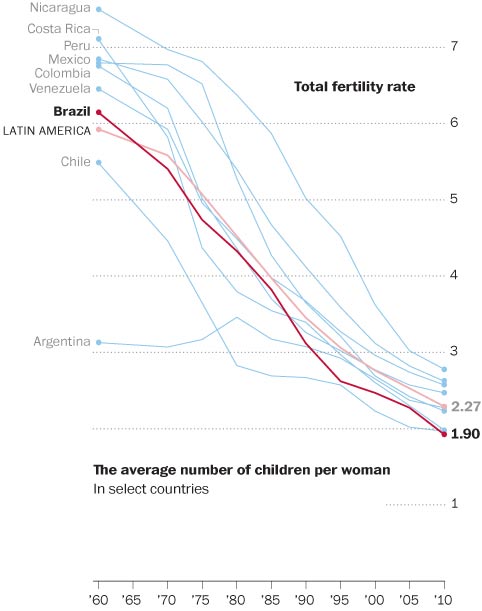
This photograph is of the Love Canal neighborhood in Niagara Falls, New York, where Hooker Chemical (now Occidental Petroleum Corporation) buried 21,000 tons of toxic, chemical waste:
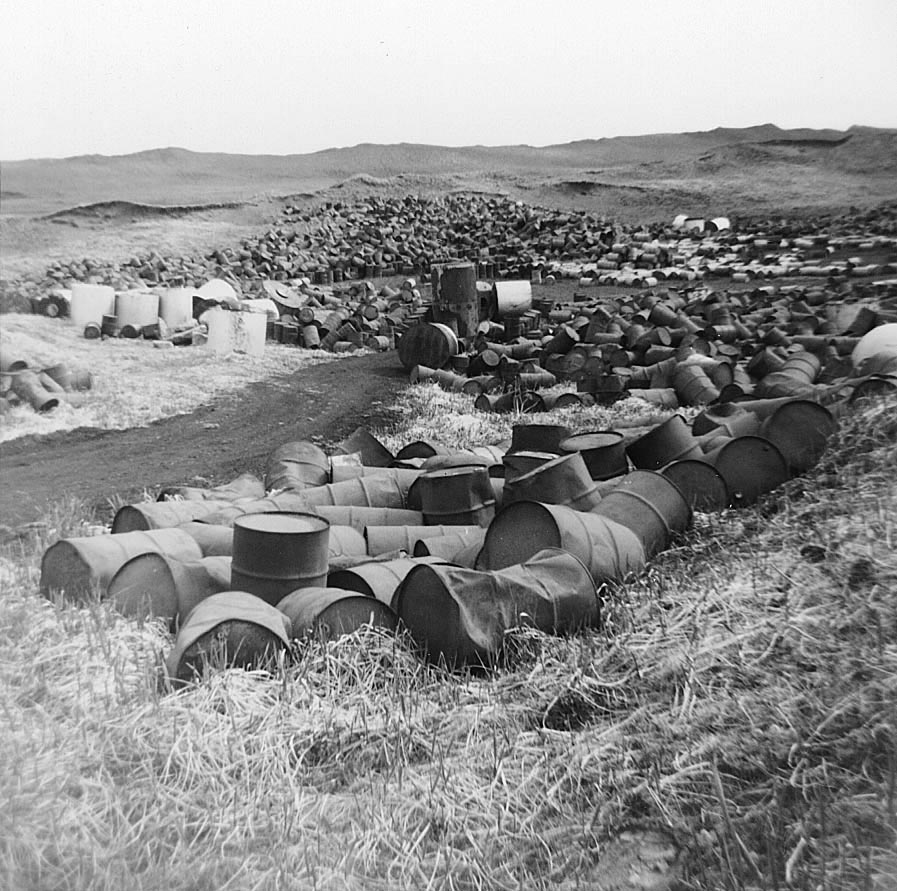 In 1953, Hooker Chemical sold the land that they had been using for toxic waste disposal to the Niagara Falls School Board for $1. The sale deed contained warnings about the chemical waste and a disclaimer of liability. However, planners hastily built schools and homes on the contaminated land to accommodate the city’s growing postwar population. By the late 1970s, residents were reporting a litany of illnesses and birth defects. Scientists discovered high levels of carcinogens in the soil, groundwater, and air. The community mobilized to bring attention to the situation, and President Carter declared a federal health emergency in the area.
In 1953, Hooker Chemical sold the land that they had been using for toxic waste disposal to the Niagara Falls School Board for $1. The sale deed contained warnings about the chemical waste and a disclaimer of liability. However, planners hastily built schools and homes on the contaminated land to accommodate the city’s growing postwar population. By the late 1970s, residents were reporting a litany of illnesses and birth defects. Scientists discovered high levels of carcinogens in the soil, groundwater, and air. The community mobilized to bring attention to the situation, and President Carter declared a federal health emergency in the area.
 Elizabeth Blum, a professor of history at Troy University, has written about the environmental activism of Love Canal residents. Such activism, called “popular epidemiology,” attempts to link spikes in localized health issues to their origins. Despite such grassroots movements, though, the media tends to show little interest in the causes of cancer and greater interest in finding the cure.
Elizabeth Blum, a professor of history at Troy University, has written about the environmental activism of Love Canal residents. Such activism, called “popular epidemiology,” attempts to link spikes in localized health issues to their origins. Despite such grassroots movements, though, the media tends to show little interest in the causes of cancer and greater interest in finding the cure.
The many “Stand Up to Cancer” ads, for example, urge people to donate money (or just use their credit card for purchases) to help fund the development of cancer treatments:
When media attention is focused on the causes of cancer, it usually takes an individualistic tone. Risk factors (smoking, poor diet, etc.) are blamed for various forms of cancer.
The thing is: there’s no money in prevention.
Mainstream media outlets have a vested interest in not exposing the causes of cancer. The companies that pay to advertise on their channels, and often their parent companies or subsidiaries, often traffic in known carcinogens. Pharmaceutical companies, likewise, have a perverse incentive. Healthy people make them no money, neither do dead people; sick people though, they’re a goldmine. Many organizations, including the multi-million dollar Susan G. Komen Foundation, are in the business of raising money “for the cure,” more so than prevention.
The politics of cancer, then suffer from the individualism characteristic of modern American and capitalist imperatives, leaving the causes of the cancer epidemic invisible and, accordingly, the unethical and illegal behavior of companies like Hooker Chemical.
Dan Rose is an assistant professor of sociology at Chattanooga State Community College in Tennessee. His research focuses on medical sociology and health inequalities in minority neighborhoods.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.