—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.

—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.
Larry Harnisch, of The Daily Mirror, scanned these two ads for Grand Marnier from the latest New Yorker. Normally we don’t get too worked up over phallic imagery, but I thought these two might be good for discussion. Besides, it’s been a while since we linked to our awesome collections of ads featuring ejaculation imagery, subliminal sex, and not-so-subliminal sex (NSFW).
In the first, the woman greets a man at his door. She is wearing a dress with a very low cut back. She is holding the bottle behind her, angled provocatively. Don’t miss the shape of the bottle itself (and what exactly is that circle at the base of its neck?).

In the second ad, the woman sits deep in an armchair, her legs in the air. The bottle, being poured by a man, is tilted towards her, and spilling liquid into her glass.

So, Readers, what do you think? Is the bottle meant to be read as a penis subconsciously? Do you think it works that way, intended or not?
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.
Jessica H. S. sent in this photo:

Not that there is anything wrong with any of these games or careers, per se. It’s just the constant reinforcement of these gendered ideas of appropriate roles/careers/interests that is disheartening. Many of these games focus on roles that emphasize appearances, whether of people or homes; otherwise, you can care for children.
Though I will say, Peggle is awesome. I eventually had to delete it from my laptop for the sake of ever accomplishing anything again.
Jessica G. drew our attention to the promotional material of Panty Raid. Panty Raid is two guys, Josh Mayer and Marty Folb, who produce dance music. As you might guess from their name, their materials include a dismissal of women as fans and an endorsement of men’s entitlement to sexual access to women. Their slogan for their album, Marine Parade, is: “Audio fondling your girlfriend.”
So, “you” are a straight guy. And, like it or not, these guys are such hegemons that they are makin’ it with your girl, whether she likes it or not.
There is more of this typical misogyny at their website (you can google it), but it was the promo shot below that Jessica felt compelled to send in.

This is a great illustration of what it looks like to embrace both white and male privilege. We see the bottom half of a black woman sitting with her legs apart and her underwear at her ankles. Were it not dark between her legs, you could see her vulva. Mayer and Folb, both white men, sit in front of her and look at the camera. Their expression and posture suggest utter disinterest.
This is where I think the privilege is revealed, and embraced, loud and clear. She is not a human being, she is a vagina and, even as a vagina, she is uninteresting. She is nothing, really. Like their sneakers, their trucker hats, and their hoodies, she is only a prop. What does a sexually available black woman signify? Urban cred? Masculine domination of women? High status in a hierarchy of men? All of the above? Congratulations dudes: racist and sexist message sent and received.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.
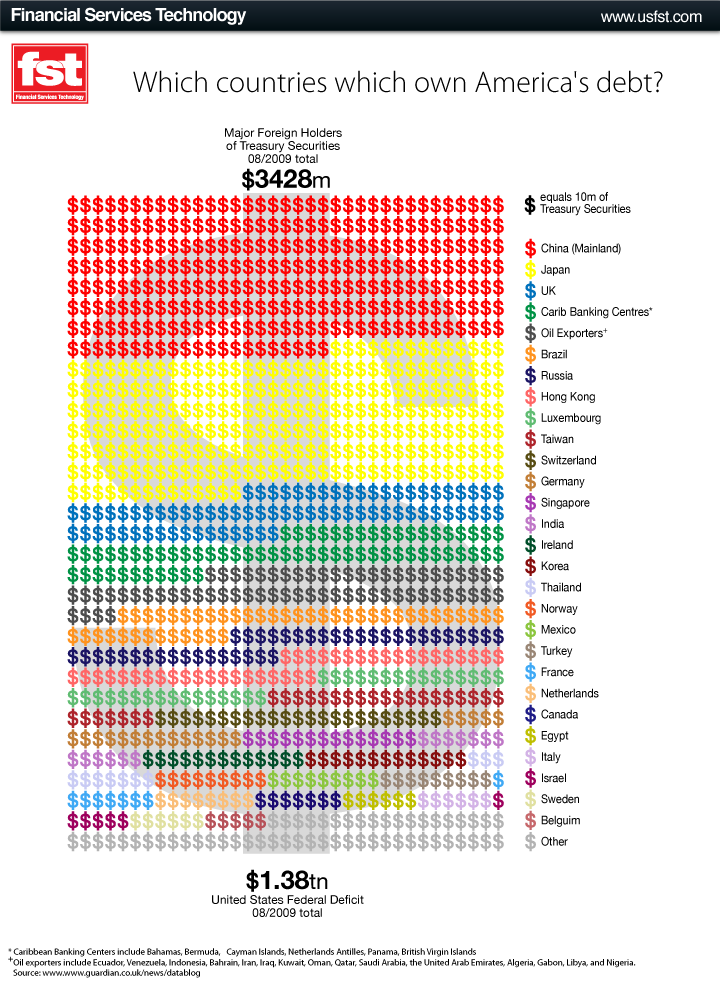
Last year I posted a table showing the dramatic rise in the birth of twins among women 45-49 (from less than 25 per 1,000 to almost 200 per 1,000 in 2002). The graphic below, included alongside a New York Times article on the topic, shows the increased risk of preterm birth and low birth weight that comes with multiple births and the cost of taking care of premature babies (almost $51,000 versus under $5,000 for a baby born at term):
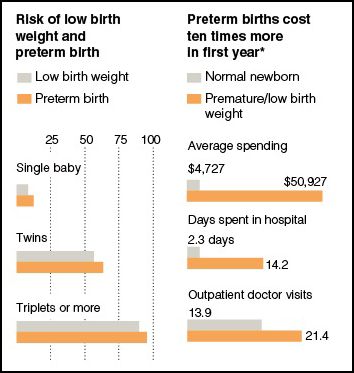
Given that the U.S. is discussing health care reform at the moment, it might be worth while to consider whether having a biological child is “worth” it.
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.
Larry Harnisch of The Daily Mirror sent in this ad, which appeared in the Los Angeles Times on September 5, 1969:


Text from the top of the ad:
Does S&A really stand for Sex Appeal?
…and how! Our shoes are so sexy we only allow mature thinking adults to buy them…or young adults accompanied by a parent. When you wear S&A shoes, people will stare at your legs who were never never aware that you had any before.
It’s a great example of how quickly fashion standards can change. Today I’m pretty sure most, if not all, of these shoes would be considered old-fashioned and wouldn’t be marketed as sexy. Our ideas of what constitutes a “sexy” woman’s shoe today includes a higher, thinner heel, meaning they’re also in general less stable, harder to walk in, and worse for your feet than shoes with a chunky heel like these.
In an earlier post I discussed how men, these days, are less likely than women to enroll and graduate from college. One theory for why involves an anti-intellectualism that is specifically male. That is, many men learn that to be a real man means rejecting prissy intellectual pursuits. Thinking is for chicks (and fags).
This commercial for Wrangler, aimed at men specifically, asserts this exactly:
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.
In the U.S., when people refer to the “traditional family,” they usually mean a family that they associate with the 1950s. But the 1950s was a really unusual time in American history. Elsewhere I’ve written about how the husband breadwinner/wife homemaker model is an American anomaly. The data below, put together by the New York Times, shows that the 1950s was an unusual time in terms of age of marriage also:
Though the data is rough (five points across 107 years), you can see a distinct dip in the age of marriage that includes the ’50s.
So history isn’t, as we often suppose, a straight line from one point to another. It’s a complicated story. And the 1950s… well, to choose that era as “traditional” is no more reasonable than to choose today or the enlightenment or the dark ages or…
Also see: everyone needs a wife and what does “traditional marriage” look like?
—————————
Lisa Wade is a professor of sociology at Occidental College. You can follow her on Twitter and Facebook.