctions are still present today, as are the White-centric rules that led Carolyn to adopt White sign language in school and the racism that privileges White spoken vernacular as “proper English.” For example, referring to the way she uses more space when she signs, student Dominique Flagg explains:
People sometimes think I am mad or have an attitude when I am just chatting with my friends, professors and other people.
The little girl who transferred schools and discovered that White people signed differently than her is now Dr. McCaskill, a professor of deaf studies. You can learn more about the racial politics of American sign language from her book, The Hidden Treasure of Black ASL.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
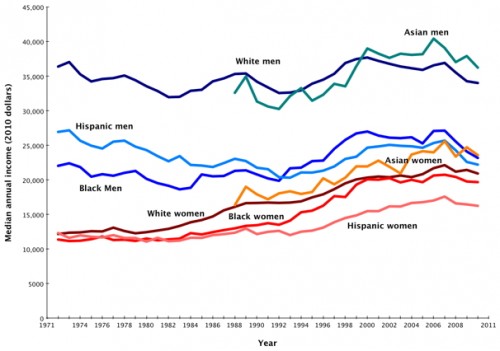
The Washington Post has a post up by Dylan Matthews that looks at the U.S. gender wage gap over time. It has several charts that illustrate trends in pay very clearly. Here’s a breakdown of median income (in constant 2010 dollars) by gender and race/ethnicity, for all workers, both full- and part-time:
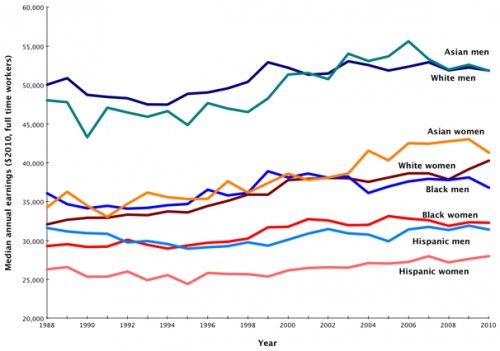
The gap remains for full-time, year-round workers, too. Women have gained ground, but within every racial/ethnic category, women’s median income is lower than men’s and every other group earns significantly less than Asian and White men. However, there’s a clear racial earnings hierarchy visible in the chart as well, which isn’t getting nearly the attention that the gender wage gap is:
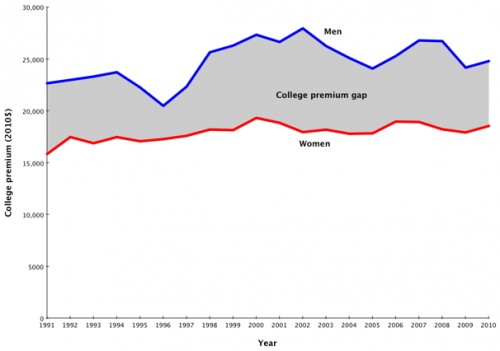
Moreover, the income bump received from earning a college degree is still higher for men than for women:
There are additional charts further breaking down differences in pay among men and women in the original post. As Matthews argues, and as Philip Cohen has posted about here at Soc Images, the data just don’t support the “impending female economic dominance” narrative that has become popular recently.
As we enter the home stretch of the presidential campaign, there’s a steady stream of media discussions of potential turnout and differences in early voters and those who vote on Election Day, analysis of the demographics of swing states, and a flood of campaign materials and phone calls aimed at both winning us over and convincing us to actually go vote (those of you not living in swing states may be blessed with less of this).
So who does vote? And how many of us do so?
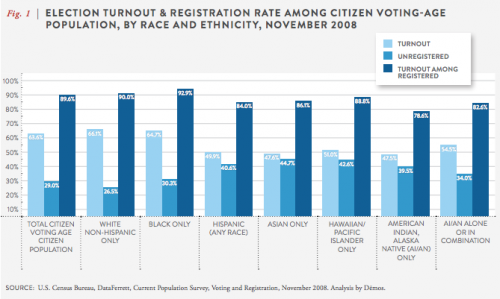
Demos.org recently released a report on voting rates and access among Native Americans. It contains a breakdown of voting and voter registration by race/ethnicity for the 2008 presidential election. That year, about 64% of all adults eligible to vote in the U.S. did so, but the rates varied widely by group. White non-Hispanics and African Americans had the highest turnout, with every other group having significantly less likely to vote. Half or less of Asians, American Indians/Alaska Natives, and Hispanics voted:
For every group, the vast majority of those who register do go on to vote. But significant numbers of people who have the right to vote aren’t registered to do so, and even among registered voters (the darkest blue columns), turnout is higher among White non-Hispanics and African Americans than other groups. This could reflect lack of interest in or enthusiasm for the election or the candidates, but likely also reflects structural and organizational differences, from poverty to the lack of concerted efforts by campaigns to make voting easier by providing shuttles to the polls and otherwise getting out the vote in these communities.
Though laws varied, American slaves generally could not legally marry. They were the subject of contracts, legally barred from entering into contracts themselves. And while some enslavers encouraged their slaves to form romantic relationships because such relationships discouraged running away, slave families were always at risk of being torn apart at the whims of the “master.”
On this day in 1863, Abraham Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation, an executive order that ended slavery for all people in territories that were under Union control. Two years later, the Thirteenth Amendment amended the constitution to prohibit slavery. The next year, two newly-freed now ex-slaves, Thomas and Jane Taylor, were married in Kentucky.
Text:
This day came before me Thomas Taylor and Jane, his wife, persons of color and servants of Christian County and declared that they have been and still aim to continue living together as husband and wife. Given under my hand this 27th day of July 1866.
G.W. Lawson, Clerk
Geo. C. Long, D.C.
Thomas and Jane are the great-great-great-grandparents of Tami, who blogs at What Tami Said. They had been together for many years before they were given the opportunity to marry and had two children. According to Dr. Tera Hunter at NPR, they were one of many newly-freed couples to marry in the years after the abolishment of slavery extended them the right. By 1900, she explains, marriage would be “nearly universal” among American blacks.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
Cross-posted at Reports from the Economic Front.
Politicians always seem to be talking about the middle class. They need some new focus groups. According to the Pew Research Center, over the past four years the percentage of adult Americans that say they are in the lower class has risen significantly, from a quarter to almost one-third (see chart below).
Pew also found that the demographic profile of the self-defined lower class has also changed. Young people, according to Pew, “are disproportionately swelling the ranks of the self-defined lower classes.” More specifically some 40% of those between 18 to 29 years of age now identify as being in the lower classs compared to only 25% in 2008.
Strikingly, the percentage of whites and blacks that see themselves in the lower class is now basically equal. The percentage of whites who consider themselves in the lower class rose from less than a quarter in 2008 to 31% in 2012. This brought them in line with blacks, whose percentage remained at a third. The percentage of Latinos describing themselves as lower class rose to 40%, a ten percentage point increase from 2008.
And not surprisingly, as the chart below shows, many who self-identify as being in the lower class are experiencing great hardships. In fact, 1 in 3 faced four or all five of the problems addressed in the survey.
In short, there is a lot of hurting in our economy.
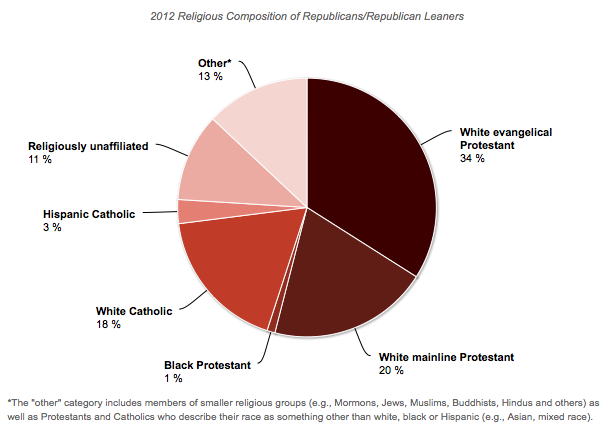
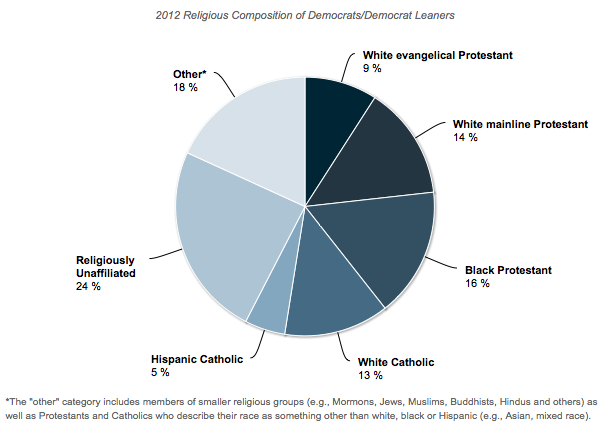
Peter N. sent in some data compiled by Chris Cillizza of the Washington Post. It reveals the intersection of race and religion among Democrats and Republicans. As Cillizza concludes, it’s “overblown” to say that the Republican party is made up of White Protestants and the Democratic of minorities and atheists, but there is definitely an argument to be made that each party is disproportionately so.
This first pie chart shows the racial and religious affiliation of people who identify with or lean towards the Republican party. More than half are White Protestants, another 18% are White Catholics. Only a small percentage of party faithfuls are religious Blacks and Hispanics (the two racial groups featured in in these data).
This second chart shows the same data for Democrats and Democratic-leaning individuals. Almost a quarter of Democrats are White Protestants, but a slightly larger percentage of Democrats are religiously unaffiliated. One in five Democrats identifies as either Black or Hispanic and religious. The larger “other” category conceals smaller blocs that nonetheless add diversity to the party.
This is just one way to slice the pie, so to speak, but these are the kinds of data that both the Obama and the Romney campaigns are working with. When they aim to bring out their “base,” this is what they’re talking about. These numbers may give us a clue as to why they pick the strategies they do, such as the sudden spike in the inclusion of the word “God” in the Republican party platform.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
The September issue of Oprah’s magazine, sent in by YetAnotherGirl, features the woman herself on the cover wearing her hair in a “natural” (that is, real and non-straightened). The O website announces that this is the first time in its 12-year history that Oprah has appeared on the cover without “blow-drying or straightening” her hair.
Black women’s hair is a touchy issue wrapped up deeply in racial power struggles. The appearance of White people — in this case, the hair White people are more likely to have (that is, straight or slightly wavy) — is often considered the most beautiful or normal. Black women who have tightly curled hair are faced with deciding to push back against white supremacy and wear their hair more-0r-less naturally (and face being seen as a “political” or “non-assimilating” Black person) or straighten their hair (and risk being accused of capitulating to racism). Whatever they do, it’s sends a message.
What I think is notable here is that Oprah, of all people in the world, has never until now appeared on the cover of her own magazine with “natural” hair. Lest we’ve forgotten who Oprah is, here’s a reminder (from wikipedia):
Winfrey was called “arguably the world’s most powerful woman” by CNN and Time.com, “arguably the most influential woman in the world” by the American Spectator, “one of the 100 people who most influenced the 20th Century” and “one of the most influential people” from 2004 to 2011 by TIME. Winfrey is the only person in the world to have appeared in the latter list on all eight occasions.
What I mean to say is, when even Oprah largely avoids being seen as she really is, we know we are seeing a powerful cultural force. In this case, a racist and sexist one demanding that women of all races conform to an unreasonable White standard of beauty. I’m glad that Oprah decided to appear this way for the cover, but I’m saddened by why it took this long.
Via Jezebel.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
Cross-posted at Racialicious.
Frances Stead Sellers at the Washington Post has a fascinating account of the differences in Black and White American sign language. Sellers profiles a 15-year-old girl named Carolyn who in 1968 was transferred from the Alabama School for the Negro Deaf and Blind to an integrated school, only to learn that she couldn’t understand much of what was being signed in class.
White American sign language used more one-handed signs, a smaller signing space, stayed generally lower, and included less repetition. Some of the signs were subtlety different, while others were significantly different.
As is typical, the White students in the class did not adapt to Carolyn’s vernacular; she had to learn theirs. So she became bilingual. Sellers explains:
She learned entirely new signs for such common nouns as “shoe” and “school.” She began to communicate words such as “why” and “don’t know” with one hand instead of two as she and her black friends had always done. She copied the white students who lowered their hands to make the signs for “what for” and “know” closer to their chins than to their foreheads. And she imitated the way white students mouthed words at the same time as they made manual signs for them.
Whenever she went home, [Carolyn] carefully switched back to her old way of communicating.
These distinctions are still present today, as are the White-centric rules that led Carolyn to adopt White sign language in school and the racism that privileges White spoken vernacular as “proper English.” For example, referring to the way she uses more space when she signs, student Dominique Flagg explains:
People sometimes think I am mad or have an attitude when I am just chatting with my friends, professors and other people.
The little girl who transferred schools and discovered that White people signed differently than her is now Dr. McCaskill, a professor of deaf studies. You can learn more about the racial politics of American sign language from her book, The Hidden Treasure of Black ASL.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
The Washington Post has a post up by Dylan Matthews that looks at the U.S. gender wage gap over time. It has several charts that illustrate trends in pay very clearly. Here’s a breakdown of median income (in constant 2010 dollars) by gender and race/ethnicity, for all workers, both full- and part-time:
The gap remains for full-time, year-round workers, too. Women have gained ground, but within every racial/ethnic category, women’s median income is lower than men’s and every other group earns significantly less than Asian and White men. However, there’s a clear racial earnings hierarchy visible in the chart as well, which isn’t getting nearly the attention that the gender wage gap is:
Moreover, the income bump received from earning a college degree is still higher for men than for women:
There are additional charts further breaking down differences in pay among men and women in the original post. As Matthews argues, and as Philip Cohen has posted about here at Soc Images, the data just don’t support the “impending female economic dominance” narrative that has become popular recently.
As we enter the home stretch of the presidential campaign, there’s a steady stream of media discussions of potential turnout and differences in early voters and those who vote on Election Day, analysis of the demographics of swing states, and a flood of campaign materials and phone calls aimed at both winning us over and convincing us to actually go vote (those of you not living in swing states may be blessed with less of this).
So who does vote? And how many of us do so?
Demos.org recently released a report on voting rates and access among Native Americans. It contains a breakdown of voting and voter registration by race/ethnicity for the 2008 presidential election. That year, about 64% of all adults eligible to vote in the U.S. did so, but the rates varied widely by group. White non-Hispanics and African Americans had the highest turnout, with every other group having significantly less likely to vote. Half or less of Asians, American Indians/Alaska Natives, and Hispanics voted:
For every group, the vast majority of those who register do go on to vote. But significant numbers of people who have the right to vote aren’t registered to do so, and even among registered voters (the darkest blue columns), turnout is higher among White non-Hispanics and African Americans than other groups. This could reflect lack of interest in or enthusiasm for the election or the candidates, but likely also reflects structural and organizational differences, from poverty to the lack of concerted efforts by campaigns to make voting easier by providing shuttles to the polls and otherwise getting out the vote in these communities.
Though laws varied, American slaves generally could not legally marry. They were the subject of contracts, legally barred from entering into contracts themselves. And while some enslavers encouraged their slaves to form romantic relationships because such relationships discouraged running away, slave families were always at risk of being torn apart at the whims of the “master.”
On this day in 1863, Abraham Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation, an executive order that ended slavery for all people in territories that were under Union control. Two years later, the Thirteenth Amendment amended the constitution to prohibit slavery. The next year, two newly-freed now ex-slaves, Thomas and Jane Taylor, were married in Kentucky.
Text:
This day came before me Thomas Taylor and Jane, his wife, persons of color and servants of Christian County and declared that they have been and still aim to continue living together as husband and wife. Given under my hand this 27th day of July 1866.
G.W. Lawson, Clerk
Geo. C. Long, D.C.
Thomas and Jane are the great-great-great-grandparents of Tami, who blogs at What Tami Said. They had been together for many years before they were given the opportunity to marry and had two children. According to Dr. Tera Hunter at NPR, they were one of many newly-freed couples to marry in the years after the abolishment of slavery extended them the right. By 1900, she explains, marriage would be “nearly universal” among American blacks.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
Cross-posted at Reports from the Economic Front.
Politicians always seem to be talking about the middle class. They need some new focus groups. According to the Pew Research Center, over the past four years the percentage of adult Americans that say they are in the lower class has risen significantly, from a quarter to almost one-third (see chart below).
Pew also found that the demographic profile of the self-defined lower class has also changed. Young people, according to Pew, “are disproportionately swelling the ranks of the self-defined lower classes.” More specifically some 40% of those between 18 to 29 years of age now identify as being in the lower classs compared to only 25% in 2008.
Strikingly, the percentage of whites and blacks that see themselves in the lower class is now basically equal. The percentage of whites who consider themselves in the lower class rose from less than a quarter in 2008 to 31% in 2012. This brought them in line with blacks, whose percentage remained at a third. The percentage of Latinos describing themselves as lower class rose to 40%, a ten percentage point increase from 2008.
And not surprisingly, as the chart below shows, many who self-identify as being in the lower class are experiencing great hardships. In fact, 1 in 3 faced four or all five of the problems addressed in the survey.
In short, there is a lot of hurting in our economy.
Peter N. sent in some data compiled by Chris Cillizza of the Washington Post. It reveals the intersection of race and religion among Democrats and Republicans. As Cillizza concludes, it’s “overblown” to say that the Republican party is made up of White Protestants and the Democratic of minorities and atheists, but there is definitely an argument to be made that each party is disproportionately so.
This first pie chart shows the racial and religious affiliation of people who identify with or lean towards the Republican party. More than half are White Protestants, another 18% are White Catholics. Only a small percentage of party faithfuls are religious Blacks and Hispanics (the two racial groups featured in in these data).
This second chart shows the same data for Democrats and Democratic-leaning individuals. Almost a quarter of Democrats are White Protestants, but a slightly larger percentage of Democrats are religiously unaffiliated. One in five Democrats identifies as either Black or Hispanic and religious. The larger “other” category conceals smaller blocs that nonetheless add diversity to the party.
This is just one way to slice the pie, so to speak, but these are the kinds of data that both the Obama and the Romney campaigns are working with. When they aim to bring out their “base,” this is what they’re talking about. These numbers may give us a clue as to why they pick the strategies they do, such as the sudden spike in the inclusion of the word “God” in the Republican party platform.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.
The September issue of Oprah’s magazine, sent in by YetAnotherGirl, features the woman herself on the cover wearing her hair in a “natural” (that is, real and non-straightened). The O website announces that this is the first time in its 12-year history that Oprah has appeared on the cover without “blow-drying or straightening” her hair.
Black women’s hair is a touchy issue wrapped up deeply in racial power struggles. The appearance of White people — in this case, the hair White people are more likely to have (that is, straight or slightly wavy) — is often considered the most beautiful or normal. Black women who have tightly curled hair are faced with deciding to push back against white supremacy and wear their hair more-0r-less naturally (and face being seen as a “political” or “non-assimilating” Black person) or straighten their hair (and risk being accused of capitulating to racism). Whatever they do, it’s sends a message.
What I think is notable here is that Oprah, of all people in the world, has never until now appeared on the cover of her own magazine with “natural” hair. Lest we’ve forgotten who Oprah is, here’s a reminder (from wikipedia):
Winfrey was called “arguably the world’s most powerful woman” by CNN and Time.com, “arguably the most influential woman in the world” by the American Spectator, “one of the 100 people who most influenced the 20th Century” and “one of the most influential people” from 2004 to 2011 by TIME. Winfrey is the only person in the world to have appeared in the latter list on all eight occasions.
What I mean to say is, when even Oprah largely avoids being seen as she really is, we know we are seeing a powerful cultural force. In this case, a racist and sexist one demanding that women of all races conform to an unreasonable White standard of beauty. I’m glad that Oprah decided to appear this way for the cover, but I’m saddened by why it took this long.
Via Jezebel.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.