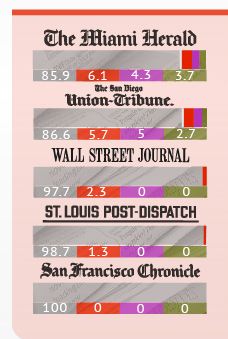
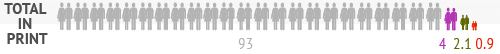
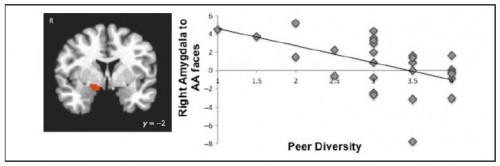
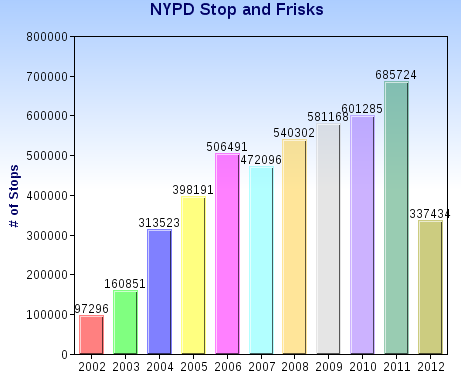
At the Washington Post, John Cohen and Rosalind Helderman report:
The 2012 election is shaping up to be more polarized along racial lines than any presidential contest since 1988, with President Obama experiencing a steep drop
in support among white voters from four years ago.
They compare data from a recent poll with exit interviews from 2004 and 2008. The results show that, while Obama is overwhelmingly the favorite among non-whites, he trails him among whites by 23 percentage points.
Cohen and Helderman say that Obama has lost support among whites even just recently. Meanwhile, a whopping 91% of Romney supporters are believed to be white. We are, truly, a deeply divided nation.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.