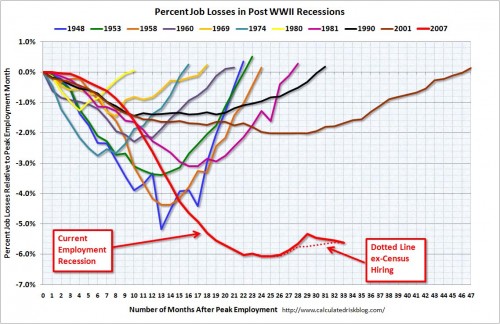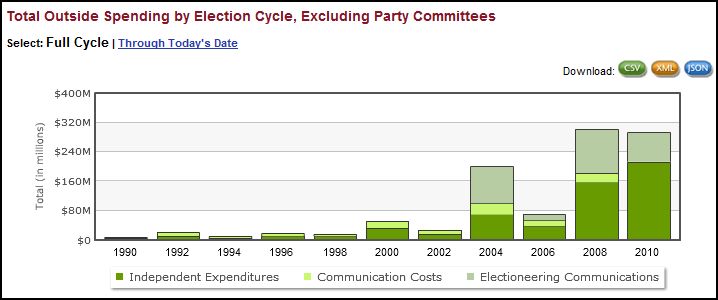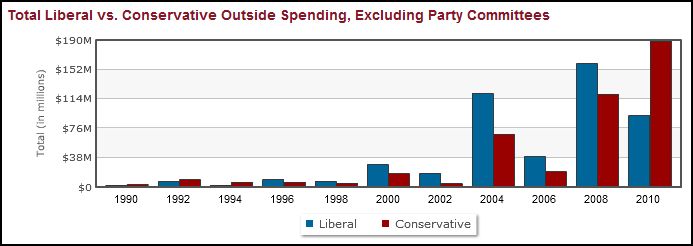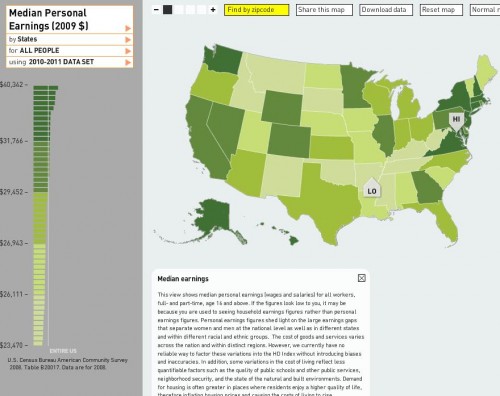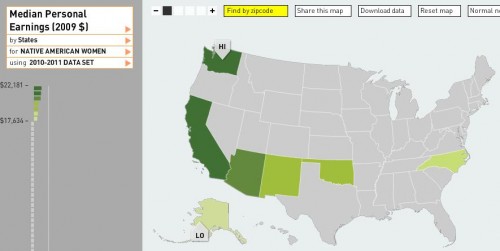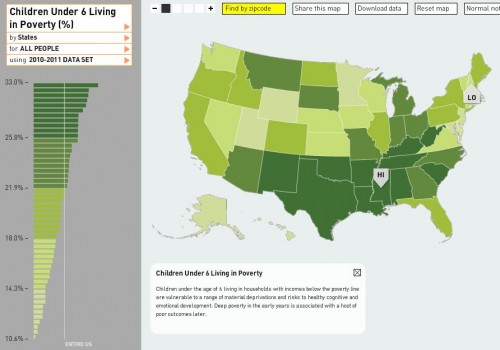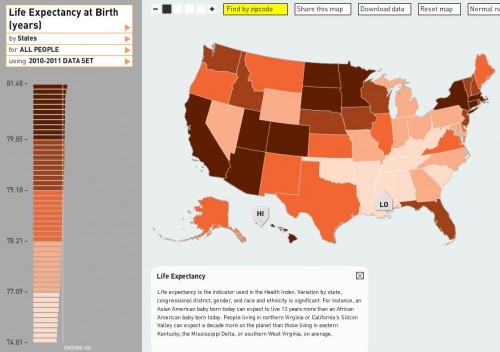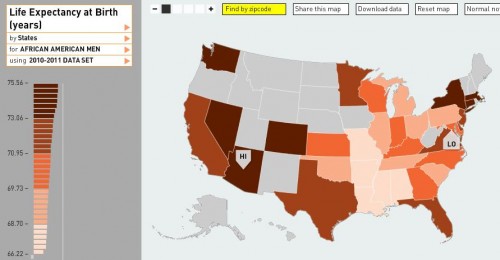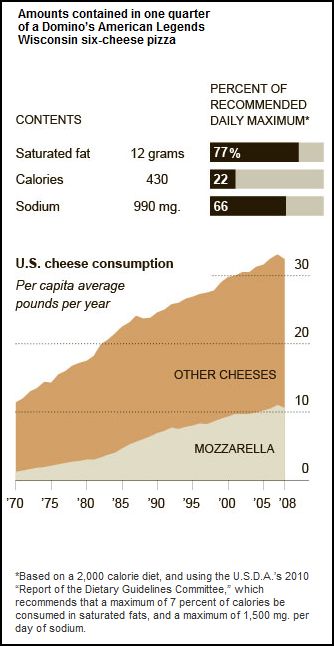
Annie Leonard tackles e-waste (what happens after we’re done with our computers, cell phones, etc) in the latest 7-minute edition in her Story of Stuff series (see also her first story of stuff and her analysis of bottled water and cap and trade).
Via Reports from the Economic Front.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.