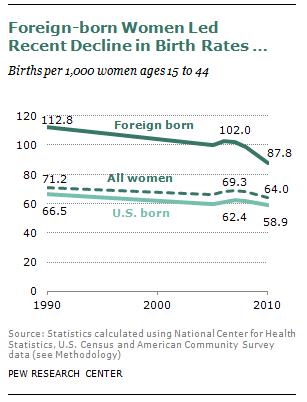
While I’m most well-known for my work on hook up culture, I’ve written extensively on a different topic altogether: how Americans talk about female genital cutting practices (FGCs), better known as female genital “mutilation.” While FGCs are passionately opposed by essentially all Americans who learn about them, our understanding of the practices is, in fact, skewed by misinformation, ethnocentrism, and a history of portraying Africa as naively “backwards” or cruelly “barbaric.”
The main source of distortion has been the mass media. Aiming to encourage journalists to think twice when covering the topic, the Hastings Center has released a report by the Public Policy Advisory Network on Female Genital Surgeries in Africa. In the rest of this post, I briefly discuss some of the things they want journalists — and the rest of us — to know and add a couple of my own:
Using the word “mutilation” is counterproductive.
People who support genital cutting typically believe that a cut body is a more aesthetically pleasing one. The term “mutilation” may appeal to certain Westerners, but people in communities where cutting occurs largely find the term confusing or offensive.
Media coverage usually focuses on one of the more rare types of genital cutting: infibulation.
Infibulation involves trimming and fusing the labia so as to close the vulva, leaving an opening in the back for intercourse, urination, and menses. In fact, 10% of the procedures involve infibulation. The remainder involve trimming, cutting, or scarification of the clitoris, clitoral hood (prepuce), or labia minora or majora. While none of these procedures likely sound appealing, some are more extensive than others.
Research has shown that women with cutting are sexually responsive.
Women who have undergone genital surgeries report “rich sexual lives, including desire, arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction…” This is true among women who have experienced clitoral reductions and undergone infibulation, as well as women who’ve undergone lesser forms of cutting.
Health complications of genital cutting “represent the exception rather than the rule.”
News reports often include long lists of acute and long-term negative medical consequences of FGCs, and these may feel intuitively true, but efforts to document their incidence suggest that health problems are, for the most part, no more common in cut than uncut women. The Report concludes: “…from a public health point of view, the vast majority of genital surgeries in Africa are safe, even with current procedures and under current conditions.”
Girls are not generally cut in response to the influence of cruel patriarchs.
Most societies that cut girls also cut boys; some groups that engage in cutting have relatively permissive sexual rules for women, some do not; and female genital cutting practices are typically controlled and organized by women (correspondingly, men control male genital surgeries).
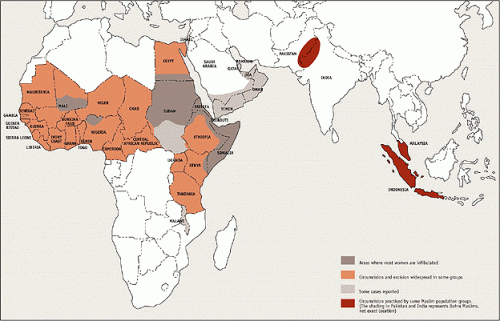
FGCs are not an “African practice.”
The procedures we label “female genital mutilation” occur only in some parts of Africa and occur outside of the continent as well (source):
Moreover, cosmetic genital surgeries in the U.S. are among the fastest growing procedures. These include clitoral reduction, circumcision of the clitoral foreskin, labia trimming, and vaginal tightening, not to mention mons liposuction, collagen injected into the g-spot, color correction of the vulva, and anal bleaching. While it would be simplistic to say that these are the same as the procedures we typically call “mutilation,” they are not totally different either.
Western-led efforts to eliminate FGCs are largely ineffective and sometimes backfire.
It turns out that people don’t appreciate being told that they are barbaric, ignorant of their own bodies, or cruel to their children. Benevolent strangers who try to stop cutting in communities, as well as top-down laws instituted by politicians (often in response to Western pressure), are very rarely successful. The most impressive interventions have involved giving communities resources to achieve whatever goals they desire and getting out of the way.
In sum, it’s high time Americans adopt a more balanced view of female genital cutting practices. Reading The Hastings Center Report is a good start. You might also pick up Genital Cutting and Transnational Sisterhood by Stanlie James and Claire Robertson. Full text links to my papers on the topic, including a discourse analysis of 30 years of the academic conversation, can be found here.
————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. She frequently delivers public lectures about female genital cutting. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.