In capitalism, owners of the “means of production” (things like land, factories, technologies, and natural resources, or the money to buy these things) employ labor to do the work of actually producing things. If the system is working correctly, the value of the labor that goes into making something is worth less than the value of the thing. This way the capitalist can sell the thing, pay the worker, and skim some profit off the top.
But how much profit? In a less exploitative system, the worker is paid close to what his work is worth (after accounting for the expenses of maintaining the means of production). In a more exploitative system, the capitalist takes a larger chunk of the enhanced value for himself and gives less to the worker.
What kind of system do we have in the U.S.? Let’s take a look at some data.
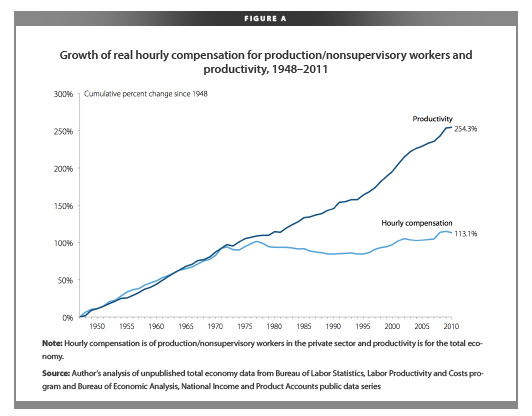
Over at Reports from the Economic Front, Martin Hart-Landsberg posted this graph. It shows that workers have become increasingly productive since 1948 (i.e., they have created more and more surplus value). Employers largely shared the increase in profitability with their workers… until the mid-1970s. Since then, wages have remained stagnant even as worker productivity has continued to rise. “In other words,” Hart-Landsberg writes, “the owners of the means of production have basically stopped sharing gains in output with their workers.”
You wonder why the middle class is shrinking? This is one reason.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.