Way back in 1978, Mark Fishman wrote an article titled “Crime Waves as Ideology.” It referred to the way in which TV news gets organized thematically in ways that make non-trends appear to be trends. Fishman pointed out that the news directors can unwittingly create media crime waves — sudden increases in the number of stories even as the the actual number of crimes remains unchanged. Once the theme is established, it’s just a matter of combing the city or the entire country for incidents that fit. Today we’re so used to it that when we watch the local news at eleven, we barely notice.
Now, thanks to hyperlinks, online news can do the same thematic grouping. Consider: on a recent Sunday, both New York tabloids put the same story on page one — the stabbing death of a woman and four children in their apartment in Sunset Park, Brooklyn.
Early word from the police was that “it’s looking a domestic violence case.” Apparently the killer knew the victims and may have been a relative.
What caught my attention was the “related” story that the Daily News linked to on its website version of the story. What kind of story might be related? A story about the family? About difficulties faced by Chinese immigrants or conflicts within an immigrant community? About mental illness and violence? About ethnic and demographic changes in Sunset Park? No. None of the above. The related story is actually an entirely unrelated story.
The story the Daily News chose as “related” concerns the “Green Gang goon who was caught on video slugging a female New England Patriots fan in the face after the Jets’ upset victory” a week earlier. It turns out that in a fight twenty years ago, when he was 17, he fatally stabbed another kid. He served three years.
How are these two stories related? There is no connection between the two killers or their victims. The incidents are separated by two decades. The motives and circumstances are entirely different. If the Jets fan had not been caught on camera punching the female Patriots fan, no journalist following the Sunday killing would have dug up information on this crime of twenty years ago in an attempt to elaborate on the Sunset Park killings. Knowing about that “related” crime gives us no better understanding of Sunday’s stabbing.
Instead, the two stories are related by a common theme — they are both about killing where the weapon is a knife. The Daily News seems to be taking a page from Amazon’s marketing strategy. “Readers who liked this story also liked . . .” or Netflix recommendations. Television news often groups stories thematically. A story about a commercial arson in one part of town will be followed by a story about an accidental fire in a house in a distant neighborhood. The circumstances, location, and causes of the two fires are completely different, and if the big fire had not occurred, that house fire might not have been newsworthy. But that night, it fit with the fire theme.
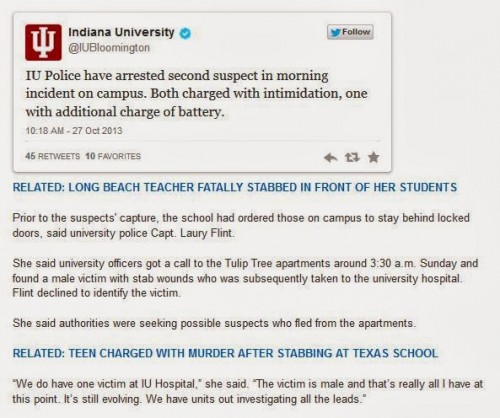
Here is another example in a screengrab from the Daily News website:
A stabbing at the University of Indiana. The related stories are a stabbing death of a teacher in Long Beach, California and of a teacher in a Texas high school.
So, students stabbing people at schools — is that a real trend? Probably not, but it is a news theme.
Cross-posted at Montclair Socioblog.
Jay Livingston is the chair of the Sociology Department at Montclair State University. You can follow him at Montclair SocioBlog or on Twitter.