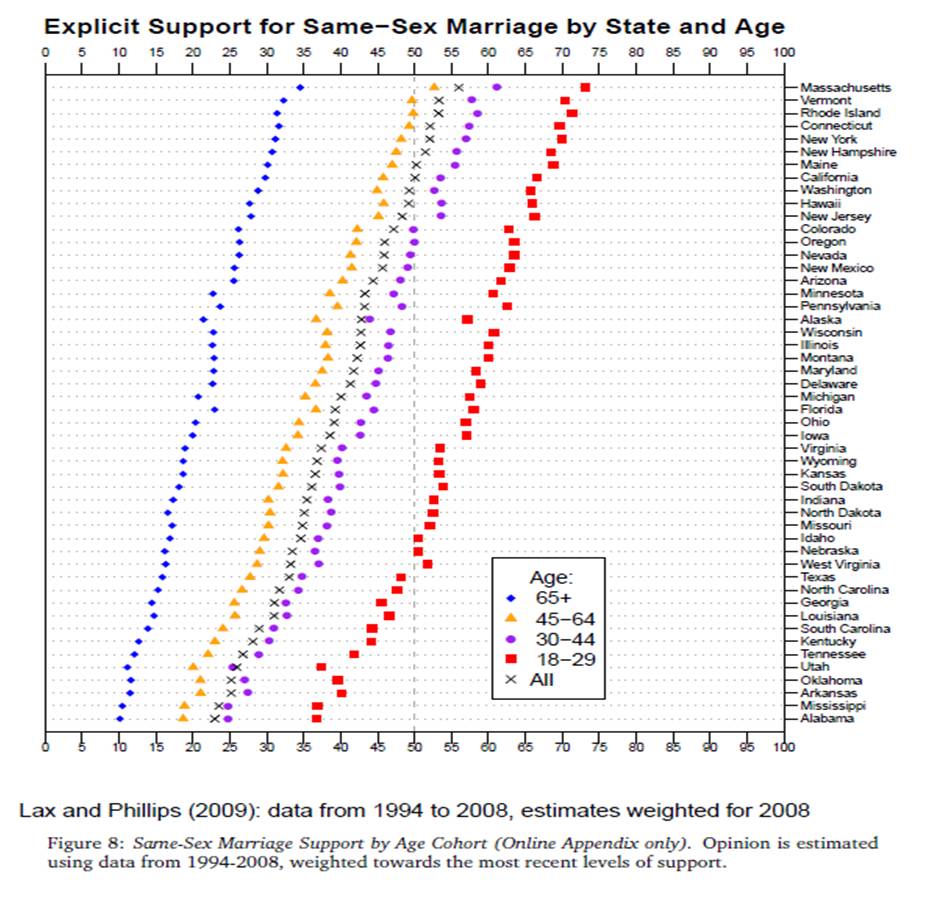
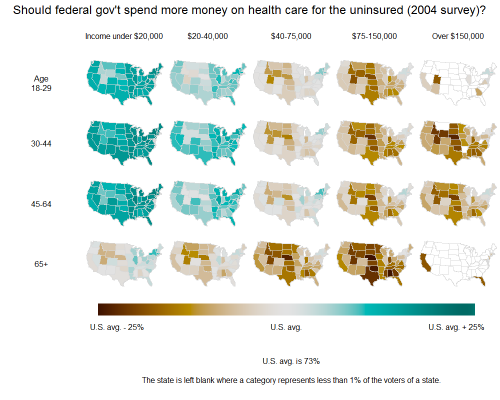
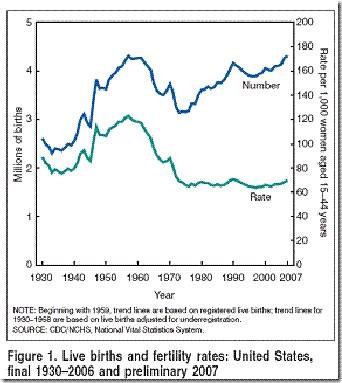
Flowing Data presented a number of figures revealing data about life expectancy (via). It is well known that women live longer than men in Western countries (to age 81 versus age 76), but this graph, displaying the probability of dying in any given year, caught my eye:
Men have a higher probability of dying than women in any given year starting (it looks like) at about age 55. It’s a small difference (maybe 5 percentage points at its largest), but over time it adds up. Until about age 112, when men and women die at the same rates.
Awesomely, even at 119, your chance of dying in the next year isn’t quite 100%. And that goes for men and women alike.
Also interesting, life expectancy by state:
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.