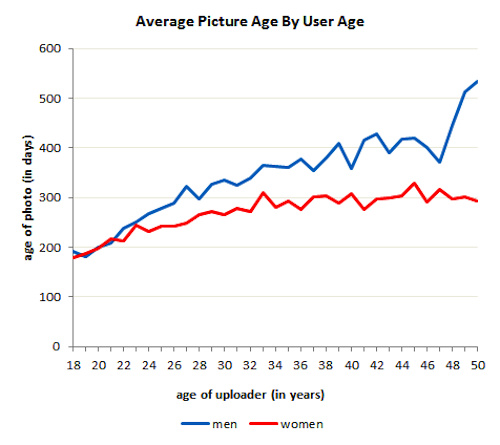
Anna M., Naomi B., Amanda C., Ben Z., and SpeZek sent in a new PETA ad campaign, the latest in a twisted story of objectification metaphor.
Feminists in the ’70s protested the objectification of women by metaphorically linking meat and female bodies (e.g., “we should not be treating women like pieces of meat”). Meat is meat, so the argument went, but women are human beings and should be treated as such.
In mocking response, in 1978 Larry Flynt put a woman being chewed up by a meat grinder on the cover of Hustler magazine. We will treat women like meat if we want, was the message. And we did, and we do, seemingly endlessly.
Forty years later, Pamela Anderson submits to being symbolically carved up for butchering by PETA in order to metaphorically link meat and female bodies again. But this time, in an ironic reversal, it’s designed to condemn the way we treat animals, not the way we treat women.

And, forty years later, feminists are still saying “Please, can we not do the women/meat thing?”
So Canada denies PETA a permit for the launching of this new ad campaign. An official explains: “…it goes against all principles public organizations are fighting for in the everlasting battle of equality between men and women” (source). What a nice thing to say, feminists think.
But Anderson fights feminism with feminism:
How sad that a woman would be banned from using her own body in a political protest over the suffering of cows and chickens… In some parts of the world, women are forced to cover their whole bodies with burqas—is that next?
Yes, Pamela, I’m sure that’s next.
But I digress.
So PETA and Anderson must think that Canadians super-super-respect women like totally and never-never-objectify them to the degree that saying that animals are like women will suddenly inspire horror at the prospect of using animals for food? Or is it that they think men will see the image and be like “oooh I’d really like to rub up against that rump” and then suddenly find cows too sexy to eat? Or they don’t give a shit about women and are willing to use whatever attention-getting tactic they can to save animals from going under the knife (including using the body of a woman that has, um, gone under the knife)?
I submit this for discussion because I just don’t know.
More from PETA: women packaged like meat, and in cages, women who love animals get naked (men wear clothes), the banned superbowl ad, and a collection of various PETA advertising using (mostly women’s) nudity. See also my post on leftist balkanization, or the way that leftist social movements tend to undermine each other.
If you’re interested further, you may want to read Carol Adams’ The Sexual Politics of Meat and The Pornography of Meat.
Lisa Wade, PhD is an Associate Professor at Tulane University. She is the author of American Hookup, a book about college sexual culture; a textbook about gender; and a forthcoming introductory text: Terrible Magnificent Sociology. You can follow her on Twitter and Instagram.