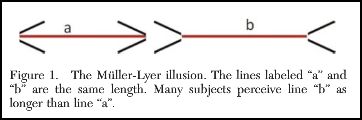
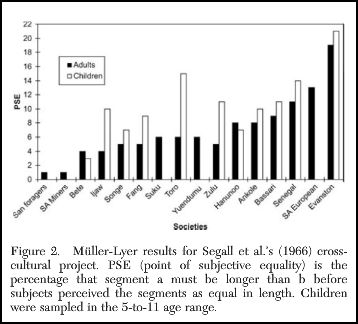
How does the U.S. compare to other developed countries on measures of social justice? According to the New York Times, not very well. The visual below compares countries’ poverty rates, poverty prevention measures, income inequality, spending on pre-primary education, and citizen health. The “overall” rating is on the far left and the U.S. ranks 27th out of 31.
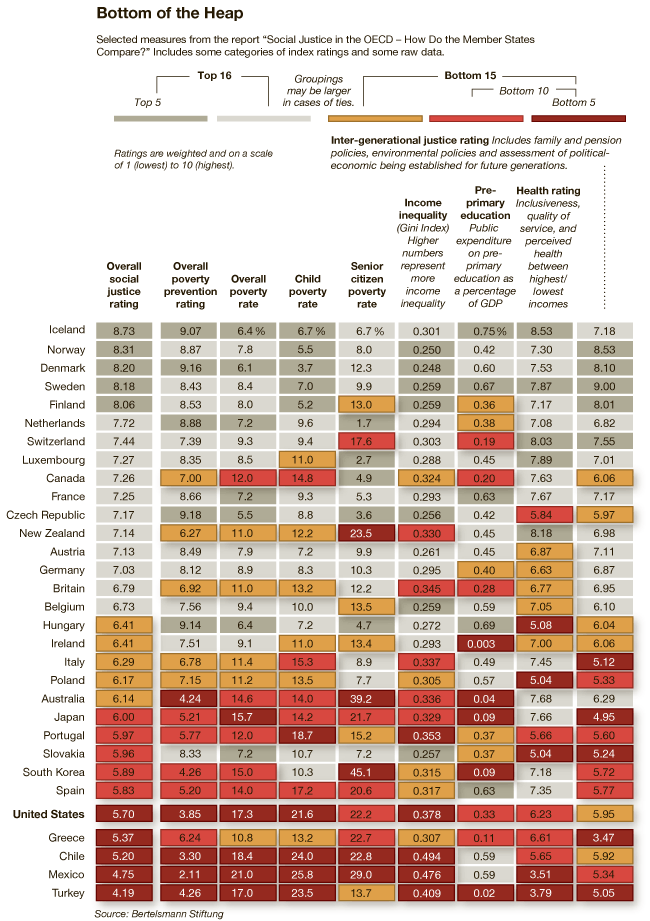
Via Feministing. See also how the U.S. ranks on measures of equality and prosperity(33 out of 33, for what it’s worth). Thanks to Dolores R. for the link!
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.