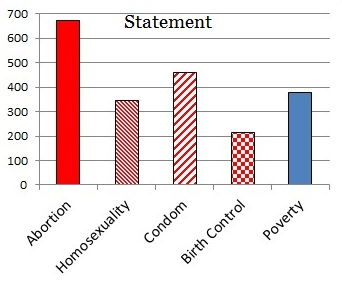
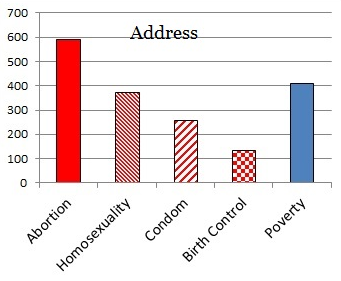
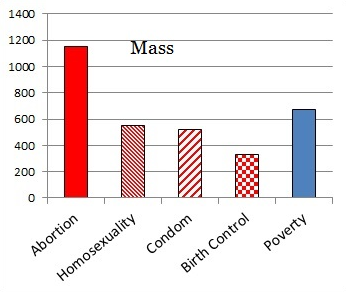
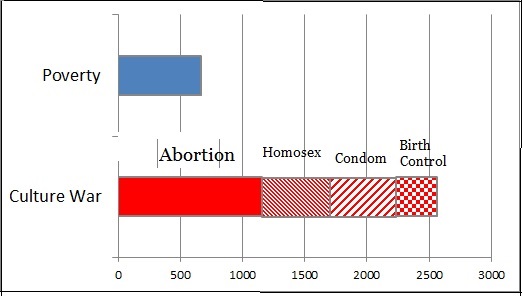
Jennifer Pozner, Kat Lazo, Zerlina Maxwell, and Samhita Mukhopadhyay join Jay Smooth to discuss a few no-nos for the media this campaign season. Pozner sums it up:
Look, this matters. By focusing on personal, gendered, irrelevant details about women politicians, this conditions the American public to think that woman are ladies first [and] leaders only a distant second. Media play a serious role in keeping half the population out of the political talent pool.
Enjoy:
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.